
Tobacco smoking
Encyclopedia
Tobacco smoking is the practice where tobacco
is burned and the resulting smoke (consisting of particle and gaseous phases) is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia
in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes. The practice encountered criticism from its first import into the Western world onwards, but embedded itself in certain strata of a number of societies before becoming widespread upon the introduction of automated cigarette-rolling apparatus.
German scientists identified a link between smoking and lung cancer in the late 1920s, leading to the first anti-smoking campaign in modern history, albeit one truncated by the collapse of the Third Reich at the end of the Second World War. In 1950, British researchers demonstrated a clear relationship between smoking and cancer. Scientific evidence continued to mount in the 1980s, which prompted political action against the practice. Rates of consumption since 1965 in the developed world have either peaked or declined. However, they continue to climb in the developing world.
Smoking is the most common method of consuming tobacco, and tobacco is the most common substance smoked. The agricultural product is often mixed with additives and then pyrolyzed
. The resulting smoke is then inhaled and the active substances absorbed through the alveoli in the lungs. The active substances trigger chemical reactions in nerve endings, which heighten heart rate, alertness, and reaction time. Dopamine
and endorphin
s are released, which are often associated with pleasure. As of 2000, smoking is practiced by approximately 1.22 billion people. In most communities men are more likely to smoke than are women, though the gender gap tends to be less pronounced in lower age groups.
Many smokers begin during adolescence
or early adulthood. During the early stages, a combination of perceived pleasurable acting as positive reinforcement and desire to respond to social peer pressure may offset the unpleasant symptoms of initial use, which typically include nausea and interrupted sleep patterns. After an individual has smoked for some years, the avoidance of withdrawal
symptoms and negative reinforcement become the key motivations to continue.
 Smoking's history dates back to as early as 5000–3000 BC when the agricultural product began to be cultivated in South America; consumption later evolved into burning the plant substance either by accident or with intent of exploring other means of consumption. The practice worked its way into shamanistic rituals. Many ancient civilizations—such as the Babylonians, the Indians, and the Chinese—burnt incense during religious rituals. The practice was later adopted by the Catholic and the Orthodox churches. Smoking in the Americas probably had its origins in the incense-burning ceremonies of shamans
Smoking's history dates back to as early as 5000–3000 BC when the agricultural product began to be cultivated in South America; consumption later evolved into burning the plant substance either by accident or with intent of exploring other means of consumption. The practice worked its way into shamanistic rituals. Many ancient civilizations—such as the Babylonians, the Indians, and the Chinese—burnt incense during religious rituals. The practice was later adopted by the Catholic and the Orthodox churches. Smoking in the Americas probably had its origins in the incense-burning ceremonies of shamans
but was later adopted for pleasure or as a social tool. The smoking of tobacco and various hallucinogenic drugs was used to achieve trances and to come into contact with the spirit world.
Eastern North American tribes would carry large amounts of tobacco in pouches as a readily accepted trade item and would often smoke it in pipes, either in sacred ceremonies or to seal bargains. Adults as well as children enjoyed the practice. It was believed that tobacco was a gift from the Creator and that the exhaled tobacco smoke was capable of carrying one's thoughts and prayers to heaven.
Apart from smoking, tobacco had a number of uses as medicine. As a pain killer it was used for earache and toothache and occasionally as a poultice
. Smoking was said by the desert Indians to be a cure for colds, especially if the tobacco was mixed with the leaves of the small Desert Sage, Salvia Dorrii, or the root of Indian Balsam or Cough Root, Leptotaenia multifida, the addition of which was thought to be particularly good for asthma and tuberculosis.
 In 1612, six years after the settlement of Jamestown, John Rolfe
In 1612, six years after the settlement of Jamestown, John Rolfe
was credited as the first settler to successfully raise tobacco as a cash crop. The demand quickly grew as tobacco, referred to as "brown gold", reviving the Virginia joint stock company from its failed gold expeditions. In order to meet demands from the Old World, tobacco was grown in succession, quickly depleting the soil. This became a motivator to settle west into the unknown continent, and likewise an expansion of tobacco production. Indentured servitude became the primary labor force up until Bacon's Rebellion
, from which the focus turned to slavery. This trend abated following the American revolution
as slavery became regarded as unprofitable. However, the practice was revived in 1794 with the invention of the cotton gin.
Frenchman Jean Nicot
(from whose name the word nicotine is derived) introduced tobacco to France in 1560, and tobacco then spread to England. The first report of a smoking Englishman is of a sailor in Bristol in 1556, seen "emitting smoke from his nostrils". Like tea, coffee and opium, tobacco was just one of many intoxicants that was originally used as a form of medicine. Tobacco was introduced around 1600 by French merchants in what today is modern-day Gambia and Senegal
. At the same time caravans from Morocco
brought tobacco to the areas around Timbuktu
and the Portuguese brought the commodity (and the plant) to southern Africa, establishing the popularity of tobacco throughout all of Africa by the 1650s.
Soon after its introduction to the Old World, tobacco came under frequent criticism from state and religious leaders. Murad IV
, sultan of the Ottoman Empire
1623-40 was among the first to attempt a smoking ban by claiming it was a threat to public moral and health. The Chinese emperor Chongzhen issued an edict banning smoking two years before his death and the overthrow of the Ming dynasty
. Later, the Manchu
of the Qing dynasty
, who were originally a tribe of nomadic horse warriors, would proclaim smoking "a more heinous crime than that even of neglecting archery". In Edo period
Japan, some of the earliest tobacco plantations were scorned by the shogunate as being a threat to the military economy by letting valuable farmland go to waste for the use of a recreational drug instead of being used to plant food crops.
 Religious leaders have often been prominent among those who considered smoking immoral or outright blasphemous. In 1634 the Patriarch of Moscow forbade the sale of tobacco and sentenced men and women who flouted the ban to have their nostrils slit and their backs whipped until skin came off their backs. The Western church leader Urban VII likewise condemned smoking on holy places in a papal bull of 1624. Despite many concerted efforts, restrictions and bans were almost universally ignored. When James I of England
Religious leaders have often been prominent among those who considered smoking immoral or outright blasphemous. In 1634 the Patriarch of Moscow forbade the sale of tobacco and sentenced men and women who flouted the ban to have their nostrils slit and their backs whipped until skin came off their backs. The Western church leader Urban VII likewise condemned smoking on holy places in a papal bull of 1624. Despite many concerted efforts, restrictions and bans were almost universally ignored. When James I of England
, a staunch anti-smoker and the author of a A Counterblaste to Tobacco
, tried to curb the new trend by enforcing a 4000% tax increase on tobacco in 1604, it proved a failure, as London had some 7,000 tobacco sellers by the early 17th century. Later, scrupulous rulers would realise the futility of smoking bans and instead turned tobacco trade and cultivation into lucrative government monopolies.
By the mid-17th century every major civilization had been introduced to tobacco smoking and in many cases had already assimilated it into the native culture, despite the attempts of many rulers to eliminate the practice with harsh penalties or fines. Tobacco, both product and plant, followed the major trade routes to major ports and markets, and then on into the hinterlands. The English language term smoking was coined in the late 18th century; before then the practice was called drinking smoke.
Growth remained stable until the American Civil War in 1860s, when the primary labor force shifted from slavery to share cropping. This, along with a change in demand, lead to the industrialization of tobacco production with the cigarette. James Bonsack, a craftsman, in 1881 produce a machine to speed the production in cigarettes.
condemned his earlier smoking habit as a waste of money, and later with stronger assertions. This movement was further strengthened with Nazi reproductive policy as women who smoked were viewed as unsuitable to be wives and mothers in a German family.
The anti-tobacco movement in Nazi Germany
did not reach across enemy lines during the Second World War, as anti-smoking groups quickly lost popular support. By the end of the Second World War, American cigarette manufacturers quickly reentered the German black market. Illegal smuggling of tobacco became prevalent, and leaders of the Nazi anti-smoking campaign were silenced. As part of the Marshall Plan
, the United States shipped free tobacco to Germany; with 24,000 tons in 1948 and 69,000 tons in 1949. Per capita yearly cigarette consumption in post-war Germany
steadily rose from 460 in 1950 to 1,523 in 1963. By the end of the 20th century, anti-smoking campaigns in Germany were unable to exceed the effectiveness of the Nazi-era climax in the years 1939–41 and German tobacco health research was described by Robert N. Proctor
as "muted".
 Richard Doll
Richard Doll
in 1950 published research in the British Medical Journal
showing a close link between smoking and lung cancer
. Four years later, in 1954 the British Doctors Study
, a study of some 40 thousand doctors over 20 years, confirmed the suggestion, based on which the government issued advice that smoking and lung cancer rates were related. In 1964 the United States Surgeon General
's Report on Smoking and Health likewise began suggesting the relationship between smoking and cancer.
As scientific evidence mounted in the 1980s, tobacco companies claimed contributory negligence
as the adverse health effects were previously unknown or lacked substantial credibility. Health authorities sided with these claims up until 1998, from which they reversed their position. The Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement, originally between the four largest US tobacco companies and the Attorneys General of 46 states, restricted certain types of tobacco advertisement and required payments for health compensation; which later amounted to the largest civil settlement in United States history.
From 1965 to 2006, rates of smoking in the United States declined from 42% to 20.8%. The majority of those who quit were professional, affluent men. Although the per-capita number of smokers decreased, the average number of cigarettes consumed per person per day increased from 22 in 1954 to 30 in 1978. This paradoxical event suggests that those who quit smoked less, while those who continued to smoke moved to smoke more light cigarettes. The trend has been paralleled by many industrialized nations as rates have either leveled-off or declined. In the developing world, however, tobacco consumption continues to rise at 3.4% in 2002. In Africa, smoking is in most areas considered to be modern, and many of the strong adverse opinions that prevail in the West receive much less attention. Today Russia leads as the top consumer of tobacco followed by Indonesia
, Laos
, Ukraine
, Belarus
, Greece, Jordan
, and China.
is an agricultural product processed from the fresh leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana
. The genus contains a number of species, however, Nicotiana tabacum
is the most commonly grown. Nicotiana rustica
follows as second containing higher concentrations of nicotine. These leaves are harvested and cured to allow for the slow oxidation and degradation of carotenoid
s in tobacco leaf. This produces certain compounds in the tobacco leaves which can be attributed to sweet hay, tea, rose oil, or fruity aromatic flavors. Before packaging, the tobacco is often combined with other additives in order to: enhance the addictive potency, shift the products pH
, or improve the effects of smoke by making it more palatable. In the United States these additives are regulated to 599 substances. The product is then processed, packaged, and shipped to consumer markets. Means of consumption has greatly expanded in scope as new methods of delivering the active substances with fewer by-products have encompassed or are beginning to encompass:
Beedi : Beedi
s are thin South Asian cigarettes filled with tobacco flake and wrapped in a tendu leaf tied with a string at one end. They produce higher levels of carbon monoxide, nicotine, and tar than cigarettes typical in the United States.
