
Truncated normal distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability and statistics, the truncated normal distribution is the probability distribution of a normally distributed random variable whose value is either bounded below or above (or both). The truncated normal distribution has wide applications in statistics and econometrics
. For example, it is used to model the probabilities of the binary outcomes in the probit model
and to model censored data in the tobit model
.
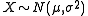 has a normal distribution and lies within the interval
has a normal distribution and lies within the interval 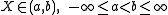 . Then
. Then 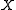 conditional on
conditional on 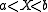 has a truncated normal distribution.
has a truncated normal distribution.
Its probability density function
, ƒ, for a≤x≤b, is given by
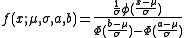
and by ƒ=0 otherwise.
Here,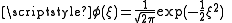 is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and
is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and 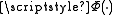 is its cumulative distribution function
is its cumulative distribution function
. There is an understanding that if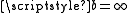 , then
, then 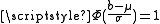 , and similarly, if
, and similarly, if 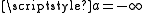 , then
, then 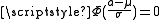 .
.
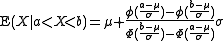
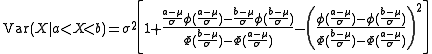
One sided truncation (lower tail) :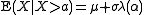
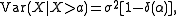
where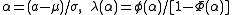 and
and 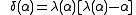 .
.
One sided truncation (upper tail):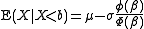
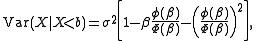
where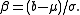
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
. For example, it is used to model the probabilities of the binary outcomes in the probit model
Probit model
In statistics, a probit model is a type of regression where the dependent variable can only take two values, for example married or not married....
and to model censored data in the tobit model
Tobit model
The Tobit model is a statistical model proposed by James Tobin to describe the relationship between a non-negative dependent variable y_i and an independent variable x_i....
.
Definition
Suppose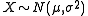 has a normal distribution and lies within the interval
has a normal distribution and lies within the interval 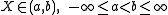 . Then
. Then 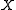 conditional on
conditional on 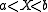 has a truncated normal distribution.
has a truncated normal distribution.Its probability density function
Probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function , or density of a continuous random variable is a function that describes the relative likelihood for this random variable to occur at a given point. The probability for the random variable to fall within a particular region is given by the...
, ƒ, for a≤x≤b, is given by
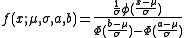
and by ƒ=0 otherwise.
Here,
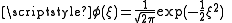 is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and
is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution and 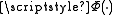 is its cumulative distribution function
is its cumulative distribution functionCumulative distribution function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function , or just distribution function, describes the probability that a real-valued random variable X with a given probability distribution will be found at a value less than or equal to x. Intuitively, it is the "area so far"...
. There is an understanding that if
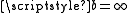 , then
, then 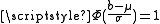 , and similarly, if
, and similarly, if 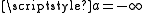 , then
, then 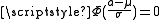 .
.Moments
Two sided truncation :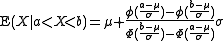
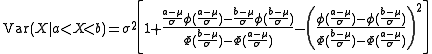
One sided truncation (lower tail) :
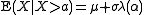
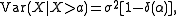
where
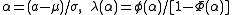 and
and 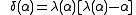 .
.One sided truncation (upper tail):
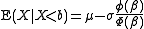
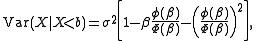
where
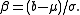
Simulating
For more on simulating a draw from the truncated normal distribution, see Roberts (1995) or Lynch (2007) Section 8.1.3 (pages 200–206)See also
- Normal distribution
- Truncated distributionTruncated distributionIn statistics, a truncated distribution is a conditional distribution that results from restricting the domain of some other probability distribution. Truncated distributions arise in practical statistics in cases where the ability to record, or even to know about, occurrences is limited to values...

