
Transformity
Encyclopedia
The concept of transformity was first introduced by David M. Scienceman
in collaboration with the late Howard T. Odum
. In 1987 Scienceman proposed that the phrases, "energy quality
", "energy quality factor", and "energy transformation ratio", all used by H.T.Odum, be replaced by the word "transformity" (p. 261). This approach aims to solve a long standing issue about the relation of qualitative phenomena to quantitative phenomena often analysed in the physical sciences, which in turn is a synthesis of rationalism with phenomenology
. That is to say that it aims to quantify quality.
In 1996 H.T.Odum defined transformity as,
G.P.Genoni expanded on this definition and maintained that, "the energy input of one kind required to sustain one unit of energy of another kind, is used to quantify hierarchical position" (1997, p. 97). According to Scienceman, the concept of transformity introduces a new basic dimension into physics (1987, p. 261). However there is ambiguity in the dimensional analysis of transformity as Bastianoni et al. (2007) state that transformity is a dimensionless ratio.
viewpoint associated with modernity
and science
is to contrast qualitatively different phenomena under transformation through quantitative ratios, with the aim of uncovering any constancy amidst the transformation change. Like the efficiency
ratio, transformity is quantitatively defined by a simple input-output ratio. However the transformity ratio is the inverse of efficiency and involves both indirect and direct energy flows rather than simply direct input-output energy ratio of energy efficiency. This is to say that it is defined as the ratio of emergy input to energy
output.
Original version::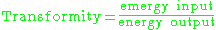
, and an alternative name for 'non-useful energy' is 'unavailability', or anergy (Nag 1984, p. 156)). But as E.Sciubba and S.Ulgiati observed, the notion of transformity meant to capture the emergy invested per unit product, or useful output. The concept of Transformity was therefore further specified as the ratio of "input emergy dissipated (availability used up)" to the "unit output exergy" (Sciubba and Ulgiati 2005, p. 1957). For Jørgensen (2000, p. 61) transformity is a strong indicator of the efficiency of the system.
Revised version: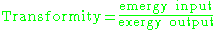 or
or 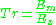
(after Giannantoni 2002, p. 8).
Substituting in the mathematical definition of emergy given in that article.
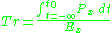
have posited that there are two transformity values;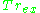 and
and 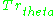 (Lourenci and Zuffo 2004, p. 411).
(Lourenci and Zuffo 2004, p. 411).
Under these definitions "emergy" can always be structured as follows:

David M. Scienceman
Dr David M. Scienceman is an Australian scientist; he changed his name from David Slade by deed poll in 1972.Dr Scienceman has a mathematics and physics degree and gained his PhD from the chemical engineering department at Sydney University on a scholarship from the Australian Atomic Energy...
in collaboration with the late Howard T. Odum
Howard T. Odum
Howard Thomas Odum was an American ecologist...
. In 1987 Scienceman proposed that the phrases, "energy quality
Energy quality
Energy quality is the contrast between different forms of energy, the different trophic levels in ecological systems and the propensity of energy to convert from one form to another. The concept refers to the empirical experience of the characteristics, or qualia, of different energy forms as they...
", "energy quality factor", and "energy transformation ratio", all used by H.T.Odum, be replaced by the word "transformity" (p. 261). This approach aims to solve a long standing issue about the relation of qualitative phenomena to quantitative phenomena often analysed in the physical sciences, which in turn is a synthesis of rationalism with phenomenology
Phenomenology (science)
The term phenomenology in science is used to describe a body of knowledge that relates empirical observations of phenomena to each other, in a way that is consistent with fundamental theory, but is not directly derived from theory. For example, we find the following definition in the Concise...
. That is to say that it aims to quantify quality.
Definition of transformity in words
Scienceman then defined transformity as,
"a quantitative variable describing the measurable property of a form of energy, its ability to amplify as feedback, relative to the source energy consumed in its formation, under maximum power conditions. As a quantitative variable analogous to themodynamic temperature, transformity requires specification of units." (1987, p. 261. My emphasis).
In 1996 H.T.Odum defined transformity as,
"the emergyEmergyEmergy is the available energy of one kind that is used up in transformations directly and indirectly to make a product or service. Emergy accounts for, and in effect, measures quality differences between forms of energy. Emergy is an expression of all the energy used in the work processes that...
of one type required to make a unit of energy of another type. For example, since 3 coal emjoules (cej) of coal and 1 cej of services are required to generate 1 J of electricity, the coal transformity of electricity is 4 cej/J"
G.P.Genoni expanded on this definition and maintained that, "the energy input of one kind required to sustain one unit of energy of another kind, is used to quantify hierarchical position" (1997, p. 97). According to Scienceman, the concept of transformity introduces a new basic dimension into physics (1987, p. 261). However there is ambiguity in the dimensional analysis of transformity as Bastianoni et al. (2007) state that transformity is a dimensionless ratio.
Definition as a ratio
One part of the rationalistRationalism
In epistemology and in its modern sense, rationalism is "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification" . In more technical terms, it is a method or a theory "in which the criterion of the truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive"...
viewpoint associated with modernity
Modernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
and science
Science
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
is to contrast qualitatively different phenomena under transformation through quantitative ratios, with the aim of uncovering any constancy amidst the transformation change. Like the efficiency
Mechanical efficiency
Mechanical efficiency measures the effectiveness of a machine in transforming the energy and power that is input to the device into an output force and movement...
ratio, transformity is quantitatively defined by a simple input-output ratio. However the transformity ratio is the inverse of efficiency and involves both indirect and direct energy flows rather than simply direct input-output energy ratio of energy efficiency. This is to say that it is defined as the ratio of emergy input to energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
output.
Original version::
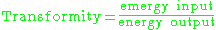
Development
However, it was realised that the term "energy output" refers to both the useful energy output and the non-useful energy output. (Note: that as given by P.K.Nag, an alternative name for 'useful energy' is 'availability' or exergyExergy
In thermodynamics, the exergy of a system is the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with a heat reservoir. When the surroundings are the reservoir, exergy is the potential of a system to cause a change as it achieves equilibrium with its...
, and an alternative name for 'non-useful energy' is 'unavailability', or anergy (Nag 1984, p. 156)). But as E.Sciubba and S.Ulgiati observed, the notion of transformity meant to capture the emergy invested per unit product, or useful output. The concept of Transformity was therefore further specified as the ratio of "input emergy dissipated (availability used up)" to the "unit output exergy" (Sciubba and Ulgiati 2005, p. 1957). For Jørgensen (2000, p. 61) transformity is a strong indicator of the efficiency of the system.
Revised version:
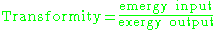 or
or 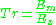
(after Giannantoni 2002, p. 8).
Substituting in the mathematical definition of emergy given in that article.
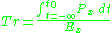
Two transformities
Albertina Lourenci and João Antonio Zuffo from the Department of Electronic Systems Engineering at São PauloSão Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
have posited that there are two transformity values;
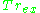 and
and 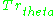 (Lourenci and Zuffo 2004, p. 411).
(Lourenci and Zuffo 2004, p. 411).-
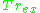 : compensates for the dissipation of exergy, and is defined in words as the Quality Factor which takes into account the emerging Quality associated to other forms of Energy
: compensates for the dissipation of exergy, and is defined in words as the Quality Factor which takes into account the emerging Quality associated to other forms of Energy -
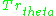 : accounts for the increase of Transformity as a consequence of the Emergy generated by the Source Terms of the Universe
: accounts for the increase of Transformity as a consequence of the Emergy generated by the Source Terms of the Universe
Under these definitions "emergy" can always be structured as follows:


