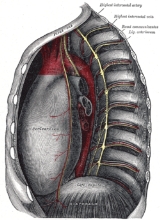
Thoracic cavity
Overview
Body cavity
By the broadest definition, a body cavity is any fluid-filled space in a multicellular organism. However, the term usually refers to the space located between an animal’s outer covering and the outer lining of the gut cavity, where internal organs develop...
of the human body (and other animal bodies) that is protected by the thoracic wall
Thoracic wall
The thoracic wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.The bony portion is known as the thoracic cage. However, the wall also includes muscle, skin, and fascia....
(thoracic cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia
Fascia
A fascia is a layer of fibrous tissue that permeates the human body. A fascia is a connective tissue that surrounds muscles, groups of muscles, blood vessels, and nerves, binding those structures together in much the same manner as plastic wrap can be used to hold the contents of sandwiches...
).
The thoracic area includes the tendons as well as the cardiovascular system which could be damaged from injury to the back, spine or the neck.
Structures within the thoracic cavity include:
- structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heartHeartThe heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
and great vessels, which include the thoracic aortaAortaThe aorta is the largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries...
, the pulmonary arteryPulmonary arteryThe pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
and all its branches, the superiorSuperior vena cavaThe superior vena cava is truly superior, a large diameter, yet short, vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the heart's right atrium...
and inferior vena cavaInferior vena cavaThe inferior vena cava , also known as the posterior vena cava, is the large vein that carries de-oxygenated blood from the lower half of the body into the right atrium of the heart....
, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos veinAzygos veinThe azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column. It can also provide an alternate path for blood to the right atrium by allowing the blood to flow between the venae cavae when one vena cava is blocked.-Structure:... - structures of the respiratory systemRespiratory systemThe respiratory system is the anatomical system of an organism that introduces respiratory gases to the interior and performs gas exchange. In humans and other mammals, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles...
, including the tracheaVertebrate tracheaIn tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
, bronchi and lungs - structures of the digestive system, including the esophagusEsophagusThe esophagus is an organ in vertebrates which consists of a muscular tube through which food passes from the pharynx to the stomach. During swallowing, food passes from the mouth through the pharynx into the esophagus and travels via peristalsis to the stomach...
, - endocrine glands, including the thymus gland,
- structures of the nervous systemNervous systemThe nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
including the paired vagus nerves, and the paired sympathetic chains, - lymphatics including the thoracic ductThoracic ductIn human anatomy, the thoracic duct of the lymphatic system is the largest lymphatic vessel in the body. It is also known as the left lymphatic duct, alimentary duct, chyliferous duct, and Van Hoorne's canal....
.
It contains three potential spaces lined with mesothelium
Mesothelium
The mesothelium is a membrane that forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura , peritoneum and pericardium . Mesothelial tissue also surrounds the male internal reproductive organs and covers the internal reproductive organs of women...
: the paired pleural cavities
Pleural cavity
In human anatomy, the pleural cavity is the potential space between the two pleura of the lungs. The pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered, membrane structure. The thin space between the two pleural layers is known as the pleural cavity; it normally...
and the pericardial cavity
Pericardium
The pericardium is a double-walled sac that contains the heart and the roots of the great vessels.-Layers:...
.
Unanswered Questions

