
Third molar
Encyclopedia
A wisdom tooth, in humans, is any of the usually four third molars
. Wisdom teeth usually appear between the ages of 17 and 25. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, but it is possible to have fewer (oligodontia), or more, in which case they are called supernumerary teeth
. Wisdom teeth commonly affect other teeth as they develop, becoming impacted or "coming in sideways." They are often extracted when this occurs. About 35% of the population do not develop wisdom teeth at all.
Typically mesioangular impactions are the most difficult to extract in the maxilla
and easiest to extract in the mandible, while distoangular impactions are the easiest to extract in the maxilla and most difficult to extract in the mandible. Frequently, a fully erupted upper wisdom tooth requires bone removal if the tooth does not yield easily to forceps or elevators. Failure to remove distal or buccal bone while removing one of these teeth can cause the entire maxillary tuberosity to be fractured off, thereby tearing out the floor of the maxillary sinus
.
Impacted wisdom teeth may also be categorized on whether they are still completely encased in the jawbone. If it is completely encased in the jawbone, it is a bony impaction. If the wisdom tooth has erupted out of the jawbone but not through the gumline, it is called a soft tissue
impaction.
In a small portion of patients, cysts and tumors occur around impacted wisdom teeth, requiring surgical extraction. Estimates of the incidence of cysts around impacted teeth vary from 0.001% to 11%, with a higher incidence in older patients, suggesting that the chance of a cyst or tumor increases the longer an impaction exists. Only 1-2% of impactions result in malignant tumors.
The oldest known impacted wisdom tooth belonged to a European woman of the Magdalenian
period (18,000 - 10,000 BC).
. Additional cleaning techniques can include using a needle-less plastic syringe
to vigorously wash the tooth with moderately pressured water or to softly wash it with hydrogen peroxide
.
However, debris and bacteria
can easily accumulate under an operculum, which may cause pericoronitis
, a common infection
problem in young adults with partial impactions that is often exacerbated by occlusion
with opposing third or second molars. Common symptoms include a swelling and redness of the gum around the eruption
site, difficulty in opening the mouth, a bad odor or taste in the mouth, and pain in the general area which may also run down the entire lower jaw
or possibly the neck
. Untreated pericoronitis can progress to a much more severe infection.
If the operculum does not disappear, recommended treatment is extraction of the wisdom tooth. An alternative treatment involving removal of the operculum, called operculectomy, has been advocated. There is a high risk of permanent or temporary numbness of the tongue due to damage of the nerve with this treatment and it is no longer recommended as a standard treatment in oral surgery.
Chronic inflammation
in the gingival tissue of the partially erupted third-molar, i.e. chronic pericoronitis
, may be the etiology for the development of paradental cyst
, an inflammatory
odentogenic
cyst
.
 Wisdom teeth are extracted for two general reasons: either the wisdom teeth have already become impacted, or the wisdom teeth could potentially become problematic if not extracted. Potential problems caused by the presence of properly grown-in wisdom teeth include infections caused by food particles easily trapped in the jaw area behind the wisdom teeth where regular brushing and flossing is difficult and ineffective. Such infections may be frequent, and cause considerable pain and medical danger. Other reasons wisdom teeth are removed include misalignment which rubs up against the tongue or cheek causing pain, potential crowding or malocclusion
Wisdom teeth are extracted for two general reasons: either the wisdom teeth have already become impacted, or the wisdom teeth could potentially become problematic if not extracted. Potential problems caused by the presence of properly grown-in wisdom teeth include infections caused by food particles easily trapped in the jaw area behind the wisdom teeth where regular brushing and flossing is difficult and ineffective. Such infections may be frequent, and cause considerable pain and medical danger. Other reasons wisdom teeth are removed include misalignment which rubs up against the tongue or cheek causing pain, potential crowding or malocclusion
of the remaining teeth (a result of there being not enough room on the jaw or in the mouth), as well as orthodontics
.
) to potentially life-threatening (serious infection of the extraction sites).