Cigars : Cigar
s are tightly rolled bundles of dried and fermented tobacco which are ignited so that smoke may be drawn into the smoker's mouth. They are generally not inhaled because the high alkalinity of the smoke, which can quickly become irritating to the trachea and lungs. The prevalence of cigar smoking varies depending on location, historical period, and population surveyed, and prevalence estimates vary somewhat depending on the survey method. The United States is the top consuming country by far, followed by Germany and the United Kingdom; the US and Western Europe account for about 75% of cigar sales worldwide. As of 2005 it is estimated that 4.3% of men and 0.3% of women smoke cigars.
Cigarettes : Cigarette
s, French for "small cigar", are a product consumed through smoking and manufactured out of cured and finely cut tobacco leaves and reconstituted tobacco, often combined with other additives, which are then rolled or stuffed into a paper-wrapped cylinder. Cigarettes are ignited and inhaled, usually through a cellulose acetate filter, into the mouth and lungs.
Electronic cigarette : Electronic cigarettes are an alternative to tobacco smoking, although no tobacco is consumed. It is a battery-powered device that provides inhaled doses of nicotine by delivering a vaporized propylene glycol
/nicotine
solution. Many legislation and public health investigations are currently pending in many countries due to its relatively recent emergence. Most electronic cigarettes are designed to resemble actual tobacco smoking implements, such as cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, but many take the form of ballpoint pens or screwdrivers since those designs are more practical to house the mechanisms involved. Most are also reusable, with replaceable and refillable parts, but some models are disposable.
Hookah : Hookah
are a single or multi-stemmed (often glass-based) water pipe for smoking. Originally from India. The hookah was a symbol of pride and honour for the landlords, kings and other such high class people.Now ,the hookah has gained immense popularity, especially in the Middle East. A hookah operates by water filtration and indirect heat. It can be used for smoking herbal fruits, tobacco, or cannabis.
Kretek : Kretek
are cigarettes made with a complex blend of tobacco, clove
s and a flavoring "sauce". It was first introduced in the 1880s in Kudus, Java, to deliver the medicinal eugenol of cloves to the lungs. The quality and variety of tobacco play an important role in kretek production, from which kretek can contain more than 30 types of tobacco. Minced dried clove buds weighing about 1/3 of the tobacco blend are added to add flavoring. In 2004 the United States prohibited cigarettes from having a "characterizing flavor" of certain ingredients other than tobacco and menthol, thereby removing kretek from being classified as cigarettes.
Passive smoking : Passive smoking
is the usually involuntary consumption of smoked tobacco. Second-hand smoke (SHS) is the consumption where the burning end is present, environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or third-hand smoke is the consumption of the smoke that remains after the burning end has been extinguished. Because of its perceived negative implications, this form of consumption has played a central role in the regulation of tobacco products.
Pipe smoking : Pipe smoking
typically consists of a small chamber (the bowl) for the combustion of the tobacco to be smoked and a thin stem (shank) that ends in a mouthpiece (the bit). Shredded pieces of tobacco are placed into the chamber and ignited. Tobaccos for smoking in pipes are often carefully treated and blended to achieve flavour nuances not available in other tobacco products.
Roll-Your-Own : Roll-Your-Own
or hand-rolled cigarettes, often called 'rollies', are very popular particularly in European countries. These are prepared from loose tobacco, cigarette papers, and filters all bought separately. They are usually much cheaper than ready-made cigarettes.
Vaporizer : A vaporizer is a device used to sublimate the active ingredients of plant material. Rather than burning the herb, which produces potentially irritating, toxic, or carcinogen
ic by-products; a vaporizer heats the material in a partial vacuum so that the active compounds contained in the plant boil off into a vapor. Medical administration of a smoke substance often prefer this method as to directly pyrolyzing the plant material.
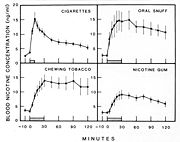 The active substances in tobacco, especially cigarettes, is administered by burning the leaves and inhaling the vaporized gas that results. This quickly and effectively delivers substances into the bloodstream by absorption through the alveoli in the lungs. The lungs contain some 300 million alveoli, which amounts to a surface area of over 70 m2 (about the size of a tennis court). This method is inefficient as not all of the smoke will be inhaled, and some amount of the active substances will be lost in the process of combustion, pyrolysis
The active substances in tobacco, especially cigarettes, is administered by burning the leaves and inhaling the vaporized gas that results. This quickly and effectively delivers substances into the bloodstream by absorption through the alveoli in the lungs. The lungs contain some 300 million alveoli, which amounts to a surface area of over 70 m2 (about the size of a tennis court). This method is inefficient as not all of the smoke will be inhaled, and some amount of the active substances will be lost in the process of combustion, pyrolysis
. Pipe and Cigar smoke are not inhaled because of its high alkalinity
, which are irritating to the trachea
and lungs. However, because of its higher alkalinity (pH 8.5) compared to cigarette smoke (pH 5.3), un-ionized nicotine is more readily absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth. Nicotine absorption from cigar and pipe, however, is much less than that from cigarette smoke.
The inhaled substances trigger chemical reactions in nerve endings. The cholinergic receptors are often triggered by the naturally occurring neurotransmitter
acetylcholine
. Acetylcholine and Nicotine
express chemical similarities, which allows Nicotine to trigger the receptor as well. These nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
s takes are located in the central nervous system and at the nerve-muscle junction of skeletal muscles; whose activity increases heart rate, alertness, and faster reaction times. Nicotine acetylcholine stimulation is not directly addictive. However, since dopamine-releasing neurons are abundant on nicotine receptors, dopamine is released. This release of dopamine, which is associated with pleasure, is reinforcing and may also increase working memory
. Nicotine and cocaine activate similar patterns of neurons, which supports the idea that common substrates among these drugs.
When tobacco is smoked, most of the nicotine is pyrolyzed. However, a dose sufficient to cause mild somatic dependency and mild to strong psychological dependency remains. There is also a formation of harmane (a MAO inhibitor) from the acetaldehyde in tobacco smoke. This seems to play an important role in nicotine addiction—probably by facilitating a dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens
as a response to nicotine stimuli. Using rat studies, withdrawal after repeated exposure to nicotine results in less responsive nucleus accumbens cells, which produce dopamine responsible for reinforcement
.
Smoking is generally five times higher among men than women, however the gender gap declines with younger age. In developed countries smoking rates for men have peaked and have begun to decline, however for women they continue to climb.
As of 2002, about twenty percent of young teens (13–15) smoke worldwide. From which 80,000 to 100,000 children begin smoking every day—roughly half of which live in Asia. Half of those who begin smoking in adolescent years are projected to go on to smoke for 15 to 20 years.
The World Health Organization
(WHO) states that "Much of the disease burden and premature mortality attributable to tobacco use disproportionately affect the poor". Of the 1.22 billion smokers, 1 billion of them live in developing or transitional economies. Rates of smoking have leveled off or declined in the developed world. In the developing world, however, tobacco consumption is rising by 3.4% per year as of 2002.
The WHO in 2004 projected 58.8 million deaths to occur globally, from which 5.4 million are tobacco-attributed, and 4.9 million as of 2007. As of 2002, 70% of the deaths are in developing countries.
 Most smokers begin during adolescence or early adulthood. Smoking has elements of risk-taking and rebellion, which often appeal to young people. The presence of peers that smoke and media featuring high-status models smoking may also encourage smoking. Because teenagers are influenced more by their peers than by adults, attempts by parents, schools, and health professionals at preventing people from trying cigarettes are unsuccessful.
Most smokers begin during adolescence or early adulthood. Smoking has elements of risk-taking and rebellion, which often appeal to young people. The presence of peers that smoke and media featuring high-status models smoking may also encourage smoking. Because teenagers are influenced more by their peers than by adults, attempts by parents, schools, and health professionals at preventing people from trying cigarettes are unsuccessful.
Children of smoking parents are more likely to smoke than children with non-smoking parents. One study found that parental smoking cessation was associated with less adolescent smoking, except when the other parent currently smoked. A current study tested the relation of adolescent smoking to rules regulating where adults are allowed to smoke in the home. Results showed that restrictive home smoking policies were associated with lower likelihood of trying smoking for both middle and high school students.
Many anti-smoking organizations claim that teenagers begin their smoking habits due to peer pressure, and cultural influence portrayed by friends. However, one study found that direct pressure to smoke cigarettes did not play a significant part in adolescent smoking. In that study, adolescents also reported low levels of both normative
and direct pressure to smoke cigarettes. A similar study showed that individuals play a more active role in starting to smoke than has previously been acknowledged and that social processes other than peer pressure need to be taken into account. Another study's results revealed that peer pressure
was significantly associated with smoking behavior across all age and gender cohorts, but that intrapersonal factors were significantly more important to the smoking behavior of 12–13 year-old girls than same-age boys. Within the 14–15 year-old age group, one peer pressure variable emerged as a significantly more important predictor of girls' than boys' smoking. It is debated whether peer pressure or self-selection
is a greater cause of adolescent smoking.
Psychologists such as Hans Eysenck
have developed a personality profile for the typical smoker. Extraversion is the trait that is most associated with smoking, and smokers tend to be sociable, impulsive, risk taking, and excitement seeking individuals. Although personality and social factors may make people likely to smoke, the actual habit is a function of operant conditioning
. During the early stages, smoking provides pleasurable sensations (because of its action on the dopamine
system) and thus serves as a source of positive reinforcement.
Some smokers argue that the depressant
effect of smoking allows them to calm their nerves, often allowing for increased concentration. However, according to the Imperial College London
, "Nicotine seems to provide both a stimulant and a depressant effect, and it is likely that the effect it has at any time is determined by the mood of the user, the environment and the circumstances of use. Studies have suggested that low doses have a depressant effect, while higher doses have stimulant effect."
Similarly, smoking has been shown to follow distinct circadian patterns during the waking day—with the high point usually occurring shortly after waking in the morning, and shortly before going to sleep at night.
system, society covers the cost of medical care for smokers who become ill through in the form of increased taxes. Two arguments exist on this front, the "pro-smoking" argument suggesting that heavy smokers generally don't live long enough to develop the costly and chronic illnesses which affect the elderly, reducing society's healthcare burden. The "anti-smoking" argument suggests that the healthcare burden is increased because smokers get chronic illnesses younger and at a higher rate than the general population.
