
Transmission delay
Encyclopedia
In a network
based on packet switching
, transmission delay (or store-and-forward delay) is the amount of time required to push all of the packet's bits into the wire. In other words, this is the delay caused by the data-rate of the link.
Transmission delay is a function of the packet's length and has nothing to do with the distance between the two nodes. This delay is proportional to the packet's length in bits,
It is given by the following formula: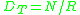
where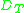 is the transmission delay
is the transmission delay
Most packet switched
networks use store-and-forward transmission at the input of the link. A switch using store-and-forward transmission will receive (save) the entire packet to the buffer and check it for CRC errors or other problems before sending the first bit of the packet into the outbound link. Thus store-and-forward packet switches introduce a store-and-forward delay at the input to each link along the packet's route.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
based on packet switching
Packet switching
Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets. Packet switching features delivery of variable-bit-rate data streams over a shared network...
, transmission delay (or store-and-forward delay) is the amount of time required to push all of the packet's bits into the wire. In other words, this is the delay caused by the data-rate of the link.
Transmission delay is a function of the packet's length and has nothing to do with the distance between the two nodes. This delay is proportional to the packet's length in bits,
It is given by the following formula:
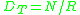
where
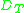 is the transmission delay
is the transmission delay
- N is the number of bits, and
- R is the rate of transmission (say in bits per second)
Most packet switched
Packet switching
Packet switching is a digital networking communications method that groups all transmitted data – regardless of content, type, or structure – into suitably sized blocks, called packets. Packet switching features delivery of variable-bit-rate data streams over a shared network...
networks use store-and-forward transmission at the input of the link. A switch using store-and-forward transmission will receive (save) the entire packet to the buffer and check it for CRC errors or other problems before sending the first bit of the packet into the outbound link. Thus store-and-forward packet switches introduce a store-and-forward delay at the input to each link along the packet's route.
See also
- Packet transfer delayPacket transfer delayPacket transfer delay is a concept in packet switching technology.The sum of store-and-forward delay that a packet experiences in each router gives the transfer or queuing delay of that packet across the network...
- Processing delayProcessing delayIn a network based on packet switching, processing delay is the time it takes routers to process the packet header. Processing delay is a key component in network delay....
- Queuing delayQueuing delayIn telecommunication and computer engineering, the queuing delay is the time a job waits in a queue until it can be executed. It is a key component of network delay....
- Propagation delayPropagation delayPropagation delay is a technical term that can have a different meaning depending on the context. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics...