Due to the blood clots that form in the exposed sockets as well as the abundant bacterial flora in the mouth, an offensive smell may be noticeable a short time after surgery. The persistent odor often is accompanied by an equally rancid-tasting fluid seeping from the wounds. These symptoms will diminish over an indeterminate amount of time, although one to two weeks is normal. While not a cause for great concern, a post-operative appointment with one's surgeon seven to ten days after surgery is highly recommended to make sure that the healing process has no complications and that the wounds are relatively clean. If infection does enter the socket, a qualified dental professional can gently plunge a plastic syringe (without the hypodermic needle) full of a mixture of equal parts hydrogen peroxide and water or chlorohexidine gluconate, which also comes in the form of a mouth wash, into the sockets to remove any food or bacteria that may collect in the back of the mouth. This is less likely if the person has his/her wisdom teeth removed at an early age.
may be prescribed by the surgeon for pain relief. Generally dry sockets are self limiting and heal in a couple of weeks without treatment.
should be expected and is a sign that the healing process is progressing normally. There is no general duration for this problem; the severity and duration of the swelling vary from case to case. The surgeon
will tell the patient
how long they should expect swelling to last, including when to expect the swelling to peak and when the swelling will start to subside. If the swelling does not begin to subside when it is supposed to, the patient should contact his or her surgeon immediately. Swelling usually lasts one week. While the swelling will generally not disappear completely for several days after it peaks, swelling that does not begin to subside or gets worse may be an indication of infection. Swelling that re-appears after a few weeks is an indication of infection caused by a bone or tooth fragment still in the wound and should be treated immediately.
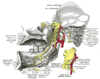 Nerve injury is primarily an issue with extraction of third molars but can occur with the extraction of any tooth should the nerve
Nerve injury is primarily an issue with extraction of third molars but can occur with the extraction of any tooth should the nerve
be near the surgical site. Two nerves are typically of concern and are found in duplicate (on the left and right side):
Such injuries can occur while lifting teeth (typically the inferior alveolar) but are most commonly caused by inadvertent damage with a surgical drill. Such injuries are rare and are usually temporary. Depending on the type of injury (i.e. Seddon classification: neuropraxia, axonotmesis
, and neurotmesis
) they can be prolonged or permanent. In rare cases it is also possible for bleeding into the nerve canal to also cause an injury to the nerve due to the increased pressure of the blood build up.
Several dental textbooks encourage the removal of third molars. From Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 5th Edition:
The rationale of prophylactically removing third molars prior to their complete root formation is that the likelihood of nerve damage or other complications is extremely low. This is not the case however with symptomatic removal of a third molar after root formation is complete and more intimate with the inferior alveolar nerve and as the mandible becomes more dense with age.
However, studies have shown that dentists graduated from different countries—or even from different dental school
s in the same country—may have different clinical decisions regarding third molar removal for the same clinical condition. For example, dentists graduated from Israel
i dental schools may recommend more often for the removal of asymptomatic impacted third molar than dentists graduated from Latin-American or Eastern European dental schools.
published a systematic review
of randomized controlled trials in order to evaluate the effect of preventive removal of asymptomatic wisdom teeth. The authors found no evidence to either support or refute this practice. There was reliable evidence showing that preventative removal did not reduce or prevent late incisor crowding. The authors of the review suggested that the number of surgical procedures could be reduced by 60% or more. Likewise, ClinicalEvidence published a summary largely based on the Cochrane review that concluded prophylactic extraction is "likely to be ineffective or harmful." It advised against extracting asymptomatic, disease-free wisdom teeth because of the risk of damage to the inferior alveolar nerve.
Some evidence suggests that the extraction of the asymptomatic tooth may be beneficial if caries are present in the adjacent second molar, or if periodontal pockets
are present distal to the second molar.
It may be argued, however, that these meta-analyses are inappropriate in that the lack of randomized control trials is likely the result of the expense and impracticality of studying diseases already strongly linked to third molar tissues. For example odontogenic cysts arising from the third molar follicle and odontogenic tumors from the third molar epithelium are relatively rare and can take decades to develop, making controlled trials extremely expensive and challenging (especially high loss to follow up).
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
has published an extensive White Paper on Third Molar Data summarizing the most current research into the subject of third molar extraction. It states that, "The presence of visible third molars is associated with elevated levels of periodontitis . . . which involves adjacent teeth and is progressive and only partially responsive to therapy." In developed countries, the presence of wisdom teeth is associated with substandard dental care, leading to an increased likelihood of periodontitis, which may be caused by a lack of dental care rather than the presence of wisdom teeth. Periodontal bacteria causes gum disease, and may travel through the blood stream, resulting in systemic infections associated with the heart, kidneys and other organs. Further, studies have found such bacteria in amniotic fluid and is considered a factor in low birth weight infants.
