
Umayyad
Encyclopedia
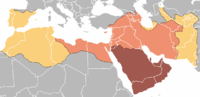
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab
caliphate
s established after the death of Muhammad
. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams
, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the city of Mecca
, their capital was Damascus
. At its greatest extent, it covered more than five million square miles (13,000,000 km2), making it one of the largest empires the world had yet seen, and the fifth largest contiguous empire ever to exist. After the Umayyads were overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate, they fled across North Africa
to Spain
(Al-Andalus
), where they established the Caliphate of Córdoba
, which lasted until 1031.

 According to tradition, the Umayyad family (also known as the Banu Abd-Shams) and Muhammad both descended from a common ancestor, Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
According to tradition, the Umayyad family (also known as the Banu Abd-Shams) and Muhammad both descended from a common ancestor, Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
and they are originally from the city of Mecca
. Muhammad descended from Abd Manāf via his son Hashim
, while the Umayyads descended from Abd Manaf via a different son, Abd-Shams
, whose son was Umayya
. The two families are therefore considered to be different clans (those of Hashim
and of Umayya, respectively) of the same tribe (that of the Quraish). However Muslim Shia historians point out that Umayya
was an adopted son of Abd Shams so he was not a blood relative of Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
. Umayya
was later discarded from the noble family.
While the Umayyads and the Hashimites may have had bitterness between the two clans before Muhammad
, the rivalry turned into a severe case of tribal animosity after the Battle of Badr
. The battle saw three top leaders of the Umayyad clan (Utba ibn Rabi'ah
, Walid ibn Utbah and Shaybah) killed by Hashmites (Ali, Hamza ibn ‘Abd al-Muttalib
and Ubaydah ibn al-Harith
) in a three-on-three melee. This fueled the opposition of Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
, the grandson of Umayya, to Muhammad and to Islam. Abu Sufyan sought to exterminate the adherents of the new religion by waging another battle with Muslims based in Medina only a year after the Battle of Badr
. He did this to avenge the defeat at Badr. The Battle of Uhud
is generally believed by scholars to be the first defeat for the Muslims, as they had incurred greater losses than the Meccans. After the battle, Abu Sufyan's wife Hind, who was also the daughter of Utba ibn Rabi'ah
is reported to have cut open the corpse of Hamza, taking out his liver which she then attempted to eat. Within five years after his defeat in the Battle of Uhud
however, Muhammad took control of Mecca
and announced a general amnesty for all. Scared for their lives and the hatred from Muslims, Abu Sufyan and his wife Hind embraced Islam
on the eve of the conquest of Mecca, as did their son (the future caliph Muawiyah I
). The Conquest of Mecca
while overwhelming for the Umayyads for the time being, further fueled their hatred towards the Hashmites; this would later result in battles between Muawiyah I
and Ali
and then killing of Husayn ibn Ali
along with his family and a few friends on the orders of Yazid ibn Muawiyah at the Battle of Karbala
.
Most historians consider Caliph Muawiyah (661–80) to have been the second ruler of the Umayyad dynasty, even though he was the first to assert the Umayyads' right to rule on a dynastic principle. It was really the caliphate of Uthman Ibn Affan (644–656), a member of Umayyad clan himself, that witnessed the revival and then the ascendancy of the Umayyad clan to the corridors of power. Uthman, during his reign, placed some of the trusted members of his clan at prominent and strong positions throughout the state. Most notable was the appointment of Marwan ibn al-Hakam, Uthman's first cousin, as his top advisor, which created a stir amongst the Hashmite companions of Muhammad, as Marwan along with his father Al-Hakam ibn Abi al-'As had been permanently exiled from Medina by Muhammad during his lifetime. Uthman also appointed Walid ibn Uqba
, Uthman's half-brother, as the governor of Kufah
, who was accused, by Hashmites, of leading prayer while under the influence of alcohol. Uthman also consolidated Muawiyah's Governorship of Syria by granting him control over a larger area and appointed his foster brother Abdullah ibn Saad
as the Governor of Egypt. However, since Uthman never named an heir, he cannot be considered the founder of a dynasty.
After the assassination of Uthman in 656
, Ali
, a member of the Hashimite clan and a cousin of Muhammad, was elected as the caliph. He soon met with resistance from several factions, owing to his relative political inexperience. Fearing a danger to his life, Ali moved his capital from Medina
to Kufa
. The resulting conflict, which lasted from 656 until 661, is known as the First Fitna
("civil war").
Ali was first opposed by an alliance led by Aisha
, the wife of Muhammad, and Talhah and Al-Zubayr, two of the companions of Muhammad. The two sides clashed at the Battle of the Camel in 656, where Ali won a decisive victory.
Following this battle, Ali fought a battle against Muawiyah, known as the Battle of Siffin. For reasons that remain obscure, the battle was stopped before either side had achieved victory, and the two parties agreed to arbitrate their dispute. Both the terms and the result of the arbitration, however, are subjects of contradictory and sometimes confused reports.
Following the battle, a large group of Ali's soldiers, who resented his decision to submit the dispute to arbitration, broke away from Ali's force, rallying under the slogan, "arbitration belongs to God alone." This group came to be known as the Kharijites
("those who leave").