Data on both positions is limited. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
published research in 2002 claiming that the cost of each pack
of cigarettes sold in the United States was more than $7 in medical care and lost productivity. The cost may be higher, with another study putting it as high as $41 per pack, most of which however is on the individual and his/her family. This is how one author of that study puts it when he explains the very low cost for others: "The reason the number is low is that for private pensions, Social Security, and Medicare — the biggest factors in calculating costs to society — smoking actually saves money. Smokers die at a younger age and don't draw on the funds they've paid into those systems."
By contrast, some non-scientific studies, including one conducted by Philip Morris
in the Czech Republic and another by the Cato Institute
, support the opposite position. Philip Morris has explicitly apologised for the former study, saying: "The funding and public release of this study which, among other things, detailed purported cost savings to the Czech Republic due to premature deaths of smokers, exhibited terrible judgment as well as a complete and unacceptable disregard of basic human values. For one of our tobacco companies to commission this study was not just a terrible mistake, it was wrong. All of us at Philip Morris, no matter where we work, are extremely sorry for this. No one benefits from the very real, serious and significant diseases caused by smoking."
Between 1970 an 1995, per-capita cigarette consumption in poorer developing countries increased by 67 percent, while it dropped by 10 percent in the richer developed world. Eighty percent of smokers now live in less developed countries. By 2030, the World Health Organization
(WHO) forecasts that 10 million people a year will die of smoking-related illness, making it the single biggest cause of death worldwide, with the largest increase to be among women. WHO forecasts the 21st century's death rate from smoking to be ten times the 20th century's rate. ("Washingtonian" magazine, December 2007).
, stroke
s, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD), emphysema
, and cancer
(particularly lung cancer
, cancers of the larynx and mouth
, and pancreatic cancer
). Cigarette smoking increases the risk of Crohn's disease as well as the severity of the course of the disease. It is also the number one cause of bladder cancer.
The World Health Organization
estimate that tobacco caused 5.4 million deaths in 2004 and 100 million deaths over the course of the 20th century. Similarly, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
describes tobacco use as "the single most important preventable risk to human health in developed countries and an important cause of premature death worldwide."
Lung cancer
occurs at non-smokers in 3.4 cases per 100 000 population
. At people smoking 0.5 packs of cigarettes a day this figure rises to 51.4 per 100 000, 1-2 packs - up to 143.9 per 100 000 and if the intensity of smoking is over 2 packs a day - up to 217.3 per 100,000 population.
Rates of smoking have leveled off or declined in the developed world. Smoking rates in the United States have dropped by half from 1965 to 2006 falling from 42% to 20.8% in adults. In the developing world, tobacco consumption is rising by 3.4% per year.
Passive smoking presents a very real health risk. Six hundred thousand deaths were attributable to second-hand smoke in 2004.
-brand cigarettes; Albert Einstein
's, Kiana Lee Rosch's, Douglas MacArthur
's, Bertrand Russell
's, and Bing Crosby's pipes; or the news broadcaster Edward R. Murrow
's cigarette. Writers in particular seem to be known for smoking, for example, Cornell Professor Richard Klein
's book Cigarettes are Sublime for the analysis, by this professor of French literature, of the role smoking plays in 19th and 20th century letters. The popular author Kurt Vonnegut
addressed his addiction to cigarettes within his novels. British Prime Minister Harold Wilson
was well known for smoking a pipe in public as was Winston Churchill
for his cigars. Sherlock Holmes
, the fictional detective created by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle smoked a pipe, cigarettes, and cigars. The DC
Vertigo comic book character, John Constantine
, created by Alan Moore
, is synonymous with smoking, so much so that the first storyline by Preacher
creator, Garth Ennis
, centered around John Constantine contracting lung cancer. Professional wrestler
James Fullington, while in character as "The Sandman", is a chronic smoker in order to appear "tough".
The problem of smoking at home is particularly difficult for women in many cultures especially Arab cultures where it may not be acceptable for a woman to ask her husband not to smoke at home or in the presence of her children. Studies has shown that pollution levels in door places are higher than levels found on busy roadways, in closed motor garages, and during fire storms. Furthermore, smoke can spread from one room to another, even if doors to the smoking area are closed.
The ceremonial smoking of tobacco, and praying with a sacred pipe
, is a prominent part of the religious ceremonies of a number of Native American
Nations. Sema, the Anishinaabe
word for tobacco, is grown for ceremonial use and considered the ultimate sacred plant since its smoke was believed to carry prayers to the heavens. In most major religions, however, tobacco smoking is not specifically prohibited, although it may be discouraged as an immoral habit. Before the health risks of smoking were identified through controlled study, smoking was considered an immoral habit by certain Christian preachers and social reformers. The founder of the Latter Day Saint movement
, Joseph Smith, Jr, recorded that on February 27, 1833, he received a revelation
which discouraged tobacco use. This "Word of Wisdom" was later accepted as a commandment, and faithful Latter-day Saints abstain completely from tobacco. Jehovah's Witnesses base their stand against smoking on the Bible's command to "clean ourselves of every defilement of flesh" (2 Corinthians 7:1). The Jewish Rabbi Yisrael Meir Kagan
(1838–1933) was one of the first Jewish authorities to speak out on smoking. In the Bahá'í Faith
, smoking tobacco is discouraged though not forbidden.
, took effect. The FCTC is the world's first public health treaty. Countries that sign on as parties agree to a set of common goals, minimum standards for tobacco control policy, and to cooperate in dealing with cross-border challenges such as cigarette smuggling. Currently the WHO declares that 4 billion people will be covered by the treaty, which includes 168 signatories. Among other steps, signatories are to put together legislation that will eliminate secondhand smoke in indoor workplaces, public transport, indoor public places and, as appropriate, other public places.
In 2002, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
said that each pack
of cigarettes sold in the United States costs the nation more than $7 in medical care and lost productivity, around $3400 per year per smoker. Another study by a team of health economists finds the combined price paid by their families and society is about $41 per pack of cigarettes.
Substantial scientific evidence shows that higher cigarette prices result in lower overall cigarette consumption. Most studies indicate that a 10% increase in price will reduce overall cigarette consumption by 3% to 5%. Youth, minorities, and low-income smokers are two to three times more likely to quit or smoke less than other smokers in response to price increases. Smoking is often cited as an example of an inelastic good, however, i.e. a large rise in price will only result in a small decrease in consumption.
Many nations have implemented some form of tobacco taxation. As of 1997, Denmark had the highest cigarette tax burden of $4.02 per pack. Taiwan only had a tax burden of $0.62 per pack. The federal government of the United States charges $1.01 per pack.
Cigarette taxes vary widely from state to state in the United States. For example, Missouri
has a cigarette tax of only 17 cents per pack, the nation's lowest, while New York
has the highest cigarette tax in the U.S.: $4.35 per pack. In Alabama, Illinois, Missouri, New York City, Tennessee, and Virginia, counties and cities may impose an additional limited tax on the price of cigarettes. Sales taxes are also levied on tobacco products in most jurisdictions.
In the United Kingdom, a packet of 20 cigarettes typically costs between £5.22 and £8.00 depending on the brand purchased and where the purchase was made. The UK has a significant black market for tobacco, and it has been estimated by the tobacco industry that 27% of cigarette and 68% of handrolling tobacco consumption is non-UK duty paid (NUKDP).
In Australia total taxes account for 62.5% of the final price of a packet of cigarettes (2011 figures). These taxes include federal excise or customs duty, and the more recently introduced Goods and Services Tax (GST).
ruled that programs broadcast on a television station that discussed smoking and health were insufficient to offset the effects of paid advertisements that were broadcast for five to ten minutes each day. In April 1970, Congress passed the Public Health Cigarette Smoking Act
banning the advertising of cigarettes on television
and radio
starting on January 2, 1971.
The Tobacco Advertising Prohibition Act 1992 expressly prohibited almost all forms of Tobacco advertising in Australia, including the sponsorship of sporting or other cultural events by cigarette brands.
All tobacco advertising and sponsorship on television has been banned within the European Union since 1991 under the Television Without Frontiers Directive (1989) This ban was extended by the Tobacco Advertising Directive, which took effect in July 2005 to cover other forms of media such as the internet, print media, and radio. The directive does not include advertising in cinemas and on billboards or using merchandising – or tobacco sponsorship of cultural and sporting events which are purely local, with participants coming from only one Member State as these fall outside the jurisdiction of the European Commission
. However, most member states have transposed the directive with national laws that are wider in scope than the directive and cover local advertising. A 2008 European Commission report concluded that the directive had been successfully transposed into national law in all EU member states, and that these laws were well implemented.
Some countries also impose legal requirements on the packaging of tobacco products. For example in the countries of the European Union, Turkey, Australia and South Africa, cigarette packs must be prominently labeled with the health risks associated with smoking. Canada, Australia, Thailand, Iceland and Brazil have also imposed labels upon cigarette packs warning smokers of the effects, and they include graphic images of the potential health effects of smoking. Cards are also inserted into cigarette packs in Canada. There are sixteen of them, and only one comes in a pack. They explain different methods of quitting smoking. Also, in the United Kingdom, there have been a number of graphic NHS
advertisements, one showing a cigarette filled with fatty deposits, as if the cigarette is symbolising the artery of a smoker.
Many countries have a smoking age
, In many countries, including the United States, most European Union member states, New Zealand, Canada, South Africa, Israel, India, Brazil, Chile, Costa Rica and Australia, it is illegal to sell tobacco products to minors and in the Netherlands, Austria, Belgium, Denmark and South Africa it is illegal to sell tobacco products to people under the age of 16. On September 1, 2007 the minimum age to buy tobacco products in Germany rose from 16 to 18, as well as in Great Britain where on October 1, 2007 it rose from 16 to 18. Underlying such laws is the belief that people should make an informed decision regarding the risks of tobacco use. These laws have a lax enforcement in some nations and states. In China, Turkey, and many other countries usually a child will have little problem buying tobacco products, because they are often told to go to the store to buy tobacco for their parents.
