
Thermal velocity
Encyclopedia
The thermal velocity or thermal speed is a typical velocity of the thermal motion of particles which make up a gas, liquid, etc. Thus, indirectly, thermal velocity is a measure of temperature. Technically speaking it is a measure of the width of the peak in the Maxwell-Boltzmann particle velocity distribution. Note that in the strictest sense thermal velocity is not a velocity
, since velocity usually describes a vector rather than simply a scalar
speed
.
Since the thermal velocity is only a "typical" velocity, a number of different definitions can be and are used.
Taking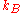 to be the Boltzmann constant,
to be the Boltzmann constant,  is the temperature, and
is the temperature, and 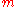 is the mass of a particle, then we can write the different thermal velocities:
is the mass of a particle, then we can write the different thermal velocities:
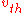 is defined as the root mean square
is defined as the root mean square
of the velocity in any one dimension (i.e. any single direction), then
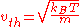
If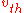 is defined as the mean
is defined as the mean
of the magnitude of the velocity in any one dimension (i.e. any single direction), then
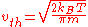
If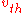 is defined as the
is defined as the 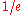 half-width of the thermal distribution or
half-width of the thermal distribution or
if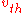 is defined such that a particle with this speed has an energy of
is defined such that a particle with this speed has an energy of 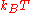 , then
, then
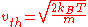 .
.
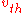 is defined as the root mean square of the total velocity (in three dimensions), then
is defined as the root mean square of the total velocity (in three dimensions), then
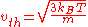 .
.
If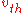 is defined as the mean of the magnitude of the velocity of the atoms or molecules is given by
is defined as the mean of the magnitude of the velocity of the atoms or molecules is given by

Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
, since velocity usually describes a vector rather than simply a scalar
Scalar (physics)
In physics, a scalar is a simple physical quantity that is not changed by coordinate system rotations or translations , or by Lorentz transformations or space-time translations . This is in contrast to a vector...
speed
Speed
In kinematics, the speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity ; it is thus a scalar quantity. The average speed of an object in an interval of time is the distance traveled by the object divided by the duration of the interval; the instantaneous speed is the limit of the average speed as...
.
Since the thermal velocity is only a "typical" velocity, a number of different definitions can be and are used.
Taking
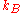 to be the Boltzmann constant,
to be the Boltzmann constant,  is the temperature, and
is the temperature, and  is the mass of a particle, then we can write the different thermal velocities:
is the mass of a particle, then we can write the different thermal velocities:In one dimension
If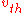 is defined as the root mean square
is defined as the root mean squareRoot mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
of the velocity in any one dimension (i.e. any single direction), then
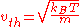
If
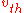 is defined as the mean
is defined as the meanMean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
of the magnitude of the velocity in any one dimension (i.e. any single direction), then
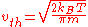
If
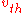 is defined as the
is defined as the 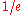 half-width of the thermal distribution or
half-width of the thermal distribution orif
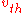 is defined such that a particle with this speed has an energy of
is defined such that a particle with this speed has an energy of 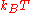 , then
, then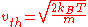 .
.In three dimensions
If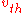 is defined as the root mean square of the total velocity (in three dimensions), then
is defined as the root mean square of the total velocity (in three dimensions), then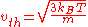 .
.If
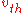 is defined as the mean of the magnitude of the velocity of the atoms or molecules is given by
is defined as the mean of the magnitude of the velocity of the atoms or molecules is given by

