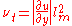Turbulence modeling
Encyclopedia
Turbulence modeling is the construction and use of a model
to predict the effects of turbulence
. Averaging is often used to simplify the solution of the governing equations of turbulence, but models are needed to represent scales of the flow that are not resolved.
A closure problem arises in the RANS equation because of the non-linear term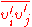 from the convective acceleration, known as the Reynolds stress,
from the convective acceleration, known as the Reynolds stress,
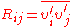
Closing the RANS equation requires modeling the Reynold's stress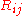 . Joseph Boussinesq was the first practitioner of this, introducing the concept of eddy viscosity
. Joseph Boussinesq was the first practitioner of this, introducing the concept of eddy viscosity
. In 1887 Boussinesq proposed relating the turbulent stresses to the mean flow to close the system of equations. Here the Boussinesq hypothesis is applied to model the Reynolds stress term. Note that a new proportionality constant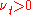 , the turbulent eddy viscosity, has been introduced. Models of this type are known as eddy viscosity models or EVM's.
, the turbulent eddy viscosity, has been introduced. Models of this type are known as eddy viscosity models or EVM's.
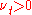
In this model, the additional turbulent stresses are given by augmenting the molecular
viscosity with an eddy viscosity. This can be a simple constant eddy viscosity (which works well for some free shear flows such as axisymmetric jets, 2-D jets, and mixing layers). Later, Ludwig Prandtl introduced the additional concept of the mixing length, along with the idea of a boundary layer
. For wall-bounded turbulent flows, the eddy viscosity must vary with distance from the wall, hence the addition of the concept of a 'mixing length'. In the simplest wall-bounded flow model, the eddy viscosity is given by the equation:
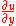 is the partial derivative of the streamwise velocity (u) with respect to the wall normal direction (y);
is the partial derivative of the streamwise velocity (u) with respect to the wall normal direction (y);
 is the mixing length.
is the mixing length.
This simple model is the basis for the "Law of the Wall", which is a surprisingly accurate model for wall-bounded, attached (not separated) flow fields with small pressure gradient
s.
More general turbulence models have evolved over time, with most modern turbulence models given by field equation
s similar to the Navier-Stokes equations.
Among many others , Joseph Smagorinsky
(1964) proposed a useful formula for the eddy viscosity in numerical models, based on the local derivatives of the velocity field and the local grid size:
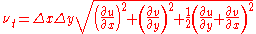
The Boussinesq hypothesis is employed in the Spalart-Allmaras (S-A), k-ε (k-epsilon), and k-ω (k-omega) models and offers a relatively low cost computation for the turbulent viscosity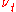 . The S-A model uses only one additional equation to model turbulent viscosity transport, while the k models use two.
. The S-A model uses only one additional equation to model turbulent viscosity transport, while the k models use two.
Mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used not only in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines A mathematical model is a...
to predict the effects of turbulence
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
. Averaging is often used to simplify the solution of the governing equations of turbulence, but models are needed to represent scales of the flow that are not resolved.
A closure problem arises in the RANS equation because of the non-linear term
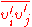 from the convective acceleration, known as the Reynolds stress,
from the convective acceleration, known as the Reynolds stress,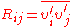
Closing the RANS equation requires modeling the Reynold's stress
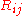 . Joseph Boussinesq was the first practitioner of this, introducing the concept of eddy viscosity
. Joseph Boussinesq was the first practitioner of this, introducing the concept of eddy viscosityViscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
. In 1887 Boussinesq proposed relating the turbulent stresses to the mean flow to close the system of equations. Here the Boussinesq hypothesis is applied to model the Reynolds stress term. Note that a new proportionality constant
 , the turbulent eddy viscosity, has been introduced. Models of this type are known as eddy viscosity models or EVM's.
, the turbulent eddy viscosity, has been introduced. Models of this type are known as eddy viscosity models or EVM's.
- Which can be written in shorthand as
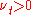
- where
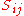 is the mean rate of strain tensor
is the mean rate of strain tensor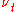 is the turbulent eddy viscosity
is the turbulent eddy viscosity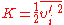 is the turbulent kinetic energy
is the turbulent kinetic energy - and
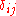 is the Kronecker delta.
is the Kronecker delta.
In this model, the additional turbulent stresses are given by augmenting the molecular
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
viscosity with an eddy viscosity. This can be a simple constant eddy viscosity (which works well for some free shear flows such as axisymmetric jets, 2-D jets, and mixing layers). Later, Ludwig Prandtl introduced the additional concept of the mixing length, along with the idea of a boundary layer
Boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where effects of viscosity of the fluid are considered in detail. In the Earth's atmosphere, the planetary boundary layer is the air layer near the ground affected by diurnal...
. For wall-bounded turbulent flows, the eddy viscosity must vary with distance from the wall, hence the addition of the concept of a 'mixing length'. In the simplest wall-bounded flow model, the eddy viscosity is given by the equation:
- where:
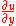 is the partial derivative of the streamwise velocity (u) with respect to the wall normal direction (y);
is the partial derivative of the streamwise velocity (u) with respect to the wall normal direction (y); is the mixing length.
is the mixing length.This simple model is the basis for the "Law of the Wall", which is a surprisingly accurate model for wall-bounded, attached (not separated) flow fields with small pressure gradient
Pressure gradient
In atmospheric sciences , the pressure gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pressure per unit length...
s.
More general turbulence models have evolved over time, with most modern turbulence models given by field equation
Field equation
A field equation is an equation in a physical theory that describes how a fundamental force interacts with matter...
s similar to the Navier-Stokes equations.
Among many others , Joseph Smagorinsky
Joseph Smagorinsky
Joseph Smagorinsky was an American meteorologist and the first director of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory.- Early life :...
(1964) proposed a useful formula for the eddy viscosity in numerical models, based on the local derivatives of the velocity field and the local grid size:
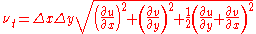
The Boussinesq hypothesis is employed in the Spalart-Allmaras (S-A), k-ε (k-epsilon), and k-ω (k-omega) models and offers a relatively low cost computation for the turbulent viscosity
 . The S-A model uses only one additional equation to model turbulent viscosity transport, while the k models use two.
. The S-A model uses only one additional equation to model turbulent viscosity transport, while the k models use two.Common Models
The following is a list of commonly employed models in modern engineering applications.- Spalart–Allmaras (S-A)
- k-ε (k-epsilon)
- k-ω (k-omega)
- SSTSSTThe acronym SST may refer to:In aircraft and naval vehicles*Scaled Composites SpaceShipTwo*SST class blimp SS class blimp*Supersonic transport , civil aircraft for transporting passengers faster than the speed of sound....
(Menter’s Shear Stress Transport)