
Three-tier education
Encyclopedia
Three-tier education refers to those structures of schooling, which exist in some parts of England, where pupils are taught in three distinct school types. A similar experiment was also trialled in Scotland. (See separate article
)
In three-tier authorities
children begin their compulsory education
in a First school
. Sometimes also called a Lower school (or more simply, primary school), these schools cater for children aged up to an age between 8 and 10, and cover all of Key Stage 1
and the first years of Key Stage 2
. Children then transfer to a Middle school
, sometimes called an Intermediate school. These schools cater for children during a period of 3 to 4 years between the ages of 8 and 14, depending on the local authority. These years cover parts of both Key Stage 2
and Key Stage 3
. Following this, children transfer to a High school
, sometimes known as an Upper school for the remainder of their compulsory education, and sometimes on into sixth form
.
Many local authorities trialled systems as this for a period from as early as 1968, with many more following suit during the early 1970s
, particularly in 1972 when the Raising of school leaving age in England and Wales
from 15 to 16 saw many secondary schools lacking the adequate class space for 11-16 year olds.
However, most have since reverted to align their schools to the National Curriculum.
Some areas reverted to the traditional age ranges as long ago as the late 1970s. One of the first areas to revert to the traditional age ranges was Halesowen
in the West Midlands
, which abandoned 5-9 first, 9-13 middle and 13-16/18 secondary schools in 1982 after just 10 years in use.
Authorities which still retain 3-tier education across their area are Bedfordshire
, Northumberland
, Harrow
and the Isle of Wight
. Leicestershire
operate a three-tier system also, with children moving from primary school into secondary school after year six, and then to upper school after year nine.
A similar system exists in Gibraltar
.
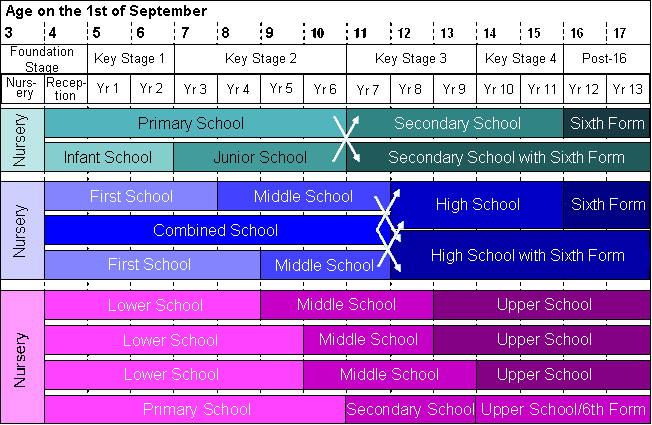
The main routes through education are shown in the diagram below, with three-tier routes being shown in blue and mauve:
Grangemouth middle schools
Two middle schools operated in the town of Grangemouth between 1974 and 1988. Grangemouth is in the historic county of Stirlingshire in central Scotland and, following local government reorganisation in 1975, became part of the Falkirk District of the Central Region....
)
In three-tier authorities
Local Education Authority
A local education authority is a local authority in England and Wales that has responsibility for education within its jurisdiction...
children begin their compulsory education
Compulsory education
Compulsory education refers to a period of education that is required of all persons.-Antiquity to Medieval Era:Although Plato's The Republic is credited with having popularized the concept of compulsory education in Western intellectual thought, every parent in Judea since Moses's Covenant with...
in a First school
First School
First school and lower school are terms used in some areas of the United Kingdom to describe the first stage of primary education. Some English Local Education Authorities have introduced First Schools since the 1960s...
. Sometimes also called a Lower school (or more simply, primary school), these schools cater for children aged up to an age between 8 and 10, and cover all of Key Stage 1
Key Stage 1
Key Stage 1 is the legal term for the two years of schooling in maintained schools in England and Wales normally known as Year 1 and Year 2, when pupils are aged between 5 and 7. This Key Stage normally covers pupils during infant school, although in some cases this might form part of a first or...
and the first years of Key Stage 2
Key Stage 2
Key Stage 2 is the legal term for the four years of schooling in maintained schools in England and Wales normally known as Year 3, Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6, when pupils are aged between 7 and 11. The term is applied differently in Northern Ireland where it refers to pupils in Year 5, Year 6 and...
. Children then transfer to a Middle school
Middle school
Middle School and Junior High School are levels of schooling between elementary and high schools. Most school systems use one term or the other, not both. The terms are not interchangeable...
