
Track bicycle
Encyclopedia

Velodrome
A velodrome is an arena for track cycling. Modern velodromes feature steeply banked oval tracks, consisting of two 180-degree circular bends connected by two straights...
or outdoor track. Unlike road bicycle
Road bicycle
The term road bicycle is used to describe bicycles built for traveling at speed on paved roads. Some sources use the term to mean racing bicycle...
s, the track bike is a fixed-gear bicycle
Fixed-gear bicycle
A fixed-gear bicycle is a bicycle that has no freewheel, meaning it cannot coast, as the pedals are always in motion when the bicycle is moving....
and so has a single gear and neither freewheel
Freewheel
thumb|Freewheel mechanismIn mechanical or automotive engineering, a freewheel or overrunning clutch is a device in a transmission that disengages the driveshaft from the driven shaft when the driven shaft rotates faster than the driveshaft...
nor brakes. Tires
Bicycle tire
A bicycle tire is a tire that fits on the wheel of a bicycle, unicycle, tricycle, quadracycle, bicycle trailer, or trailer bike. They may also be used on wheelchairs and handcycles, especially for racing...
are narrow and inflated to high pressure to reduce rolling resistance
Rolling resistance
Rolling resistance, sometimes called rolling friction or rolling drag, is the resistance that occurs when a round object such as a ball or tire rolls on a flat surface, in steady velocity straight line motion. It is caused mainly by the deformation of the object, the deformation of the surface, or...
. Tubular tires are most often used in track racing and training though advances in clincher tire design has seen them being used somewhat more often.
Frame design
A track frameBicycle frame
A bicycle frame is the main component of a bicycle, on to which wheels and other components are fitted. The modern and most common frame design for an upright bicycle is based on the safety bicycle, and consists of two triangles, a main triangle and a paired rear triangle...
is specific to its use. Rigidity is more important than lightness. Frames for sprinting are as rigid as possible, while those for general racing as aerodynamic as possible.
Rules
The governing body, the International Cycling Union (UCI), sets limits on design and dimensions as well as the shape and diameter of the tubes used to construct the frame.Geometry
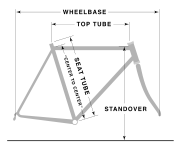
- higher bottom bracketBottom bracketThe bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle that the crankset attaches to, and the bearings that allow the spindle and cranks to rotate. The chainrings and pedals attach to the cranks...
so the pedals do not touch a steeply banked track - steeper seat tube for a more aerodynamic position and a shorter wheelbase
- steeper head tubeHead tubeMost bicycles, tricycles and motorcycles have a tubular frame. The front fork pivots within the head tube . On a motorcycle, the "head tube" is normally called the steering head...
for more responsive steering, - less forkBicycle forkA bicycle fork is the portion of a bicycle that holds the front wheel and allows the rider to steer and balance the bicycle. A fork consists of two fork ends which hold the front wheel axle, two blades which join at a fork crown, and a steerer or steering tube to which the handlebars attach ...
rake.
Typical track frames use 120mm spacing for the rear hub. The dropouts
Dropout (bicycle part)
A bicycle dropout is a type of fork end that allows the rear wheel to be removed without first derailing the chain. The more inclusive term fork end refers to a slot in a frame or fork where the axle of the wheel is attached....
or track ends face rearwards to facilitate chain tension adjustment.
Material
Frames can be made of steelSteel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
, carbon fiber, or titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
. Carbon fiber is most common at the professional level.
Gears
Track bicycles have only one gear so its size is important. A lower gear allows quicker acceleration or 'jump.' But a bigger gear makes sustained speed easier, important in pursuitPursuit
Pursuit may refer to:In aircraft:*Rans S-11 Pursuit, lifting body style light aircraft designIn cars:*Pontiac G5, formerly called Pontiac PursuitIn film and television:*Pursuit , a 1950s anthology...
, time trial
Time trial
In many racing sports an athlete will compete in a time trial against the clock to secure the fastest time. In cycling, for example, a time trial can be a single track cycling event, or an individual or team time trial on the road, and either or both of the latter may form components of...
and bunched races such as points or scratch events.
Without a good jump, the rider risks opponents accelerating away; without good sustained speed, he will be unable to keep up with a fast race. Track cyclists practice fast pedalling (cadence) as a compromise.
Long-distance attempts such as the hour record
Hour record
The hour record for bicycles is the record for the longest distance cycled in one hour on a bicycle. There are several records. The most famous is for upright bicycles meeting the requirements of the Union Cycliste Internationale . It is one of the most prestigious in cycling...
sometimes use high gear combinations such as 52x12 or 55x14. Ondřej Sosenka
Ondrej Sosenka
Ondřej Sosenka is a Czech professional cyclist and rides for the UCI Professional Continental team PSK Whirlpool-Author. He won the Peace Race in 2002. He broke the nine-year old UCI hour record on July 19, 2005 in Moscow, Russia, riding in one hour.Sosenka was known as one of the largest...
used 54x13 with 190mm cranks to set the 2005 record.
Chain
There are two common widths of single speed and fixed gear bicycle chainBicycle chain
A bicycle chain is a roller chain that transfers power from the pedals to the drive-wheel of a bicycle, thus propelling it. Most bicycle chains are made from plain carbon or alloy steel, but some are nickel-plated to prevent rust, or simply for aesthetics. Nickel also confers a measure of...
s: 1/8 inch and 3/32 inch. The chainring, sprocket and chain should all be the same width. Although an 1/8-inch chain will work on a 3/32-inch chainring or sprocket, it is not ideal. A 3/32-inch chain will not work on a 1/8-inch chainring or sprocket. Because they do not need to shift from sprocket to sprocket, track chains use a full bushing to allow little flex and to be stronger. All bicycles with derailleur gears use bushingless chains which flex, making gear changing possible.