, which appraises the cost-effectiveness of treatments for the National Health Service
, has argued that there is no evidence that removing disease-free impacted wisdom teeth is beneficial, and recommends against removal to avoid the various risks and discomforts of the procedure.
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
recommends that third molars be removed in patients who, in the opinion of their family dentists, suffer from periodontal infections where the probing depth exceeds 3 mm. It argues that it is advisable to have the third molars of such patients removed in young adulthood to avoid the complications that may occur when third molars have grown to maturity. In these cases, there is a greater likelihood of nerve damage and other potential concerns.
The American Public Health Association
recommends against prophylactic removal of asymptomatic, non-pathological wisdom teeth, including wisdom teeth that are impacted,
on the basis that the removal of third molars (wisdom teeth), like the removal of any teeth, should be based on evidence of diagnosed pathology or demonstrable need, rather than anticipated future pathology. The APHA's position is based on scientific research that documents the risks of injury to the nerves of the jaw that can cause permanent numbness of the lip and tongue, damage to the temporomandibular (jaw) joint and adjacent teeth.
that makes up a plant cell wall. As human diets changed, smaller jaws gradually evolved, yet the third molars, or "wisdom teeth", still commonly develop in human mouths.
Agenesis
of wisdom teeth in human populations ranges from practically zero in Tasmanian Aborigines
to nearly 100% in indigenous Mexicans. The difference is related to the PAX9
gene (and perhaps other genes).
s from wisdom teeth. This discovery is of great clinical importance, as wisdom tooth extractions are a relatively common type of oral surgery. Patients who have their wisdom teeth removed are currently able to opt to have stem cells from those teeth isolated and saved, in case they should ever need the cells.
Wisdom teeth can be transplanted to replace lost molars. Rejection applies to teeth just like it does to other body tissue and donor trials so far have been unsuccessful. The transplantation will cause some damage to the tooth during the transplant process, most notably the nerve, but moving the tooth to another position for the same person is now considered successful and beneficial.
Molar (tooth)
Molars are the rearmost and most complicated kind of tooth in most mammals. In many mammals they grind food; hence the Latin name mola, "millstone"....
. Wisdom teeth usually appear between the ages of 17 and 25. Most adults have four wisdom teeth, but it is possible to have fewer (oligodontia), or more, in which case they are called supernumerary teeth
Hyperdontia
Hyperdontia is the condition of having supernumerary teeth, or teeth which appear in addition to the regular number of teeth.-Types:Supernumerary teeth can be classified by shape and by position...
. Wisdom teeth commonly affect other teeth as they develop, becoming impacted or "coming in sideways." They are often extracted when this occurs. About 35% of the population do not develop wisdom teeth at all.
Impaction
Impacted wisdom teeth fall into one of several categories:- Mesioangular impaction is the most common form (44%), and means the tooth is angled forward, towards the front of the mouth.
- Vertical impaction (38%) occurs when the formed tooth does not erupt fully through the gum line.
- Distoangular impaction (6%) means the tooth is angled backward, towards the rear of the mouth.
- Horizontal impaction (3%) is the least common form, which occurs when the tooth is angled fully 90 degrees sideways, growing into the roots of the second molar.
Typically mesioangular impactions are the most difficult to extract in the maxilla
Maxilla
The maxilla is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper jaw. This is similar to the mandible , which is also a fusion of two halves at the mental symphysis. Sometimes The maxilla (plural: maxillae) is a fusion of two bones along the palatal fissure that form the upper...
and easiest to extract in the mandible, while distoangular impactions are the easiest to extract in the maxilla and most difficult to extract in the mandible. Frequently, a fully erupted upper wisdom tooth requires bone removal if the tooth does not yield easily to forceps or elevators. Failure to remove distal or buccal bone while removing one of these teeth can cause the entire maxillary tuberosity to be fractured off, thereby tearing out the floor of the maxillary sinus
Maxillary sinus
The pyramid shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the nose. It is present at birth as rudimentary air cells, and develops throughout childhood.-General characteristics:...