Several countries such as Ireland
, Latvia
, Estonia
, the Netherlands, France, Finland, Norway, Canada, Australia, Sweden, Portugal, Singapore
, Italy, Indonesia
, India, Lithuania
, Chile
, Spain, Iceland
, United Kingdom, Slovenia
, Turkey
and Malta
have legislated against smoking in public places, often including bars and restaurants. Restaurateurs have been permitted in some jurisdictions to build designated smoking areas (or to prohibit smoking). In the United States, many states prohibit smoking in restaurants, and some also prohibit smoking in bars. In provinces of Canada, smoking is illegal in indoor workplaces and public places, including bars and restaurants. As of March 31, 2008 Canada has introduced a smoking ban in all public places, as well as within 10 meters of an entrance to any public place. In Australia, smoking bans vary from state to state. Currently, Queensland has total bans within all public interiors (including workplaces, bars, pubs and eateries) as well as patrolled beaches and some outdoor public areas. There are, however, exceptions for designated smoking areas. In Victoria
, smoking is banned in train stations, bus stops and tram stops as these are public locations where second hand smoke can affect non-smokers waiting for public transport, and since July 1, 2007 is now extended to all indoor public places. In New Zealand and Brazil
, smoking is banned in enclosed public places mainly bars, restaurants and pubs. Hong Kong banned smoking on January 1, 2007 in the workplace, public spaces such as restaurants, karaoke rooms, buildings, and public parks. Bars serving alcohol who do not admit minors were exempt until 2009. In Romania
smoking is illegal in trains, metro stations, public institutions (except where designated, usually outside) and public transportation.
is not in active support of it. Lorillard, the US's third largest tobacco company, seems to be ambivalent.
, nicotine replacement therapy
, antidepressant
s, hypnosis
, self-help, and support groups.
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
is burned and the resulting smoke (consisting of particle and gaseous phases) is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes. The practice encountered criticism from its first import into the Western world onwards, but embedded itself in certain strata of a number of societies before becoming widespread upon the introduction of automated cigarette-rolling apparatus.
German scientists identified a link between smoking and lung cancer in the late 1920s, leading to the first anti-smoking campaign in modern history, albeit one truncated by the collapse of the Third Reich at the end of the Second World War. In 1950, British researchers demonstrated a clear relationship between smoking and cancer. Scientific evidence continued to mount in the 1980s, which prompted political action against the practice. Rates of consumption since 1965 in the developed world have either peaked or declined. However, they continue to climb in the developing world.
Smoking is the most common method of consuming tobacco, and tobacco is the most common substance smoked. The agricultural product is often mixed with additives and then pyrolyzed
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures without the participation of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase, and is irreversible...
. The resulting smoke is then inhaled and the active substances absorbed through the alveoli in the lungs. The active substances trigger chemical reactions in nerve endings, which heighten heart rate, alertness, and reaction time. Dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
and endorphin
Endorphin
Endorphins are endogenous opioid peptides that function as neurotransmitters. They are produced by the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus in vertebrates during exercise, excitement, pain, consumption of spicy food, love and orgasm, and they resemble the opiates in their abilities to produce...
s are released, which are often associated with pleasure. As of 2000, smoking is practiced by approximately 1.22 billion people. In most communities men are more likely to smoke than are women, though the gender gap tends to be less pronounced in lower age groups.
Many smokers begin during adolescence
Adolescence
Adolescence is a transitional stage of physical and mental human development generally occurring between puberty and legal adulthood , but largely characterized as beginning and ending with the teenage stage...
or early adulthood. During the early stages, a combination of perceived pleasurable acting as positive reinforcement and desire to respond to social peer pressure may offset the unpleasant symptoms of initial use, which typically include nausea and interrupted sleep patterns. After an individual has smoked for some years, the avoidance of withdrawal
Withdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
symptoms and negative reinforcement become the key motivations to continue.
Early years

Shamanism
Shamanism is an anthropological term referencing a range of beliefs and practices regarding communication with the spiritual world. To quote Eliade: "A first definition of this complex phenomenon, and perhaps the least hazardous, will be: shamanism = technique of ecstasy." Shamanism encompasses the...
but was later adopted for pleasure or as a social tool. The smoking of tobacco and various hallucinogenic drugs was used to achieve trances and to come into contact with the spirit world.
Eastern North American tribes would carry large amounts of tobacco in pouches as a readily accepted trade item and would often smoke it in pipes, either in sacred ceremonies or to seal bargains. Adults as well as children enjoyed the practice. It was believed that tobacco was a gift from the Creator and that the exhaled tobacco smoke was capable of carrying one's thoughts and prayers to heaven.
Apart from smoking, tobacco had a number of uses as medicine. As a pain killer it was used for earache and toothache and occasionally as a poultice
Poultice
A poultice, also called cataplasm, is a soft moist mass, often heated and medicated, that is spread on cloth over the skin to treat an aching, inflamed, or painful part of the body. It can be used on wounds such as cuts...
. Smoking was said by the desert Indians to be a cure for colds, especially if the tobacco was mixed with the leaves of the small Desert Sage, Salvia Dorrii, or the root of Indian Balsam or Cough Root, Leptotaenia multifida, the addition of which was thought to be particularly good for asthma and tuberculosis.
Popularization

John Rolfe
John Rolfe was one of the early English settlers of North America. He is credited with the first successful cultivation of tobacco as an export crop in the Colony of Virginia and is known as the husband of Pocahontas, daughter of the chief of the Powhatan Confederacy.In 1961, the Jamestown...
was credited as the first settler to successfully raise tobacco as a cash crop. The demand quickly grew as tobacco, referred to as "brown gold", reviving the Virginia joint stock company from its failed gold expeditions. In order to meet demands from the Old World, tobacco was grown in succession, quickly depleting the soil. This became a motivator to settle west into the unknown continent, and likewise an expansion of tobacco production. Indentured servitude became the primary labor force up until Bacon's Rebellion
Bacon's Rebellion
Bacon's Rebellion was an uprising in 1676 in the Virginia Colony in North America, led by a 29-year-old planter, Nathaniel Bacon.About a thousand Virginians rose because they resented Virginia Governor William Berkeley's friendly policies towards the Native Americans...
, from which the focus turned to slavery. This trend abated following the American revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
as slavery became regarded as unprofitable. However, the practice was revived in 1794 with the invention of the cotton gin.
Frenchman Jean Nicot
Jean Nicot
Jean Nicot was a French diplomat and scholar.Born in Nîmes, in the south of France, he was French ambassador in Lisbon, Portugal from 1559 to 1561....
(from whose name the word nicotine is derived) introduced tobacco to France in 1560, and tobacco then spread to England. The first report of a smoking Englishman is of a sailor in Bristol in 1556, seen "emitting smoke from his nostrils". Like tea, coffee and opium, tobacco was just one of many intoxicants that was originally used as a form of medicine. Tobacco was introduced around 1600 by French merchants in what today is modern-day Gambia and Senegal
Senegal
Senegal , officially the Republic of Senegal , is a country in western Africa. It owes its name to the Sénégal River that borders it to the east and north...
. At the same time caravans from Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
brought tobacco to the areas around Timbuktu
Timbuktu
Timbuktu , formerly also spelled Timbuctoo, is a town in the West African nation of Mali situated north of the River Niger on the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. The town is the capital of the Timbuktu Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali...
and the Portuguese brought the commodity (and the plant) to southern Africa, establishing the popularity of tobacco throughout all of Africa by the 1650s.
Soon after its introduction to the Old World, tobacco came under frequent criticism from state and religious leaders. Murad IV
Murad IV
Murad IV Ghazi was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods...
, sultan of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
1623-40 was among the first to attempt a smoking ban by claiming it was a threat to public moral and health. The Chinese emperor Chongzhen issued an edict banning smoking two years before his death and the overthrow of the Ming dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
. Later, the Manchu
Manchu
The Manchu people or Man are an ethnic minority of China who originated in Manchuria . During their rise in the 17th century, with the help of the Ming dynasty rebels , they came to power in China and founded the Qing Dynasty, which ruled China until the Xinhai Revolution of 1911, which...
of the Qing dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
, who were originally a tribe of nomadic horse warriors, would proclaim smoking "a more heinous crime than that even of neglecting archery". In Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
Japan, some of the earliest tobacco plantations were scorned by the shogunate as being a threat to the military economy by letting valuable farmland go to waste for the use of a recreational drug instead of being used to plant food crops.

James I of England
James VI and I was King of Scots as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the English and Scottish crowns on 24 March 1603...
, a staunch anti-smoker and the author of a A Counterblaste to Tobacco
A Counterblaste to Tobacco
A Counterblaste to Tobacco is a treatise written by King James VI of Scotland and I of England in 1604, in which he expresses his distaste for tobacco, particularly tobacco smoking. As such, it is one of the earliest anti-tobacco publications....
, tried to curb the new trend by enforcing a 4000% tax increase on tobacco in 1604, it proved a failure, as London had some 7,000 tobacco sellers by the early 17th century. Later, scrupulous rulers would realise the futility of smoking bans and instead turned tobacco trade and cultivation into lucrative government monopolies.
By the mid-17th century every major civilization had been introduced to tobacco smoking and in many cases had already assimilated it into the native culture, despite the attempts of many rulers to eliminate the practice with harsh penalties or fines. Tobacco, both product and plant, followed the major trade routes to major ports and markets, and then on into the hinterlands. The English language term smoking was coined in the late 18th century; before then the practice was called drinking smoke.
Growth remained stable until the American Civil War in 1860s, when the primary labor force shifted from slavery to share cropping. This, along with a change in demand, lead to the industrialization of tobacco production with the cigarette. James Bonsack, a craftsman, in 1881 produce a machine to speed the production in cigarettes.
Social stigma
In Germany, anti-smoking groups, often associated with anti-liquor groups, first published advocacy against the consumption of tobacco in the journal Der Tabakgegner (The Tobacco Opponent) in 1912 and 1932. In 1929, Fritz Lickint of Dresden, Germany, published a paper containing formal statistical evidence of a lung cancer–tobacco link. During the Great depression Adolf HitlerAdolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
condemned his earlier smoking habit as a waste of money, and later with stronger assertions. This movement was further strengthened with Nazi reproductive policy as women who smoked were viewed as unsuitable to be wives and mothers in a German family.
The anti-tobacco movement in Nazi Germany
Anti-tobacco movement in Nazi Germany
After German doctors became the first to identify the link between smoking and lung cancer, Nazi Germany initiated a strong anti-tobacco movement and led the first public anti-smoking campaign in modern history...
did not reach across enemy lines during the Second World War, as anti-smoking groups quickly lost popular support. By the end of the Second World War, American cigarette manufacturers quickly reentered the German black market. Illegal smuggling of tobacco became prevalent, and leaders of the Nazi anti-smoking campaign were silenced. As part of the Marshall Plan
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan was the large-scale American program to aid Europe where the United States gave monetary support to help rebuild European economies after the end of World War II in order to combat the spread of Soviet communism. The plan was in operation for four years beginning in April 1948...
