
Time-domain reflectometry
Encyclopedia
Measurement
Measurement is the process or the result of determining the ratio of a physical quantity, such as a length, time, temperature etc., to a unit of measurement, such as the metre, second or degree Celsius...
used to determine the characteristics of electrical lines
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
by observing reflected waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
s. Time-domain transmissometry (TDT) is an analogous technique that measures the transmitted (rather than reflected) impulse. Together, they provide a powerful means of analysing electrical or optical transmission media such as coaxial cable
Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable, or coax, has an inner conductor surrounded by a flexible, tubular insulating layer, surrounded by a tubular conducting shield. The term coaxial comes from the inner conductor and the outer shield sharing the same geometric axis...
s and optical fiber
Optical fiber
An optical fiber is a flexible, transparent fiber made of a pure glass not much wider than a human hair. It functions as a waveguide, or "light pipe", to transmit light between the two ends of the fiber. The field of applied science and engineering concerned with the design and application of...
s.
Variations of TDR exist. For example, spread-spectrum time-domain reflectometry
Spread-spectrum time-domain reflectometry
Spread-spectrum time-domain reflectometry is a measurement technique to identify faults, usually in electrical wires, by observing reflected spread spectrum signals. SSTDR is a type of time-domain reflectometry that can be advantageous to other systems due to the ability to use SSTDR in high-noise...
(SSTDR) is used to detect intermittent faults in complex and high-noise systems such as aircraft wiring. Coherent optical time domain reflectometry (COTDR) is another variant, used in optical systems, in which the returned signal is mixed with a local oscillator and then filtered to reduce noise.
The amplitude
Amplitude
Amplitude is the magnitude of change in the oscillating variable with each oscillation within an oscillating system. For example, sound waves in air are oscillations in atmospheric pressure and their amplitudes are proportional to the change in pressure during one oscillation...
of the reflected signal can be determined from the impedance
Electrical impedance
Electrical impedance, or simply impedance, is the measure of the opposition that an electrical circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current circuit...
of the discontinuity
Discontinuity
Discontinuity may refer to:*Discontinuity , a harmless irregularity in a casting*Discontinuity in geotechnics is a plane or surface marking a change in physical or chemical properties in a soil or rock mass...
. The distance
Distance
Distance is a numerical description of how far apart objects are. In physics or everyday discussion, distance may refer to a physical length, or an estimation based on other criteria . In mathematics, a distance function or metric is a generalization of the concept of physical distance...
to the reflecting impedance can also be determined from the time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
that a pulse
Pulse (signal processing)
In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
takes to return. The limitation of this method is the minimum system rise time
Rise time
In electronics, when describing a voltage or current step function, rise time refers to the time required for a signal to change from a specified low value to a specified high value...
. The total rise time consists of the combined rise time of the driving pulse and that of the oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
that monitors the reflections.
Method
The TDR analysis begins with the propagation of a stepStep function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals...
or impulse of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
into a system
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
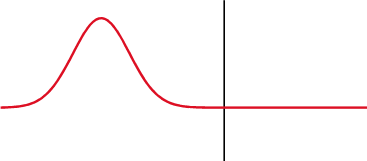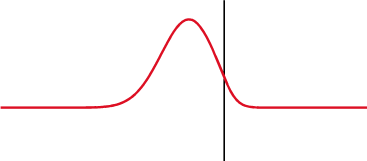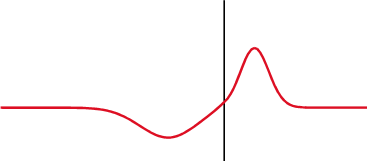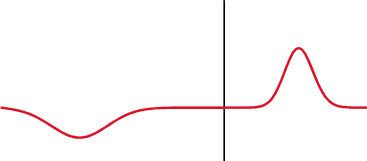
and the subsequent observation of the energy reflected by the system. By analyzing the magnitude, duration and shape of the reflected waveform, the nature of the impedance variation in the transmission system can be determined.
Resistive load
If a pure resistive loadResistor
A linear resistor is a linear, passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element.The current through a resistor is in direct proportion to the voltage across the resistor's terminals. Thus, the ratio of the voltage applied across a resistor's...
is placed on the output of the reflectometer
Reflectometer
Some scientific instruments commonly designated Reflectometer are:*Vector Network Analyser *Spectrophotometer: in optics, an instrument for measuring the reflectivity or reflectance of reflecting surfaces*Optical time domain reflectometer...
and a step signal
Step function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals...
is applied, a step signal is observed on the CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
, and its height is a function of the resistance. The magnitude of the step caused by the resistive load may be expressed as a fraction of the input signal as given by:
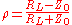
where
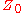 is the characteristic impedance
is the characteristic impedanceCharacteristic impedance
The characteristic impedance or surge impedance of a uniform transmission line, usually written Z_0, is the ratio of the amplitudes of a single pair of voltage and current waves propagating along the line in the absence of reflections. The SI unit of characteristic impedance is the ohm...
of the transmission line
Transmission line
In communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...
.
Reactive load
For reactive loads, the observed waveform depends upon the time constant formed by the load and the characteristic impedance of the line.See also
- Time-domain reflectometerTime-domain reflectometerA time-domain reflectometer is an electronic instrument used to characterize and locate faults in metallic cables . It can also be used to locate discontinuities in a connector, printed circuit board, or any other electrical path...
- Noise-Domain ReflectometryNoise-Domain ReflectometryNoise-domain reflectometry is a type of reflectometry where the reflectometer leverages existing data signals on wiring and does not have to generate any signals itself...
- Transmission lineTransmission lineIn communications and electronic engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable designed to carry alternating current of radio frequency, that is, currents with a frequency high enough that its wave nature must be taken into account...

