
Ultrasonic flow meter
Encyclopedia
Liquid
Liquid is one of the three classical states of matter . Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Some liquids resist compression, while others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly...
or gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
(fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
) by using the principle of ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
. Using ultrasonic transducers, the flow meter can measure the average velocity along the path of an emitted beam of ultrasound, by averaging the difference in measured transit time between the pulses of ultrasound propagating into and against the direction of the flow. Ultrasonic flow meters are affected by the temperature, density and viscosity of the flowing medium. They are inexpensive to use and maintain because they do not use moving parts
Moving parts
The moving parts of a machine are those parts of it that move. Machines comprise both moving and fixed parts. The moving parts have controlled and constrained motions....
, unlike mechanical flow meters.
Means of operation
There are three different types of ultrasonic flow meters. Transmission (or contrapropagating transit-time) flow meters can be distinguished into in-line (intrusive, wetted) and clamp-on (non-intrusive) varieties. Ultrasonic flow meters that use the Doppler shift are called Reflection or Doppler flow meters. The third type is the Open-Channel flow meter.Principle
Ultrasonic flow meterUltrasonic flow meter
An ultrasonic flow meter is a type of flow meter that measures the velocity of a liquid or gas by using the principle of ultrasound. Using ultrasonic transducers, the flow meter can measure the average velocity along the path of an emitted beam of ultrasound, by averaging the difference in...
s measure the difference of the transit time of ultrasonic pulses propagating in and against flow direction. This time difference is a measure for the average velocity of the fluid along the path of the ultrasonic beam. By using the absolute transit times both the averaged fluid velocity and the speed of sound can be calculated. Using the two transit times
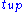 and
and 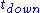 and the distance between receiving and transmitting transducers
and the distance between receiving and transmitting transducers 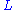 and the inclination angle
and the inclination angle  one can write the equations:
one can write the equations: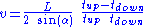 and
and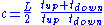
where
 is the average velocity of the fluid along the sound path and
is the average velocity of the fluid along the sound path and  is the speed of sound.
is the speed of sound.Doppler shift flow meters
A recent innovation in ultrasonic flow metering is the use of the Doppler shift that results from the reflection of an ultrasonic beam off sonically reflective materials, such as solid particles or entrained air bubbles in a flowing fluid, or the turbulenceTurbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is a flow regime characterized by chaotic and stochastic property changes. This includes low momentum diffusion, high momentum convection, and rapid variation of pressure and velocity in space and time...
of the fluid itself, if the liquid is clean.
Doppler flowmeters are used for slurries, liquids with bubbles, gases with sound-reflecting particles, or single-phase turbulent clean liquids.
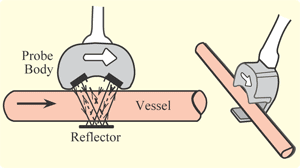
This type of flow meter can also be used to measure the rate of blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
flow, by passing an ultrasonic beam through the tissues, bouncing it off a reflective plate, then reversing the direction of the beam and repeating the measurement, the volume of blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
flow can be estimated. The frequency of the transmitted beam is affected by the movement of blood in the vessel and by comparing the frequency of the upstream beam versus downstream the flow of blood through the vessel can be measured. The difference between the two frequencies is a measure of true volume flow. A wide-beam sensor can also be used to measure flow independent of the cross-sectional area of the blood vessel.