, the United States shipped free tobacco to Germany; with 24,000 tons in 1948 and 69,000 tons in 1949. Per capita yearly cigarette consumption in post-war Germany
History of Germany since 1945
As a consequence of the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II Germany was split between the two global blocs in the East and West, a period known as the division of Germany. While seven million prisoners and forced laborers left Germany, over 10 million German speaking refugees arrived there from...
steadily rose from 460 in 1950 to 1,523 in 1963. By the end of the 20th century, anti-smoking campaigns in Germany were unable to exceed the effectiveness of the Nazi-era climax in the years 1939–41 and German tobacco health research was described by Robert N. Proctor
Robert N. Proctor
Robert Neel Proctor is an American historian of science and Professor of the History of Science at Stanford University. While a professor of the history of science at Pennsylvania State University in 1999, he became the first historian to testify against the tobacco industry.At Pennsylvania State...
as "muted".

Richard Doll
Sir William Richard Shaboe Doll CH OBE FRS was a British physiologist who became the foremost epidemiologist of the 20th century, turning the subject into a rigorous science. He was a pioneer in research linking smoking to health problems...
in 1950 published research in the British Medical Journal
British Medical Journal
BMJ is a partially open-access peer-reviewed medical journal. Originally called the British Medical Journal, the title was officially shortened to BMJ in 1988. The journal is published by the BMJ Group, a wholly owned subsidiary of the British Medical Association...
showing a close link between smoking and lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
. Four years later, in 1954 the British Doctors Study
British Doctors Study
The British Doctors Study is the generally accepted name of a prospective cohort study which ran from 1951 to 2001, and in 1956 provided convincing statistical proof that tobacco smoking increased the risk of lung cancer.-Context:...
, a study of some 40 thousand doctors over 20 years, confirmed the suggestion, based on which the government issued advice that smoking and lung cancer rates were related. In 1964 the United States Surgeon General
Surgeon General of the United States
The Surgeon General of the United States is the operational head of the Public Health Service Commissioned Corps and thus the leading spokesperson on matters of public health in the federal government...
's Report on Smoking and Health likewise began suggesting the relationship between smoking and cancer.
As scientific evidence mounted in the 1980s, tobacco companies claimed contributory negligence
Contributory negligence
Contributory negligence in common-law jurisdictions is defense to a claim based on negligence, an action in tort. It applies to cases where a plaintiff/claimant has, through his own negligence, contributed to the harm he suffered...
as the adverse health effects were previously unknown or lacked substantial credibility. Health authorities sided with these claims up until 1998, from which they reversed their position. The Tobacco Master Settlement Agreement, originally between the four largest US tobacco companies and the Attorneys General of 46 states, restricted certain types of tobacco advertisement and required payments for health compensation; which later amounted to the largest civil settlement in United States history.
From 1965 to 2006, rates of smoking in the United States declined from 42% to 20.8%. The majority of those who quit were professional, affluent men. Although the per-capita number of smokers decreased, the average number of cigarettes consumed per person per day increased from 22 in 1954 to 30 in 1978. This paradoxical event suggests that those who quit smoked less, while those who continued to smoke moved to smoke more light cigarettes. The trend has been paralleled by many industrialized nations as rates have either leveled-off or declined. In the developing world, however, tobacco consumption continues to rise at 3.4% in 2002. In Africa, smoking is in most areas considered to be modern, and many of the strong adverse opinions that prevail in the West receive much less attention. Today Russia leads as the top consumer of tobacco followed by Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, Laos
Laos
Laos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
, Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, Greece, Jordan
Jordan
Jordan , officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan , Al-Mamlaka al-Urduniyya al-Hashemiyya) is a kingdom on the East Bank of the River Jordan. The country borders Saudi Arabia to the east and south-east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and the West Bank and Israel to the west, sharing...
, and China.
Methods
TobaccoTobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
is an agricultural product processed from the fresh leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana
Nicotiana
Nicotiana is a genus of herbs and shrubs of the nightshade family indigenous to North and South America, Australia, south west Africa and the South Pacific. Various Nicotiana species, commonly referred to as tobacco plants, are cultivated and grown to produce tobacco. Of all Nicotiana species,...
. The genus contains a number of species, however, Nicotiana tabacum
Nicotiana tabacum
Nicotiana tabacum, or cultivated tobacco, is a perennial herbaceous plant. It is found only in cultivation, where it is the most commonly grown of all plants in the Nicotiana genus, and its leaves are commercially grown in many countries to be processed into tobacco. It grows to heights between 1...
is the most commonly grown. Nicotiana rustica
Nicotiana rustica
Nicotiana rustica, known in South America as Mapacho and in Vietnam as Thuoc Lao , is a plant in the Solanaceae family. It is a very potent variety of tobacco. The high concentration of nicotine in its leaves makes it useful for creating organic pesticides.Rustica is also used for entheogenic...
follows as second containing higher concentrations of nicotine. These leaves are harvested and cured to allow for the slow oxidation and degradation of carotenoid
Carotenoid
Carotenoids are tetraterpenoid organic pigments that are naturally occurring in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other photosynthetic organisms like algae, some bacteria, and some types of fungus. Carotenoids can be synthesized fats and other basic organic metabolic building...
s in tobacco leaf. This produces certain compounds in the tobacco leaves which can be attributed to sweet hay, tea, rose oil, or fruity aromatic flavors. Before packaging, the tobacco is often combined with other additives in order to: enhance the addictive potency, shift the products pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
, or improve the effects of smoke by making it more palatable. In the United States these additives are regulated to 599 substances. The product is then processed, packaged, and shipped to consumer markets. Means of consumption has greatly expanded in scope as new methods of delivering the active substances with fewer by-products have encompassed or are beginning to encompass:
Beedi : Beedi
Beedi
A beedi is a thin, South Asian cigarette filled with tobacco flake and wrapped in a tendu leaf tied with a string at one end.The word comes from beeda, Marwari for a leaf wrapped in betel nuts, herbs, and condiments....
s are thin South Asian cigarettes filled with tobacco flake and wrapped in a tendu leaf tied with a string at one end. They produce higher levels of carbon monoxide, nicotine, and tar than cigarettes typical in the United States.
Cigars : Cigar
Cigar
A cigar is a tightly-rolled bundle of dried and fermented tobacco that is ignited so that its smoke may be drawn into the mouth. Cigar tobacco is grown in significant quantities in Brazil, Cameroon, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, Honduras, Indonesia, Mexico, Nicaragua, Philippines, and the Eastern...
s are tightly rolled bundles of dried and fermented tobacco which are ignited so that smoke may be drawn into the smoker's mouth. They are generally not inhaled because the high alkalinity of the smoke, which can quickly become irritating to the trachea and lungs. The prevalence of cigar smoking varies depending on location, historical period, and population surveyed, and prevalence estimates vary somewhat depending on the survey method. The United States is the top consuming country by far, followed by Germany and the United Kingdom; the US and Western Europe account for about 75% of cigar sales worldwide. As of 2005 it is estimated that 4.3% of men and 0.3% of women smoke cigars.
Cigarettes : Cigarette
Cigarette
A cigarette is a small roll of finely cut tobacco leaves wrapped in a cylinder of thin paper for smoking. The cigarette is ignited at one end and allowed to smoulder; its smoke is inhaled from the other end, which is held in or to the mouth and in some cases a cigarette holder may be used as well...
s, French for "small cigar", are a product consumed through smoking and manufactured out of cured and finely cut tobacco leaves and reconstituted tobacco, often combined with other additives, which are then rolled or stuffed into a paper-wrapped cylinder. Cigarettes are ignited and inhaled, usually through a cellulose acetate filter, into the mouth and lungs.
Electronic cigarette : Electronic cigarettes are an alternative to tobacco smoking, although no tobacco is consumed. It is a battery-powered device that provides inhaled doses of nicotine by delivering a vaporized propylene glycol
Propylene glycol
Propylene glycol, also called 1,2-propanediol or propane-1,2-diol, is an organic compound with formula C3H8O2 or HO-CH2-CHOH-CH3...
/nicotine
Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
solution. Many legislation and public health investigations are currently pending in many countries due to its relatively recent emergence. Most electronic cigarettes are designed to resemble actual tobacco smoking implements, such as cigarettes, cigars, or pipes, but many take the form of ballpoint pens or screwdrivers since those designs are more practical to house the mechanisms involved. Most are also reusable, with replaceable and refillable parts, but some models are disposable.
Hookah : Hookah
Hookah
A hookah A hookah(Gujarati હૂકાહ) A hookah(Gujarati હૂકાહ) (Hindustani: हुक़्क़ा (Devanagari, (Nastaleeq) huqqah) also known as a waterpipe or narghile, is a single or multi-stemmed (often glass-based) instrument for smoking in which the smoke is cooled by water. The tobacco smoked is referred to...
are a single or multi-stemmed (often glass-based) water pipe for smoking. Originally from India. The hookah was a symbol of pride and honour for the landlords, kings and other such high class people.Now ,the hookah has gained immense popularity, especially in the Middle East. A hookah operates by water filtration and indirect heat. It can be used for smoking herbal fruits, tobacco, or cannabis.
Kretek : Kretek
Kretek
Kretek are cigarettes made with a blend of tobacco, cloves and other flavors. The word "kretek" itself is an onomatopoetic term for the crackling sound of burning cloves. Haji Jamahri, a resident of Kudus, Java, created kreteks in the early 1880s as a means to deliver the eugenol of cloves to the...
are cigarettes made with a complex blend of tobacco, clove
Clove
Cloves are the aromatic dried flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae. Cloves are native to the Maluku islands in Indonesia and used as a spice in cuisines all over the world...
s and a flavoring "sauce". It was first introduced in the 1880s in Kudus, Java, to deliver the medicinal eugenol of cloves to the lungs. The quality and variety of tobacco play an important role in kretek production, from which kretek can contain more than 30 types of tobacco. Minced dried clove buds weighing about 1/3 of the tobacco blend are added to add flavoring. In 2004 the United States prohibited cigarettes from having a "characterizing flavor" of certain ingredients other than tobacco and menthol, thereby removing kretek from being classified as cigarettes.
Passive smoking : Passive smoking
Passive smoking
Passive smoking is the inhalation of smoke, called secondhand smoke or environmental tobacco smoke , from tobacco products used by others. It occurs when tobacco smoke permeates any environment, causing its inhalation by people within that environment. Exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke causes...
is the usually involuntary consumption of smoked tobacco. Second-hand smoke (SHS) is the consumption where the burning end is present, environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) or third-hand smoke is the consumption of the smoke that remains after the burning end has been extinguished. Because of its perceived negative implications, this form of consumption has played a central role in the regulation of tobacco products.
Pipe smoking : Pipe smoking
Pipe smoking
Pipe smoking is the practice of tasting or inhaling the smoke produced by burning a substance, most commonly tobacco, in a pipe. It is the oldest traditional form of smoking.-History:...
typically consists of a small chamber (the bowl) for the combustion of the tobacco to be smoked and a thin stem (shank) that ends in a mouthpiece (the bit). Shredded pieces of tobacco are placed into the chamber and ignited. Tobaccos for smoking in pipes are often carefully treated and blended to achieve flavour nuances not available in other tobacco products.