.
Impacted wisdom teeth may also be categorized on whether they are still completely encased in the jawbone. If it is completely encased in the jawbone, it is a bony impaction. If the wisdom tooth has erupted out of the jawbone but not through the gumline, it is called a soft tissue
Soft tissue
In anatomy, the term soft tissue refers to tissues that connect, support, or surround other structures and organs of the body, not being bone. Soft tissue includes tendons, ligaments, fascia, skin, fibrous tissues, fat, and synovial membranes , and muscles, nerves and blood vessels .It is sometimes...
impaction.
In a small portion of patients, cysts and tumors occur around impacted wisdom teeth, requiring surgical extraction. Estimates of the incidence of cysts around impacted teeth vary from 0.001% to 11%, with a higher incidence in older patients, suggesting that the chance of a cyst or tumor increases the longer an impaction exists. Only 1-2% of impactions result in malignant tumors.
The oldest known impacted wisdom tooth belonged to a European woman of the Magdalenian
Magdalenian
The Magdalenian , refers to one of the later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic in western Europe, dating from around 17,000 BP to 9,000 BP...
period (18,000 - 10,000 BC).
Partial eruption
Sometimes the wisdom tooth fails to erupt completely through the gum bed and the gum at the back of the wisdom tooth extends over the biting surface, forming a soft tissue flap or lid around the tooth called an operculum. Teeth covered by an operculum can be difficult to clean with a toothbrushToothbrush
The toothbrush is an oral hygiene instrument used to clean the teeth and gums that consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles mounted on a handle, which facilitates the cleansing of hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. Toothpaste, which often contains fluoride, is commonly used in conjunction...
. Additional cleaning techniques can include using a needle-less plastic syringe
Syringe
A syringe is a simple pump consisting of a plunger that fits tightly in a tube. The plunger can be pulled and pushed along inside a cylindrical tube , allowing the syringe to take in and expel a liquid or gas through an orifice at the open end of the tube...
to vigorously wash the tooth with moderately pressured water or to softly wash it with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
.
However, debris and bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
can easily accumulate under an operculum, which may cause pericoronitis
Pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is a common problem in young adults with partial tooth impactions. It usually occurs within 17 to 24 years of age as it is when the third molars start erupting. It occurs when the tissue around the wisdom tooth has become inflamed because bacteria have invaded the area. Poor oral...
, a common infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
problem in young adults with partial impactions that is often exacerbated by occlusion
Occlusion (dentistry)
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary and mandibular teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest....
with opposing third or second molars. Common symptoms include a swelling and redness of the gum around the eruption
Tooth eruption
Tooth eruption is a process in tooth development in which the teeth enter the mouth and become visible. It is currently believed that the periodontal ligaments play an important role in tooth eruption...
site, difficulty in opening the mouth, a bad odor or taste in the mouth, and pain in the general area which may also run down the entire lower jaw
Jaw
The jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
or possibly the neck
Neck
The neck is the part of the body, on many terrestrial or secondarily aquatic vertebrates, that distinguishes the head from the torso or trunk. The adjective signifying "of the neck" is cervical .-Boner anatomy: The cervical spine:The cervical portion of the human spine comprises seven boney...
. Untreated pericoronitis can progress to a much more severe infection.
If the operculum does not disappear, recommended treatment is extraction of the wisdom tooth. An alternative treatment involving removal of the operculum, called operculectomy, has been advocated. There is a high risk of permanent or temporary numbness of the tongue due to damage of the nerve with this treatment and it is no longer recommended as a standard treatment in oral surgery.
Chronic inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
in the gingival tissue of the partially erupted third-molar, i.e. chronic pericoronitis
Pericoronitis
Pericoronitis is a common problem in young adults with partial tooth impactions. It usually occurs within 17 to 24 years of age as it is when the third molars start erupting. It occurs when the tissue around the wisdom tooth has become inflamed because bacteria have invaded the area. Poor oral...
, may be the etiology for the development of paradental cyst
Paradental cyst
Paradental cysts constitute a family of inflammatory odontogenic cyst, that typically appear in relation to crown or root of partially erupted molar tooth...