, sometimes called an Intermediate school. These schools cater for children during a period of 3 to 4 years between the ages of 8 and 14, depending on the local authority. These years cover parts of both Key Stage 2
Key Stage 2
Key Stage 2 is the legal term for the four years of schooling in maintained schools in England and Wales normally known as Year 3, Year 4, Year 5 and Year 6, when pupils are aged between 7 and 11. The term is applied differently in Northern Ireland where it refers to pupils in Year 5, Year 6 and...
and Key Stage 3
Key Stage 3
Key Stage 3 is the legal term for the three years of schooling in maintained schools in England and Wales normally known as Year 7, Year 8 and Year 9, when pupils are aged between 11 and 14...
. Following this, children transfer to a High school
High school
High school is a term used in parts of the English speaking world to describe institutions which provide all or part of secondary education. The term is often incorporated into the name of such institutions....
, sometimes known as an Upper school for the remainder of their compulsory education, and sometimes on into sixth form
Sixth form
In the education systems of England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, and of Commonwealth West Indian countries such as Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago, Belize, Jamaica and Malta, the sixth form is the final two years of secondary education, where students, usually sixteen to eighteen years of age,...
.
Many local authorities trialled systems as this for a period from as early as 1968, with many more following suit during the early 1970s
1970s
File:1970s decade montage.png|From left, clockwise: US President Richard Nixon doing the V for Victory sign after his resignation from office after the Watergate scandal in 1974; Refugees aboard a US naval boat after the Fall of Saigon, leading to the end of the Vietnam War in 1975; The 1973 oil...
, particularly in 1972 when the Raising of school leaving age in England and Wales
Raising of school leaving age in England and Wales
The Raising of school leaving age is the name given by Government to refer to changes regarding the legal age a child is permitted to leave compulsory education, usually falling under an Education Act...
from 15 to 16 saw many secondary schools lacking the adequate class space for 11-16 year olds.
However, most have since reverted to align their schools to the National Curriculum.
Some areas reverted to the traditional age ranges as long ago as the late 1970s. One of the first areas to revert to the traditional age ranges was Halesowen
Halesowen
Halesowen is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley, in the West Midlands, England.The population, as measured by the United Kingdom Census 2001, was 55,273...
in the West Midlands
West Midlands (county)
The West Midlands is a metropolitan county in western central England with a 2009 estimated population of 2,638,700. It came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972, formed from parts of Staffordshire, Worcestershire and Warwickshire. The...
, which abandoned 5-9 first, 9-13 middle and 13-16/18 secondary schools in 1982 after just 10 years in use.
Authorities which still retain 3-tier education across their area are Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire
Bedfordshire is a ceremonial county of historic origin in England that forms part of the East of England region.It borders Cambridgeshire to the north-east, Northamptonshire to the north, Buckinghamshire to the west and Hertfordshire to the south-east....
, Northumberland
Northumberland
Northumberland is the northernmost ceremonial county and a unitary district in North East England. For Eurostat purposes Northumberland is a NUTS 3 region and is one of three boroughs or unitary districts that comprise the "Northumberland and Tyne and Wear" NUTS 2 region...
, Harrow
London Borough of Harrow
The London Borough of Harrow is a London borough of north-west London. It borders Hertfordshire to the north and other London boroughs: Hillingdon to the west, Ealing to the south, Brent to the south-east and Barnet to the east.-History:...
and the Isle of Wight
Education on the Isle of Wight
Education on the Isle of Wight is provided by Local Education Authority-maintained schools on the Isle of Wight, and independent schools. As a rural community, many of these schools are small, with average numbers of pupils lower than in many urban areas. It was decided on 19 March 2008, in a...
. Leicestershire
Leicestershire
Leicestershire is a landlocked county in the English Midlands. It takes its name from the heavily populated City of Leicester, traditionally its administrative centre, although the City of Leicester unitary authority is today administered separately from the rest of Leicestershire...
operate a three-tier system also, with children moving from primary school into secondary school after year six, and then to upper school after year nine.
A similar system exists in Gibraltar
Education in Gibraltar
Education in Gibraltar generally follows the English system operating within a three tier system. Schools in Gibraltar follow the Key Stage system which teaches the National Curriculum.-Primary education:...
.
The main routes through education are shown in the diagram below, with three-tier routes being shown in blue and mauve:

External links
- Northumberland Education Action Group - campaign to retain three-tier education in Northumberland
- Parents Against Change, Suffolk UK Action Group - campaign to retain three-tier education in Suffolk