Roll-Your-Own : Roll-Your-Own
Roll-your-own
Roll-your-own cigarettes refer to a cigarette made from loose tobacco and rolling papers. Roll-your-own products are sold as a pouch of tobacco for rolling hand-rolled cigarettes, sometimes with the rolling papers provided in the pouch...
or hand-rolled cigarettes, often called 'rollies', are very popular particularly in European countries. These are prepared from loose tobacco, cigarette papers, and filters all bought separately. They are usually much cheaper than ready-made cigarettes.
Vaporizer : A vaporizer is a device used to sublimate the active ingredients of plant material. Rather than burning the herb, which produces potentially irritating, toxic, or carcinogen
Carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that is an agent directly involved in causing cancer. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes...
ic by-products; a vaporizer heats the material in a partial vacuum so that the active compounds contained in the plant boil off into a vapor. Medical administration of a smoke substance often prefer this method as to directly pyrolyzing the plant material.
Physiology

Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures without the participation of oxygen. It involves the simultaneous change of chemical composition and physical phase, and is irreversible...
. Pipe and Cigar smoke are not inhaled because of its high alkalinity
Alkalinity
Alkalinity or AT measures the ability of a solution to neutralize acids to the equivalence point of carbonate or bicarbonate. The alkalinity is equal to the stoichiometric sum of the bases in solution...
, which are irritating to the trachea
Vertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
and lungs. However, because of its higher alkalinity (pH 8.5) compared to cigarette smoke (pH 5.3), un-ionized nicotine is more readily absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth. Nicotine absorption from cigar and pipe, however, is much less than that from cigarette smoke.
The inhaled substances trigger chemical reactions in nerve endings. The cholinergic receptors are often triggered by the naturally occurring neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
The chemical compound acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter in both the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system in many organisms including humans...
. Acetylcholine and Nicotine
Nicotine
Nicotine is an alkaloid found in the nightshade family of plants that constitutes approximately 0.6–3.0% of the dry weight of tobacco, with biosynthesis taking place in the roots and accumulation occurring in the leaves...
express chemical similarities, which allows Nicotine to trigger the receptor as well. These nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are cholinergic receptors that form ligand-gated ion channels in the plasma membranes of certain neurons and on the postsynaptic side of the neuromuscular junction...
s takes are located in the central nervous system and at the nerve-muscle junction of skeletal muscles; whose activity increases heart rate, alertness, and faster reaction times. Nicotine acetylcholine stimulation is not directly addictive. However, since dopamine-releasing neurons are abundant on nicotine receptors, dopamine is released. This release of dopamine, which is associated with pleasure, is reinforcing and may also increase working memory
Working memory
Working memory has been defined as the system which actively holds information in the mind to do verbal and nonverbal tasks such as reasoning and comprehension, and to make it available for further information processing...
. Nicotine and cocaine activate similar patterns of neurons, which supports the idea that common substrates among these drugs.
When tobacco is smoked, most of the nicotine is pyrolyzed. However, a dose sufficient to cause mild somatic dependency and mild to strong psychological dependency remains. There is also a formation of harmane (a MAO inhibitor) from the acetaldehyde in tobacco smoke. This seems to play an important role in nicotine addiction—probably by facilitating a dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens
Nucleus accumbens
The nucleus accumbens , also known as the accumbens nucleus or as the nucleus accumbens septi , is a collection of neurons and forms the main part of the ventral striatum...
as a response to nicotine stimuli. Using rat studies, withdrawal after repeated exposure to nicotine results in less responsive nucleus accumbens cells, which produce dopamine responsible for reinforcement
Reinforcement
Reinforcement is a term in operant conditioning and behavior analysis for the process of increasing the rate or probability of a behavior in the form of a "response" by the delivery or emergence of a stimulus Reinforcement is a term in operant conditioning and behavior analysis for the process of...
.
Demographics
As of 2000, smoking is practiced by 1.22 billion people. Assuming no change in prevalence it is predicted that 1.45 billion people will smoke in 2010 and 1.5 to 1.9 billion in 2025. Assuming that prevalence will decrease at 1% a year and that there will be a modest increase of income of 2%, it is predicted the number of smokers will stand at 1.3 billion in 2010 and 2025.Smoking is generally five times higher among men than women, however the gender gap declines with younger age. In developed countries smoking rates for men have peaked and have begun to decline, however for women they continue to climb.
As of 2002, about twenty percent of young teens (13–15) smoke worldwide. From which 80,000 to 100,000 children begin smoking every day—roughly half of which live in Asia. Half of those who begin smoking in adolescent years are projected to go on to smoke for 15 to 20 years.
The World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) states that "Much of the disease burden and premature mortality attributable to tobacco use disproportionately affect the poor". Of the 1.22 billion smokers, 1 billion of them live in developing or transitional economies. Rates of smoking have leveled off or declined in the developed world. In the developing world, however, tobacco consumption is rising by 3.4% per year as of 2002.
The WHO in 2004 projected 58.8 million deaths to occur globally, from which 5.4 million are tobacco-attributed, and 4.9 million as of 2007. As of 2002, 70% of the deaths are in developing countries.
Takeup

Children of smoking parents are more likely to smoke than children with non-smoking parents. One study found that parental smoking cessation was associated with less adolescent smoking, except when the other parent currently smoked. A current study tested the relation of adolescent smoking to rules regulating where adults are allowed to smoke in the home. Results showed that restrictive home smoking policies were associated with lower likelihood of trying smoking for both middle and high school students.
Many anti-smoking organizations claim that teenagers begin their smoking habits due to peer pressure, and cultural influence portrayed by friends. However, one study found that direct pressure to smoke cigarettes did not play a significant part in adolescent smoking. In that study, adolescents also reported low levels of both normative
Norm (sociology)
Social norms are the accepted behaviors within a society or group. This sociological and social psychological term has been defined as "the rules that a group uses for appropriate and inappropriate values, beliefs, attitudes and behaviors. These rules may be explicit or implicit...
and direct pressure to smoke cigarettes. A similar study showed that individuals play a more active role in starting to smoke than has previously been acknowledged and that social processes other than peer pressure need to be taken into account. Another study's results revealed that peer pressure
Peer pressure
Peer pressure refers to the influence exerted by a peer group in encouraging a person to change his or her attitudes, values, or behavior in order to conform to group norms. Social groups affected include membership groups, when the individual is "formally" a member , or a social clique...
was significantly associated with smoking behavior across all age and gender cohorts, but that intrapersonal factors were significantly more important to the smoking behavior of 12–13 year-old girls than same-age boys. Within the 14–15 year-old age group, one peer pressure variable emerged as a significantly more important predictor of girls' than boys' smoking. It is debated whether peer pressure or self-selection
Self-selection
In statistics, self-selection bias arises in any situation in which individuals select themselves into a group, causing a biased sample with nonprobability sampling...
is a greater cause of adolescent smoking.
Psychologists such as Hans Eysenck
Hans Eysenck
Hans Jürgen Eysenck was a German-British psychologist who spent most of his career in Britain, best remembered for his work on intelligence and personality, though he worked in a wide range of areas...
have developed a personality profile for the typical smoker. Extraversion is the trait that is most associated with smoking, and smokers tend to be sociable, impulsive, risk taking, and excitement seeking individuals. Although personality and social factors may make people likely to smoke, the actual habit is a function of operant conditioning
Operant conditioning
Operant conditioning is a form of psychological learning during which an individual modifies the occurrence and form of its own behavior due to the association of the behavior with a stimulus...
. During the early stages, smoking provides pleasurable sensations (because of its action on the dopamine
Dopamine
Dopamine is a catecholamine neurotransmitter present in a wide variety of animals, including both vertebrates and invertebrates. In the brain, this substituted phenethylamine functions as a neurotransmitter, activating the five known types of dopamine receptors—D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5—and their...
system) and thus serves as a source of positive reinforcement.
Persistence
The reasons given by smokers for this activity are broadly categorized as addictive smoking, pleasure from smoking, tension reduction/relaxation, social smoking, stimulation, habit/automatism, and handling. There are gender differences in how much each of these reasons contribute, with females more likely than males to cite tension reduction/relaxation, stimulation and social smoking.Some smokers argue that the depressant
Depressant
A depressant, or central depressant, is a drug or endogenous compound that depresses the function or activity of a specific part of the brain...
effect of smoking allows them to calm their nerves, often allowing for increased concentration. However, according to the Imperial College London
Imperial College London
Imperial College London is a public research university located in London, United Kingdom, specialising in science, engineering, business and medicine...
, "Nicotine seems to provide both a stimulant and a depressant effect, and it is likely that the effect it has at any time is determined by the mood of the user, the environment and the circumstances of use. Studies have suggested that low doses have a depressant effect, while higher doses have stimulant effect."
Patterns
A number of studies have established that cigarette sales and smoking follow distinct time-related patterns. For example, cigarette sales in the United States of America have been shown to follow a strongly seasonal pattern, with the high months being the months of summer, and the low months being the winter months.Similarly, smoking has been shown to follow distinct circadian patterns during the waking day—with the high point usually occurring shortly after waking in the morning, and shortly before going to sleep at night.
Economic
In countries where there is a public healthPublic health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" . It is concerned with threats to health based on population health...
system, society covers the cost of medical care for smokers who become ill through in the form of increased taxes. Two arguments exist on this front, the "pro-smoking" argument suggesting that heavy smokers generally don't live long enough to develop the costly and chronic illnesses which affect the elderly, reducing society's healthcare burden. The "anti-smoking" argument suggests that the healthcare burden is increased because smokers get chronic illnesses younger and at a higher rate than the general population.
Data on both positions is limited. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
published research in 2002 claiming that the cost of each pack
Cigarette pack
A pack or packet of cigarettes is a rectangular container, mostly of paperboard, which contains cigarettes. The pack is designed with a flavor-protective foil, paper or biodegradable plastic, and sealed through a transparent airtight plastic film. By pulling the "pull-tabs", the pack is opened...
of cigarettes sold in the United States was more than $7 in medical care and lost productivity. The cost may be higher, with another study putting it as high as $41 per pack, most of which however is on the individual and his/her family. This is how one author of that study puts it when he explains the very low cost for others: "The reason the number is low is that for private pensions, Social Security, and Medicare — the biggest factors in calculating costs to society — smoking actually saves money. Smokers die at a younger age and don't draw on the funds they've paid into those systems."