, an inflammatory
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
odentogenic
Odontogenic cyst
Odontogenic cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane derived from rests of odontogenic epithelium. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. Intra-bony cysts are most common in the jaws, because the mandible and maxilla are the only bones with epithelial components. That...
cyst
Cyst
A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.- Locations :* Acne...
.
Extraction

Malocclusion
A malocclusion is a misalignment of teeth or incorrect relation between the teeth of the two dental arches. The term was coined by Edward Angle, the "father of modern orthodontics", as a derivative of occlusion, which refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet.-Presentation:Most people have...
of the remaining teeth (a result of there being not enough room on the jaw or in the mouth), as well as orthodontics
Orthodontics
Orthodontics, orthodontia, or orthodonture is the first specialty of dentistry that is concerned with the study and treatment of malocclusions , which may be a result of tooth irregularity, disproportionate jaw relationships, or both...
.
Post-extraction problems
There are several problems that might occur after the extraction(s) have been completed. Some of these problems are unavoidable and natural, while others are under the control of the patient. The suggestions contained in the sections below are general guidelines by which a patient will be expected to abide, but the patient should follow all directions that are given by the surgeon in addition to the following guidelines. Above all, the patient must not disregard the given instructions; doing so is extremely dangerous and could result in any number of problems ranging in severity from being merely inconvenient (dry socketAlveolar osteitis
Alveolar osteitis or, colloquially, a dry socket, is a complication of wound healing following extraction of a tooth. The term alveolar refers to the alveolus, which is the part of the jawbone that surrounds the teeth, and osteitis means simply "bone inflammation".- Signs and symptoms :Dry socket...
) to potentially life-threatening (serious infection of the extraction sites).
Bleeding and oozing
Bleeding and oozing is inevitable and should be expected to last up to three days (although by day three it should be less noticeable). Rinsing the mouth during this period is counter-productive, as the bleeding stops when the blood forms clots at the extraction sites, and rinsing out the mouth will most likely dislodge the clots. The end result will be a delay in healing time and a prolonged period of bleeding. Gauze pads should be placed at the extraction sites, and then should be bitten down on with firm and even pressure. This will help to stop the bleeding, but should not be overdone as it is possible to irritate the extraction sites and prolong the bleeding or remove the clot. The bleeding should decrease gradually and noticeably upon changing the gauze. If the bleeding lasts for more than a day without decreasing despite having followed the surgeon's directions, the surgeon should be contacted as soon as possible. This is not supposed to happen under normal circumstances and signals that a serious problem is present. A wet tea bag can replace the gauze pads. Tannin contained in tea can help reduce the bleeding.Due to the blood clots that form in the exposed sockets as well as the abundant bacterial flora in the mouth, an offensive smell may be noticeable a short time after surgery. The persistent odor often is accompanied by an equally rancid-tasting fluid seeping from the wounds. These symptoms will diminish over an indeterminate amount of time, although one to two weeks is normal. While not a cause for great concern, a post-operative appointment with one's surgeon seven to ten days after surgery is highly recommended to make sure that the healing process has no complications and that the wounds are relatively clean. If infection does enter the socket, a qualified dental professional can gently plunge a plastic syringe (without the hypodermic needle) full of a mixture of equal parts hydrogen peroxide and water or chlorohexidine gluconate, which also comes in the form of a mouth wash, into the sockets to remove any food or bacteria that may collect in the back of the mouth. This is less likely if the person has his/her wisdom teeth removed at an early age.
Dry socket
A dry socket, also known as alveolar osteitis, is a painful inflammation of the alveolar bone (not an infection); it occurs when the blood clots at an extraction site are dislodged, fall out prematurely, or fail to form. In some cases, this is beyond the control of the patient. However, in other cases this happens because the patient has disregarded the instructions given by the surgeon. Smoking, blowing one's nose, spitting, or drinking with a straw in disregard to the surgeon's instructions can cause this, along with other activities that change the pressure inside of the mouth, such as sneezing or playing a musical instrument. The risk of developing a dry socket is greater in smokers, in diabetics, if the patient has had a previous dry socket, in the lower jaw, and following complicated extractions. The extraction site will become irritated and painful, due to inflammation of the bone lining the tooth socket (osteitis). The symptoms are made worse when food debris is trapped in the tooth socket. The patient should contact their surgeon if they suspect that they have a case of dry socket. The surgeon may elect to clean the socket under local anesthetic to cause another blood clot to form or prescribe medication in topical form (e.g. Alvogel) to apply to the affected site. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as ibuprofenIbuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
may be prescribed by the surgeon for pain relief. Generally dry sockets are self limiting and heal in a couple of weeks without treatment.
