Traumatic aortic rupture
Encyclopedia
Traumatic aortic rupture, also called traumatic aortic disruption or transection, is a condition in which the aorta
, the largest artery
in the body, is torn or ruptured as the result of trauma. The condition is frequently fatal due to the profuse bleeding
that results from the rupture. Since the aorta branches directly from the heart
to supply blood
to the rest of the body, the pressure within it is very great, and blood may be pumped out of a tear in the blood vessel very rapidly. This can quickly result in shock and death. Thus traumatic aortic rupture is a common killer of victims of automotive accidents
and other traumas, with up to 18% of deaths that occur in automobile collisions being related to the injury. In fact, aortic disruption due to blunt chest trauma
is the second leading cause of injury death (behind traumatic brain injury
).
. Diagnosis is further complicated by the fact that many patients with the injury experienced multiple other serious injuries as well, so the attention of hospital staff may be distracted from the possibility of aortic rupture.
The preferred method of diagnosis is aortography
. Though not completely reliable, chest X-ray
s are used to diagnose the condition.
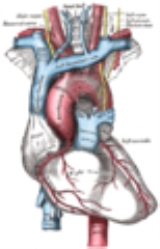
By far the most common site for tearing in traumatic aortic rupture is the aortic isthmus, near where the left subclavian artery
branches off from the aorta (distal to left subclavian artery). An angiogram will often show an irregular outpouching beyond the takeoff of the left subclavian artery at the aortic isthmus, representing an aortic pseudoaneursym caused by the trauma.
The classical findings on a chest x ray will be widened mediastinum, apical cap, and displacement of the trachea, left main bronchus, or nasogastric tube. A normal chest x-ray does not exclude transection, but will diagnose conditions
such as pneumothorax or hydrothorax. The aorta may also be torn at the point where it is connected to the heart. The aorta may be completely torn apart from the heart, but patients with such injuries very rarely survive for very long after the injury; thus it is much more common for hospital staff to treat patients with partially torn aortas. When the aorta is partially torn, it may form a "pseudoaneurysm". In patients who do live long enough to be seen in a hospital, a majority have only a partially torn blood vessel, with the layer called the adventitia
still intact. In some of these patients, the adventitia and nearby structures within the chest may serve to prevent severe hemorrhage. After trauma, the aorta can be assessed by a CT angiogram or a direct angiogram, in which contrast is introduced into the aorta via a catheter.
s for surgical repair of the aorta for this condition are among the highest of any cardiovascular surgery. For example, surgery is associated with a high rate of paraplegia
, because the spinal cord
is very sensitive to ischemia
(lack of blood supply), and the nerve tissue can be damaged or killed by the interruption of the blood supply during surgery.
Since high blood pressure
could exacerbate the tear in the aorta or even separate it completely from the heart, which would almost inevitably kill the patient, hospital staff take measures to keep the blood pressure low. Such measures include giving pain medication, keeping the patient calm, and avoiding procedures that could cause gagging or vomiting
.
Aorta
The aorta is the largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it branches off into two smaller arteries...
, the largest artery
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
in the body, is torn or ruptured as the result of trauma. The condition is frequently fatal due to the profuse bleeding
Bleeding
Bleeding, technically known as hemorrhaging or haemorrhaging is the loss of blood or blood escape from the circulatory system...
that results from the rupture. Since the aorta branches directly from the heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
to supply blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
to the rest of the body, the pressure within it is very great, and blood may be pumped out of a tear in the blood vessel very rapidly. This can quickly result in shock and death. Thus traumatic aortic rupture is a common killer of victims of automotive accidents
Car accident
A traffic collision, also known as a traffic accident, motor vehicle collision, motor vehicle accident, car accident, automobile accident, Road Traffic Collision or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other stationary obstruction,...
and other traumas, with up to 18% of deaths that occur in automobile collisions being related to the injury. In fact, aortic disruption due to blunt chest trauma
Chest trauma
Chest trauma is a serious injury of the chest. Thoracic trauma is a common cause of significant disability and mortality, the leading cause of death from physical trauma after head and spinal cord injury. Blunt thoracic injuries are the primary or a contributing cause of about a quarter of all...
is the second leading cause of injury death (behind traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
).