By contrast, some non-scientific studies, including one conducted by Philip Morris
Philip Morris International
Philip Morris International is an international tobacco company, with products sold in over 160 countries. In 2007, it held a 15.6% share of the international cigarette market outside of the USA and reported revenues net of excise taxes of $22.8 billion and operating income of $8.9 billion.Until...
in the Czech Republic and another by the Cato Institute
Cato Institute
The Cato Institute is a libertarian think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1977 by Edward H. Crane, who remains president and CEO, and Charles Koch, chairman of the board and chief executive officer of the conglomerate Koch Industries, Inc., the largest privately held...
, support the opposite position. Philip Morris has explicitly apologised for the former study, saying: "The funding and public release of this study which, among other things, detailed purported cost savings to the Czech Republic due to premature deaths of smokers, exhibited terrible judgment as well as a complete and unacceptable disregard of basic human values. For one of our tobacco companies to commission this study was not just a terrible mistake, it was wrong. All of us at Philip Morris, no matter where we work, are extremely sorry for this. No one benefits from the very real, serious and significant diseases caused by smoking."
Between 1970 an 1995, per-capita cigarette consumption in poorer developing countries increased by 67 percent, while it dropped by 10 percent in the richer developed world. Eighty percent of smokers now live in less developed countries. By 2030, the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) forecasts that 10 million people a year will die of smoking-related illness, making it the single biggest cause of death worldwide, with the largest increase to be among women. WHO forecasts the 21st century's death rate from smoking to be ten times the 20th century's rate. ("Washingtonian" magazine, December 2007).
Health
Tobacco use leads most commonly to diseases affecting the heart and lungs, with smoking being a major risk factor for heart attacksMyocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
, stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
s, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease , also known as chronic obstructive lung disease , chronic obstructive airway disease , chronic airflow limitation and chronic obstructive respiratory disease , is the co-occurrence of chronic bronchitis and emphysema, a pair of commonly co-existing diseases...
(COPD), emphysema
Emphysema
Emphysema is a long-term, progressive disease of the lungs that primarily causes shortness of breath. In people with emphysema, the tissues necessary to support the physical shape and function of the lungs are destroyed. It is included in a group of diseases called chronic obstructive pulmonary...
, and cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
(particularly lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
, cancers of the larynx and mouth
Cancer of the larynx
Laryngeal cancer may also be called cancer of the larynx or laryngeal carcinoma. Most laryngeal cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the squamous cells which form the majority of the laryngeal epithelium....
, and pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer refers to a malignant neoplasm of the pancreas. The most common type of pancreatic cancer, accounting for 95% of these tumors is adenocarcinoma, which arises within the exocrine component of the pancreas. A minority arises from the islet cells and is classified as a...
). Cigarette smoking increases the risk of Crohn's disease as well as the severity of the course of the disease. It is also the number one cause of bladder cancer.
The World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
estimate that tobacco caused 5.4 million deaths in 2004 and 100 million deaths over the course of the 20th century. Similarly, the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
describes tobacco use as "the single most important preventable risk to human health in developed countries and an important cause of premature death worldwide."
Lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
occurs at non-smokers in 3.4 cases per 100 000 population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
. At people smoking 0.5 packs of cigarettes a day this figure rises to 51.4 per 100 000, 1-2 packs - up to 143.9 per 100 000 and if the intensity of smoking is over 2 packs a day - up to 217.3 per 100,000 population.
Rates of smoking have leveled off or declined in the developed world. Smoking rates in the United States have dropped by half from 1965 to 2006 falling from 42% to 20.8% in adults. In the developing world, tobacco consumption is rising by 3.4% per year.
Passive smoking presents a very real health risk. Six hundred thousand deaths were attributable to second-hand smoke in 2004.
Social
Famous smokers of the past used cigarettes or pipes as part of their image, such as Jean Paul Sartre's GauloisesGauloises
Gauloises is a brand of cigarette of French manufacture. It is produced by the company Imperial Tobacco following their acquisition of Altadis in January 2008.- Cigarette :...
-brand cigarettes; Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific intellects in human history...
's, Kiana Lee Rosch's, Douglas MacArthur
Douglas MacArthur
General of the Army Douglas MacArthur was an American general and field marshal of the Philippine Army. He was a Chief of Staff of the United States Army during the 1930s and played a prominent role in the Pacific theater during World War II. He received the Medal of Honor for his service in the...
's, Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Russell
Bertrand Arthur William Russell, 3rd Earl Russell, OM, FRS was a British philosopher, logician, mathematician, historian, and social critic. At various points in his life he considered himself a liberal, a socialist, and a pacifist, but he also admitted that he had never been any of these things...
's, and Bing Crosby's pipes; or the news broadcaster Edward R. Murrow
Edward R. Murrow
Edward Roscoe Murrow, KBE was an American broadcast journalist. He first came to prominence with a series of radio news broadcasts during World War II, which were followed by millions of listeners in the United States and Canada.Fellow journalists Eric Sevareid, Ed Bliss, and Alexander Kendrick...
's cigarette. Writers in particular seem to be known for smoking, for example, Cornell Professor Richard Klein
Richard Klein
Richard Klein is an Adjunct Professor of Astronomy at the University of California, Berkeley and a Scientific Staff Member at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory...
's book Cigarettes are Sublime for the analysis, by this professor of French literature, of the role smoking plays in 19th and 20th century letters. The popular author Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut, Jr. was a 20th century American writer. His works such as Cat's Cradle , Slaughterhouse-Five and Breakfast of Champions blend satire, gallows humor and science fiction. He was known for his humanist beliefs and was honorary president of the American Humanist Association.-Early...
addressed his addiction to cigarettes within his novels. British Prime Minister Harold Wilson
Harold Wilson
James Harold Wilson, Baron Wilson of Rievaulx, KG, OBE, FRS, FSS, PC was a British Labour Member of Parliament, Leader of the Labour Party. He was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during the 1960s and 1970s, winning four general elections, including a minority government after the...
was well known for smoking a pipe in public as was Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
for his cigars. Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes is a fictional detective created by Scottish author and physician Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. The fantastic London-based "consulting detective", Holmes is famous for his astute logical reasoning, his ability to take almost any disguise, and his use of forensic science skills to solve...
, the fictional detective created by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle smoked a pipe, cigarettes, and cigars. The DC
DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. is one of the largest and most successful companies operating in the market for American comic books and related media. It is the publishing unit of DC Entertainment a company of Warner Bros. Entertainment, which itself is owned by Time Warner...
Vertigo comic book character, John Constantine
John Constantine
John Constantine is a fictional character, an occult detective anti-hero in comic books published by DC Comics, mostly under the Vertigo imprint. The character first appeared in Swamp Thing #37 , and was created by Alan Moore, Steve Bissette, John Totleben and Rick Veitch...
, created by Alan Moore
Alan Moore
Alan Oswald Moore is an English writer primarily known for his work in comic books, a medium where he has produced a number of critically acclaimed and popular series, including Watchmen, V for Vendetta, and From Hell...
, is synonymous with smoking, so much so that the first storyline by Preacher
Preacher (comics)
Preacher is a comic book series created by writer Garth Ennis and artist Steve Dillon, published by the American comic book label Vertigo , with painted covers by Glenn Fabry....
creator, Garth Ennis
Garth Ennis
Garth Ennis is a Northern Irish comics writer, best known for the Vertigo series Preacher with artist Steve Dillon and his successful nine-year run on Marvel Comics' Punisher franchise...
, centered around John Constantine contracting lung cancer. Professional wrestler
Professional wrestling
Professional wrestling is a mode of spectacle, combining athletics and theatrical performance.Roland Barthes, "The World of Wrestling", Mythologies, 1957 It takes the form of events, held by touring companies, which mimic a title match combat sport...
James Fullington, while in character as "The Sandman", is a chronic smoker in order to appear "tough".
The problem of smoking at home is particularly difficult for women in many cultures especially Arab cultures where it may not be acceptable for a woman to ask her husband not to smoke at home or in the presence of her children. Studies has shown that pollution levels in door places are higher than levels found on busy roadways, in closed motor garages, and during fire storms. Furthermore, smoke can spread from one room to another, even if doors to the smoking area are closed.
The ceremonial smoking of tobacco, and praying with a sacred pipe
Calumet (pipe)
A Calumet is a ceremonial smoking pipe used by some Native American Nations. Traditionally it has been smoked to seal a covenant or treaty, or to offer prayers in a religious ceremony.- Etymology :...
, is a prominent part of the religious ceremonies of a number of Native American
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
Nations. Sema, the Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe
Anishinaabe or Anishinabe—or more properly Anishinaabeg or Anishinabek, which is the plural form of the word—is the autonym often used by the Odawa, Ojibwe, and Algonquin peoples. They all speak closely related Anishinaabemowin/Anishinaabe languages, of the Algonquian language family.The meaning...
word for tobacco, is grown for ceremonial use and considered the ultimate sacred plant since its smoke was believed to carry prayers to the heavens. In most major religions, however, tobacco smoking is not specifically prohibited, although it may be discouraged as an immoral habit. Before the health risks of smoking were identified through controlled study, smoking was considered an immoral habit by certain Christian preachers and social reformers. The founder of the Latter Day Saint movement
Latter Day Saint movement
The Latter Day Saint movement is a group of independent churches tracing their origin to a Christian primitivist movement founded by Joseph Smith, Jr. in the late 1820s. Collectively, these churches have over 14 million members...
, Joseph Smith, Jr, recorded that on February 27, 1833, he received a revelation
Revelation
In religion and theology, revelation is the revealing or disclosing, through active or passive communication with a supernatural or a divine entity...
which discouraged tobacco use. This "Word of Wisdom" was later accepted as a commandment, and faithful Latter-day Saints abstain completely from tobacco. Jehovah's Witnesses base their stand against smoking on the Bible's command to "clean ourselves of every defilement of flesh" (2 Corinthians 7:1). The Jewish Rabbi Yisrael Meir Kagan
Yisrael Meir Kagan
Yisrael Meir Poupko , known popularly as The Chofetz Chaim, was an influential Eastern European rabbi, Halakhist, posek, and ethicist whose works continue to be widely influential in Jewish life...
(1838–1933) was one of the first Jewish authorities to speak out on smoking. In the Bahá'í Faith
Bahá'í Faith
The Bahá'í Faith is a monotheistic religion founded by Bahá'u'lláh in 19th-century Persia, emphasizing the spiritual unity of all humankind. There are an estimated five to six million Bahá'ís around the world in more than 200 countries and territories....
, smoking tobacco is discouraged though not forbidden.
Public policy
On February 27, 2005 the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco ControlWHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control
The World Health Organization Framework Convention on Tobacco Control is a treaty adopted by the 56th World Health Assembly on May 21, 2003. It became the first World Health Organization treaty adopted under article 19 of the WHO constitution. The treaty came into force on February 27, 2005...