Swelling
Swelling should not be confused with dry socket, although painful swellingSwelling (medical)
In medical parlance, swelling is the transient enlargement or protuberance in the body and may include tumors. According to cause, it may be congenital, traumatic, inflammatory, neoplastic or miscellaneous....
should be expected and is a sign that the healing process is progressing normally. There is no general duration for this problem; the severity and duration of the swelling vary from case to case. The surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
will tell the patient
Patient
A patient is any recipient of healthcare services. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, advanced practice registered nurse, veterinarian, or other health care provider....
how long they should expect swelling to last, including when to expect the swelling to peak and when the swelling will start to subside. If the swelling does not begin to subside when it is supposed to, the patient should contact his or her surgeon immediately. Swelling usually lasts one week. While the swelling will generally not disappear completely for several days after it peaks, swelling that does not begin to subside or gets worse may be an indication of infection. Swelling that re-appears after a few weeks is an indication of infection caused by a bone or tooth fragment still in the wound and should be treated immediately.
Nerve injury

Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
be near the surgical site. Two nerves are typically of concern and are found in duplicate (on the left and right side):
- The inferior alveolar nerveInferior alveolar nerveThe inferior alveolar nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve, which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve .-Path:...
, which enters the mandible at the mandibular foramen and exits the mandible at the sides of the chin from the mental foramen. This nerve supplies sensation to the lower teeth on the right or left half of the dental arch, as well as sense of touch to the right or left half of the chin and lower lip. - The lingual nerveLingual nerveThe lingual nerve is a branch of the mandibular nerve , itself a branch of the trigeminal nerve, which supplies sensory innervation to the tongue...
, which branches off the mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerveTrigeminal nerveThe trigeminal nerve contains both sensory and motor fibres. It is responsible for sensation in the face and certain motor functions such as biting, chewing, and swallowing. Sensory information from the face and body is processed by parallel pathways in the central nervous system...
and courses just inside the jaw bone, entering the tongue and supplying sense of touch and taste to the right and left half of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue as well as the lingual gingiva (i.e. the gums on the inside surface of the dental arch).
Such injuries can occur while lifting teeth (typically the inferior alveolar) but are most commonly caused by inadvertent damage with a surgical drill. Such injuries are rare and are usually temporary. Depending on the type of injury (i.e. Seddon classification: neuropraxia, axonotmesis
Axonotmesis
Axonotmesis is a disruption of nerve cell axon, with Wallerian degeneration occurring below and slightly proximal to the site of injury. If axons, and their myelin sheath are damaged, but schwann cells, the endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium remain intact is called axonotmesis. Axonotmesis is...
, and neurotmesis
Neurotmesis
Neurotmesis is part of Seddon's classification scheme used to classify nerve damage.It is the most serious nerve injury in the scheme.In this type of injury, both the nerve and the nerve sheath are disrupted....
) they can be prolonged or permanent. In rare cases it is also possible for bleeding into the nerve canal to also cause an injury to the nerve due to the increased pressure of the blood build up.
Treatment controversy
Preventive removal of the third molars is a common practice in developed countries and is usually recommended by dentists. According to Pediatric Dentistry: Infancy Through Adolescence, 4th Edition:Evaluation of third molars is usually completed during mid- to late adolescence. Parents commonly ask about treating these teeth. The reasons for extraction of third molars include impaction or failure to erupt; potential or existing pathosis such as cysts or ameloblastoma; decay; posteruption malposition; nonfunction as a result of an absent opposing tooth; difficulty with hygiene; and recurrent pericoronitis. If any of these are considerations, third molars should be removed during adolescence.... The evaluation of developing third molars in adolescent athletes is of particular importance. Not only can an athletic season suddenly be interrupted by the annoying and often painful eruption of third molars with associated acute pericoronitis, but mandibular fractures in the gonial angle region of developing third molars can also occur in adolescent athletes.