Symptoms
The condition is difficult to detect and may go unnoticed, since most patients have no symptoms. However, a minority of patients may be hoarse, find it difficult to breathe or speak, or have shortness of breath, or have chest or upper back painBack pain
Back pain is pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine.The pain can often be divided into neck pain, upper back pain, lower back pain or tailbone pain...
. Diagnosis is further complicated by the fact that many patients with the injury experienced multiple other serious injuries as well, so the attention of hospital staff may be distracted from the possibility of aortic rupture.
The preferred method of diagnosis is aortography
Aortography
An aortogram involves placement of a catheter in the aorta and injection of contrast material while taking x-rays of the aorta. The procedure is known as aortography...
. Though not completely reliable, chest X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s are used to diagnose the condition.
Features
The injury is usually caused by high speed impacts such as those that occur in vehicle collisions and serious falls. It may be due to different rates of deceleration of the heart and the aorta, which is in a fixed position.By far the most common site for tearing in traumatic aortic rupture is the aortic isthmus, near where the left subclavian artery
Subclavian artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are two major arteries of the upper thorax , below the clavicle . They receive blood from the top of the aorta...
branches off from the aorta (distal to left subclavian artery). An angiogram will often show an irregular outpouching beyond the takeoff of the left subclavian artery at the aortic isthmus, representing an aortic pseudoaneursym caused by the trauma.
The classical findings on a chest x ray will be widened mediastinum, apical cap, and displacement of the trachea, left main bronchus, or nasogastric tube. A normal chest x-ray does not exclude transection, but will diagnose conditions
such as pneumothorax or hydrothorax. The aorta may also be torn at the point where it is connected to the heart. The aorta may be completely torn apart from the heart, but patients with such injuries very rarely survive for very long after the injury; thus it is much more common for hospital staff to treat patients with partially torn aortas. When the aorta is partially torn, it may form a "pseudoaneurysm". In patients who do live long enough to be seen in a hospital, a majority have only a partially torn blood vessel, with the layer called the adventitia
Adventitia
Adventitia is the outermost connective tissue covering of any organ, vessel, or other structure. It is also called the tunica adventitia or the tunica externa....
still intact. In some of these patients, the adventitia and nearby structures within the chest may serve to prevent severe hemorrhage. After trauma, the aorta can be assessed by a CT angiogram or a direct angiogram, in which contrast is introduced into the aorta via a catheter.
Treatment
Traumatic aortic rupture is treated with surgery. However, morbidity and mortality rateMortality rate
Mortality rate is a measure of the number of deaths in a population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit time...
s for surgical repair of the aorta for this condition are among the highest of any cardiovascular surgery. For example, surgery is associated with a high rate of paraplegia
Paraplegia
Paraplegia is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek: παραπληγίη "half-striking". It is usually the result of spinal cord injury or a congenital condition such as spina bifida that affects the neural elements of the spinal canal...
, because the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
is very sensitive to ischemia
Ischemia
In medicine, ischemia is a restriction in blood supply, generally due to factors in the blood vessels, with resultant damage or dysfunction of tissue. It may also be spelled ischaemia or ischæmia...
(lack of blood supply), and the nerve tissue can be damaged or killed by the interruption of the blood supply during surgery.
Since high blood pressure
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
could exacerbate the tear in the aorta or even separate it completely from the heart, which would almost inevitably kill the patient, hospital staff take measures to keep the blood pressure low. Such measures include giving pain medication, keeping the patient calm, and avoiding procedures that could cause gagging or vomiting
Vomiting
Vomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
.
Prognosis
Death occurs immediately after traumatic rupture of the thoracic aorta 75%–90% of the time since bleeding is so severe, and 80–85% of patients die before arriving at a hospital. Though there is a concern that a small, stable tear in the aorta could enlarge and cause complete rupture of the aorta and heavy bleeding, this may be less common than previously believed as long as the patient's blood pressure does not get too high.External links
- Chest Trauma: Traumatic Aortic Injury from Trauma.org
- Ruptured Artery Explanation