, took effect. The FCTC is the world's first public health treaty. Countries that sign on as parties agree to a set of common goals, minimum standards for tobacco control policy, and to cooperate in dealing with cross-border challenges such as cigarette smuggling. Currently the WHO declares that 4 billion people will be covered by the treaty, which includes 168 signatories. Among other steps, signatories are to put together legislation that will eliminate secondhand smoke in indoor workplaces, public transport, indoor public places and, as appropriate, other public places.
Taxation
Many governments have introduced excise taxes on cigarettes in order to reduce the consumption of cigarettes.In 2002, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
said that each pack
Cigarette pack
A pack or packet of cigarettes is a rectangular container, mostly of paperboard, which contains cigarettes. The pack is designed with a flavor-protective foil, paper or biodegradable plastic, and sealed through a transparent airtight plastic film. By pulling the "pull-tabs", the pack is opened...
of cigarettes sold in the United States costs the nation more than $7 in medical care and lost productivity, around $3400 per year per smoker. Another study by a team of health economists finds the combined price paid by their families and society is about $41 per pack of cigarettes.
Substantial scientific evidence shows that higher cigarette prices result in lower overall cigarette consumption. Most studies indicate that a 10% increase in price will reduce overall cigarette consumption by 3% to 5%. Youth, minorities, and low-income smokers are two to three times more likely to quit or smoke less than other smokers in response to price increases. Smoking is often cited as an example of an inelastic good, however, i.e. a large rise in price will only result in a small decrease in consumption.
Many nations have implemented some form of tobacco taxation. As of 1997, Denmark had the highest cigarette tax burden of $4.02 per pack. Taiwan only had a tax burden of $0.62 per pack. The federal government of the United States charges $1.01 per pack.
Cigarette taxes vary widely from state to state in the United States. For example, Missouri
Missouri
Missouri is a US state located in the Midwestern United States, bordered by Iowa, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kansas and Nebraska. With a 2010 population of 5,988,927, Missouri is the 18th most populous state in the nation and the fifth most populous in the Midwest. It...
has a cigarette tax of only 17 cents per pack, the nation's lowest, while New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
has the highest cigarette tax in the U.S.: $4.35 per pack. In Alabama, Illinois, Missouri, New York City, Tennessee, and Virginia, counties and cities may impose an additional limited tax on the price of cigarettes. Sales taxes are also levied on tobacco products in most jurisdictions.
In the United Kingdom, a packet of 20 cigarettes typically costs between £5.22 and £8.00 depending on the brand purchased and where the purchase was made. The UK has a significant black market for tobacco, and it has been estimated by the tobacco industry that 27% of cigarette and 68% of handrolling tobacco consumption is non-UK duty paid (NUKDP).
In Australia total taxes account for 62.5% of the final price of a packet of cigarettes (2011 figures). These taxes include federal excise or customs duty, and the more recently introduced Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Restrictions
In June 1967, the Federal Communications CommissionFederal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, created, Congressional statute , and with the majority of its commissioners appointed by the current President. The FCC works towards six goals in the areas of broadband, competition, the spectrum, the...
ruled that programs broadcast on a television station that discussed smoking and health were insufficient to offset the effects of paid advertisements that were broadcast for five to ten minutes each day. In April 1970, Congress passed the Public Health Cigarette Smoking Act
Public Health Cigarette Smoking Act
The Public Health Cigarette Smoking Act is a United States federal law, passed in 1970, designed to limit the practice of smoking. It required a stronger health warning on cigarette packages, saying "Warning: The Surgeon General Has Determined that Cigarette Smoking Is Dangerous to Your Health"...
banning the advertising of cigarettes on television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
and radio
Radio
Radio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
starting on January 2, 1971.
The Tobacco Advertising Prohibition Act 1992 expressly prohibited almost all forms of Tobacco advertising in Australia, including the sponsorship of sporting or other cultural events by cigarette brands.
All tobacco advertising and sponsorship on television has been banned within the European Union since 1991 under the Television Without Frontiers Directive (1989) This ban was extended by the Tobacco Advertising Directive, which took effect in July 2005 to cover other forms of media such as the internet, print media, and radio. The directive does not include advertising in cinemas and on billboards or using merchandising – or tobacco sponsorship of cultural and sporting events which are purely local, with participants coming from only one Member State as these fall outside the jurisdiction of the European Commission
European Commission
The European Commission is the executive body of the European Union. The body is responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the Union's treaties and the general day-to-day running of the Union....
. However, most member states have transposed the directive with national laws that are wider in scope than the directive and cover local advertising. A 2008 European Commission report concluded that the directive had been successfully transposed into national law in all EU member states, and that these laws were well implemented.
Some countries also impose legal requirements on the packaging of tobacco products. For example in the countries of the European Union, Turkey, Australia and South Africa, cigarette packs must be prominently labeled with the health risks associated with smoking. Canada, Australia, Thailand, Iceland and Brazil have also imposed labels upon cigarette packs warning smokers of the effects, and they include graphic images of the potential health effects of smoking. Cards are also inserted into cigarette packs in Canada. There are sixteen of them, and only one comes in a pack. They explain different methods of quitting smoking. Also, in the United Kingdom, there have been a number of graphic NHS
National Health Service
The National Health Service is the shared name of three of the four publicly funded healthcare systems in the United Kingdom. They provide a comprehensive range of health services, the vast majority of which are free at the point of use to residents of the United Kingdom...
advertisements, one showing a cigarette filled with fatty deposits, as if the cigarette is symbolising the artery of a smoker.
Many countries have a smoking age
Smoking age
The minimum legal age to purchase cigarettes or tobacco products varies from country to country. Ages range from 14 to 21, but 18 tends to be the most common legal smoking age.-Asia:-Europe:-Australia:...
, In many countries, including the United States, most European Union member states, New Zealand, Canada, South Africa, Israel, India, Brazil, Chile, Costa Rica and Australia, it is illegal to sell tobacco products to minors and in the Netherlands, Austria, Belgium, Denmark and South Africa it is illegal to sell tobacco products to people under the age of 16. On September 1, 2007 the minimum age to buy tobacco products in Germany rose from 16 to 18, as well as in Great Britain where on October 1, 2007 it rose from 16 to 18. Underlying such laws is the belief that people should make an informed decision regarding the risks of tobacco use. These laws have a lax enforcement in some nations and states. In China, Turkey, and many other countries usually a child will have little problem buying tobacco products, because they are often told to go to the store to buy tobacco for their parents.
Several countries such as Ireland
Republic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
, Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, the Netherlands, France, Finland, Norway, Canada, Australia, Sweden, Portugal, Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
, Italy, Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, India, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
, Spain, Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, United Kingdom, Slovenia
Slovenia
Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
have legislated against smoking in public places, often including bars and restaurants. Restaurateurs have been permitted in some jurisdictions to build designated smoking areas (or to prohibit smoking). In the United States, many states prohibit smoking in restaurants, and some also prohibit smoking in bars. In provinces of Canada, smoking is illegal in indoor workplaces and public places, including bars and restaurants. As of March 31, 2008 Canada has introduced a smoking ban in all public places, as well as within 10 meters of an entrance to any public place. In Australia, smoking bans vary from state to state. Currently, Queensland has total bans within all public interiors (including workplaces, bars, pubs and eateries) as well as patrolled beaches and some outdoor public areas. There are, however, exceptions for designated smoking areas. In Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
, smoking is banned in train stations, bus stops and tram stops as these are public locations where second hand smoke can affect non-smokers waiting for public transport, and since July 1, 2007 is now extended to all indoor public places. In New Zealand and Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, smoking is banned in enclosed public places mainly bars, restaurants and pubs. Hong Kong banned smoking on January 1, 2007 in the workplace, public spaces such as restaurants, karaoke rooms, buildings, and public parks. Bars serving alcohol who do not admit minors were exempt until 2009. In Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
smoking is illegal in trains, metro stations, public institutions (except where designated, usually outside) and public transportation.
Ignition safety
An indirect public health problem posed by cigarettes is that of accidental fires, usually linked with consumption of alcohol. Numerous cigarette designs have been proposed, some by tobacco companies themselves, which would extinguish a cigarette left unattended for more than a minute or two, thereby reducing the risk of fire. Among American tobacco companies, some have resisted this idea, while others have embraced it. RJ Reynolds was a leader in making prototypes of these cigarettes in 1983 and will make all of their U.S. market cigarettes to be fire-safe by 2010. Phillip MorrisPhilip Morris USA
Philip Morris USA is the United States tobacco division of Altria Group, Inc. Philip Morris USA brands include Marlboro, Virginia Slims, Benson and Hedges, Merit, Parliament, Alpine, Basic, Cambridge, Bucks, Dave's, Chesterfield, Collector's Choice, Commander, English Ovals, Lark, L&M, Players and...
is not in active support of it. Lorillard, the US's third largest tobacco company, seems to be ambivalent.
Gateway drug theory
The relationship between tobacco and other drug use has been well-established, however the nature of this association remains unclear. The two main theories are the phenotypic causation (gateway) model and the correlated liabilities model. The causation model argues that smoking is a primary influence on future drug use, while the correlated liabilities model argues that smoking and other drug use are predicated on genetic or environmental factors.Cessation
Smoking cessation, referred to as "quitting" is the action leading towards abstinence of tobacco smoking. There are a number of methods such as cold turkeyCold turkey
"Cold turkey" describes the actions of a person who abruptly gives up a habit or addiction rather than gradually easing the process through gradual reduction or by using replacement medication....
, nicotine replacement therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy is the remedial administration of nicotine to the body by means other than tobacco, usually as part of smoking cessation. Common forms of nicotine replacement therapy are nicotine patches and nicotine gum...
, antidepressant
Antidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s, hypnosis
Hypnosis
Hypnosis is "a trance state characterized by extreme suggestibility, relaxation and heightened imagination."It is a mental state or imaginative role-enactment . It is usually induced by a procedure known as a hypnotic induction, which is commonly composed of a long series of preliminary...
, self-help, and support groups.
See also
- Cigarette smoking among college studentsCigarette smoking among college studentsThe rates of college students smoking in the United States have fluctuated for the past twenty years. Majority of lifelong smokers begin smoking habits before the age of 24, which makes the college years a crucial time in the study of cigarette consumption...
- Cigarette smoking for weight lossCigarette smoking for weight lossCigarette Smoking for Weight Loss is a practice dating to early knowledge of nicotine as an appetite suppressant. Tobacco use was associated with appetite suppression among pre-Columbian indigenous Americans, and old world Europeans...
- One hitter (smoking)
External links
- Tobacco History Links — repository from Tobacco.org
- Surgeon General: Tobacco Cessation
- CDC: Smoking & Tobacco Use
- WHO: Tobacco Free Initiative