Several dental textbooks encourage the removal of third molars. From Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, 5th Edition:
As a general rule, all impacted teeth should be removed unless removal is contraindicated. Extraction should be performed as soon as the dentist determines that the tooth is impacted. Removal of impacted teeth becomes more difficult with advancing age. The dentist should typically not recommend that impacted teeth be left in place until they cause difficulty. If the tooth is left in place until problems arise, the patient may experience an increased incidence of local tissue morbidity, loss of or damage to adjacent teeth and bone, and potential injury to adjacent vital structures. Additionally, if removal of impacted teeth is deferred until they cause problems later in life, surgery is more likely to be complicated and hazardous because the patient may have compromising systemic diseases and the surrounding bone becomes more dense. A fundamental precept of the philosophy of dentistry is that problems should be prevented. Preventive dentistry dictates that impacted teeth are to be removed before complications arise unless removal will cause more serious problems.
The rationale of prophylactically removing third molars prior to their complete root formation is that the likelihood of nerve damage or other complications is extremely low. This is not the case however with symptomatic removal of a third molar after root formation is complete and more intimate with the inferior alveolar nerve and as the mandible becomes more dense with age.
However, studies have shown that dentists graduated from different countries—or even from different dental school
Dental school
A dental school is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches dentistry. Upon successful completion, the graduate receives a degree in Dentistry, which, depending upon the jurisdiction, might be a bachelor's degree, master's degree, a professional degree, or a...
s in the same country—may have different clinical decisions regarding third molar removal for the same clinical condition. For example, dentists graduated from Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
i dental schools may recommend more often for the removal of asymptomatic impacted third molar than dentists graduated from Latin-American or Eastern European dental schools.
Scientific trials
In 2006, the Cochrane CollaborationCochrane Collaboration
The Cochrane Collaboration is a group of over 28,000 volunteers in more than 100 countries who review the effects of health care interventions tested in biomedical randomized controlled trials. A few more recent reviews have also studied the results of non-randomized, observational studies...
published a systematic review
Systematic review
A systematic review is a literature review focused on a research question that tries to identify, appraise, select and synthesize all high quality research evidence relevant to that question. Systematic reviews of high-quality randomized controlled trials are crucial to evidence-based medicine...
of randomized controlled trials in order to evaluate the effect of preventive removal of asymptomatic wisdom teeth. The authors found no evidence to either support or refute this practice. There was reliable evidence showing that preventative removal did not reduce or prevent late incisor crowding. The authors of the review suggested that the number of surgical procedures could be reduced by 60% or more. Likewise, ClinicalEvidence published a summary largely based on the Cochrane review that concluded prophylactic extraction is "likely to be ineffective or harmful." It advised against extracting asymptomatic, disease-free wisdom teeth because of the risk of damage to the inferior alveolar nerve.
Some evidence suggests that the extraction of the asymptomatic tooth may be beneficial if caries are present in the adjacent second molar, or if periodontal pockets
Gingival and periodontal pocket
Gingival and periodontal pockets are dental terms indicating the presence of an abnormal gingival sulcus near the point at which the gums contact a tooth.-The Tooth/Gingiva Interface:...
are present distal to the second molar.
It may be argued, however, that these meta-analyses are inappropriate in that the lack of randomized control trials is likely the result of the expense and impracticality of studying diseases already strongly linked to third molar tissues. For example odontogenic cysts arising from the third molar follicle and odontogenic tumors from the third molar epithelium are relatively rare and can take decades to develop, making controlled trials extremely expensive and challenging (especially high loss to follow up).
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons is the non-profit professional association serving the specialty of oral and maxillofacial surgery, the surgical arm of dentistry....
has published an extensive White Paper on Third Molar Data summarizing the most current research into the subject of third molar extraction. It states that, "The presence of visible third molars is associated with elevated levels of periodontitis . . . which involves adjacent teeth and is progressive and only partially responsive to therapy." In developed countries, the presence of wisdom teeth is associated with substandard dental care, leading to an increased likelihood of periodontitis, which may be caused by a lack of dental care rather than the presence of wisdom teeth. Periodontal bacteria causes gum disease, and may travel through the blood stream, resulting in systemic infections associated with the heart, kidneys and other organs. Further, studies have found such bacteria in amniotic fluid and is considered a factor in low birth weight infants.
Recommendations
In the U.K., the National Institute for Health and Clinical ExcellenceNational Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence is a special health authority of the English National Health Service , serving both English NHS and the Welsh NHS...
, which appraises the cost-effectiveness of treatments for the National Health Service
National Health Service
The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
, has argued that there is no evidence that removing disease-free impacted wisdom teeth is beneficial, and recommends against removal to avoid the various risks and discomforts of the procedure.
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons
The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons is the non-profit professional association serving the specialty of oral and maxillofacial surgery, the surgical arm of dentistry....
recommends that third molars be removed in patients who, in the opinion of their family dentists, suffer from periodontal infections where the probing depth exceeds 3 mm. It argues that it is advisable to have the third molars of such patients removed in young adulthood to avoid the complications that may occur when third molars have grown to maturity. In these cases, there is a greater likelihood of nerve damage and other potential concerns.
The American Public Health Association
American Public Health Association
The American Public Health Association is Washington, D.C.-based professional organization for public health professionals in the United States. Founded in 1872 by Dr. Stephen Smith, APHA has more than 30,000 members worldwide...
recommends against prophylactic removal of asymptomatic, non-pathological wisdom teeth, including wisdom teeth that are impacted,
on the basis that the removal of third molars (wisdom teeth), like the removal of any teeth, should be based on evidence of diagnosed pathology or demonstrable need, rather than anticipated future pathology. The APHA's position is based on scientific research that documents the risks of injury to the nerves of the jaw that can cause permanent numbness of the lip and tongue, damage to the temporomandibular (jaw) joint and adjacent teeth.
Vestigiality and variation
Wisdom teeth are vestigial third molars that human ancestors used to help in grinding down plant tissue. The common postulation is that the skulls of human ancestors had larger jaws with more teeth, which were possibly used to help chew down foliage to compensate for a lack of ability to efficiently digest the celluloseCellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to over ten thousand β linked D-glucose units....
that makes up a plant cell wall. As human diets changed, smaller jaws gradually evolved, yet the third molars, or "wisdom teeth", still commonly develop in human mouths.
Agenesis
Agenesis
In medicine, agenesis refers to the failure of an organ to develop during embryonic growth and development due to the absence of primordial tissue...
of wisdom teeth in human populations ranges from practically zero in Tasmanian Aborigines
Tasmanian Aborigines
The Tasmanian Aborigines were the indigenous people of the island state of Tasmania, Australia. Before British colonisation in 1803, there were an estimated 3,000–15,000 Parlevar. A number of historians point to introduced disease as the major cause of the destruction of the full-blooded...
to nearly 100% in indigenous Mexicans. The difference is related to the PAX9
PAX9
Paired box gene 9, also known as PAX9, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PAX9 gene. It is also found in mammals generally.- Function :This gene is a member of the paired box family of transcription factors...
gene (and perhaps other genes).
Potential uses for extracted teeth
In August 2008, it was revealed that scientists in Japan were able to successfully harvest stem cellStem cell
This article is about the cell type. For the medical therapy, see Stem Cell TreatmentsStem cells are biological cells found in all multicellular organisms, that can divide and differentiate into diverse specialized cell types and can self-renew to produce more stem cells...
s from wisdom teeth. This discovery is of great clinical importance, as wisdom tooth extractions are a relatively common type of oral surgery. Patients who have their wisdom teeth removed are currently able to opt to have stem cells from those teeth isolated and saved, in case they should ever need the cells.
Wisdom teeth can be transplanted to replace lost molars. Rejection applies to teeth just like it does to other body tissue and donor trials so far have been unsuccessful. The transplantation will cause some damage to the tooth during the transplant process, most notably the nerve, but moving the tooth to another position for the same person is now considered successful and beneficial.
Etymology
They are generally thought to be called wisdom teeth because they appear so late – much later than the other teeth, at an age where people are presumably "wiser" than as a child, when the other teeth erupt. The term probably came as a translation of the Latin dens sapientiae.External links
- National Institute of Clinical Health and Excellence Guideline to Wisdom teeth removal
- University of Manitoba Dental Hygiene Article on wisdom teeth.
- Wisdom tooth extraction WebMD article