In 659 Ali's forces and the Kharijites met in the Battle of Nahrawan
. Although Ali won the battle, the constant conflict had begun to affect his standing, and in the following years some Syrians seem to have acclaimed Muawiyah as a rival caliph.
Ali was assassinated in 661, apparently by a Kharijite partisan. Muawiyah marched to Kufa, where he persuaded a number of Ali's supporters to acclaim him as caliph instead of Ali's son, Hasan
. Following his elevation, Muawiyah moved the capital of the caliphate to Damascus
. Syria would remain the base of Umayyad power until the end of the dynasty in 750 AD. However, this Dynasty became reborn in Cordoba (Al Andalus, today's Portugal and Spain) in the form of an Emirate and then a Caliphate, lasting until 1031 AD. Muslim rule continued in Iberia for another 500 years in several forms: Taifas, Berber kingdoms, and under the Kingdom of Granada until the 16th century AD.
In the year 712, Muhammad bin Qasim
, an Umayyad general sailed from the khaleej into Sindh and conquered both the Sindh and the Punjab regions along the Indus river. The conquest of Sindh and Punjab in modern day Pakistan
, although costly, were major gains for the Umayyad Caliphate. However, further gains were halted by Hindu
Rajput
Kingdoms in North India.
During the later period of its existence and particularly from 1031 AD under the Ta'ifa system of Islamic Emirates (Princedoms) in the southern half of Iberia, the Emirate/Sultanate of Granada maintained its independence largely due to the payment of Tributes to the northern Christian Kingdoms which began to gradually expand south at its expense from 1031.
Muslim rule in Iberia came to an end on January 2, 1492 with the conquest of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada. The last Muslim ruler of Granada, Muhammad XII, better known as Boabdil, surrendered his kingdom to Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile, the Catholic Monarchs, los Reyes Católicos.
 Muawiyah's personal dynasty, the "Sufyanids" (descendants of Abu Sufyan), reigned from 661
Muawiyah's personal dynasty, the "Sufyanids" (descendants of Abu Sufyan), reigned from 661
to 684
, until his grandson Muawiya II
. The reign of Muawiyah I was marked by internal security and external expansion. On the internal front, only one major rebellion is recorded, that of Hujr ibn Adi
in Kufa. Hujr ibn Adi supported the claims of the descendants of Ali to the caliphate, but his movement was easily suppressed by the governor of Iraq, Ziyad ibn Abi Sufyan
.
Muawiyah also encouraged peaceful coexistence with the Christian
communities of Syria
, and one of his closest advisers was Sarjun, the father of John of Damascus
. At the same time, he waged unceasing war against the Byzantine Empire
. During his reign, Rhodes
and Crete
were occupied, and several assaults were launched against Constantinople
. Muawiyah also oversaw military expansion in North Africa (the foundation of Kairouan
) and in Central Asia (the conquest of Kabul
, Bukhara
, and Samarkand
).
Following Muawiyah's death in 680, he was succeeded by his son, Yazid I
. The hereditary accession of Yazid was opposed by a number of prominent Muslims, most notably Abd-Allah ibn al-Zubayr
, son of one of the companions of Muhammad, and Husayn ibn Ali
, grandson of Muhammad and younger son of Ali
. The resulting conflict is known as the Second Fitna
.
In 680 Ibn al-Zubayr and Husayn fled Medina for Mecca
. While Ibn al-Zubayr would stay in Mecca until his death, Husayn decided to travel on to Kufa to rally support. However, on the instructions of Yazid, a large Umayyad army (traditions mention 70,000) intercepted and mercilessly slaughtered Husayn, his family members and companions at the Battle of Karbala
. Husayn and his party numbered 128 including women, children and the elderly. 72 were killed including Husayn and his infant son of six months.
Following the death of Husayn, Ibn al-Zubayr, although remaining in Mecca, was associated with two opposition movements, one centered in Medina and the other around Kharijites in Basra
and Arabia. In 683, Yazid dispatched an army to subdue both. This army suppressed the Medinese opposition at the Battle of al-Harra, and continued on to lay siege to Mecca. At some point during the siege, the Kaaba
was badly damaged in a fire. The destruction of the Kaaba became a major cause for censure of the Umayyads in later histories of the period.
Yazid died while the siege was still in progress, and the Umayyad army returned to Damascus, leaving Ibn al-Zubayr in control of Mecca. Yazid was succeeded at first by his son, Muawiya II
(683–84), but he seems never to have been recognized as caliph outside of Syria. Two factions developed within Syria: the Confederation of Qays, who supported Ibn al-Zubayr, and the Quda'a, who supported Marwan
, a descendant of Umayya via Wa'il ibn Umayyah
. The partisans of Marwan triumphed at a battle at Marj Rahit, near Damascus, in 684, and Marwan became caliph shortly thereafter.
for the Umayyads, but died in 685, having reigned for only nine months.
Marwan was succeeded by his son, Abd al-Malik (685–705), who reconsolidated Umayyad control of the caliphate. The early reign of Abd al-Malik was marked by the revolt of Al-Mukhtar
, which was based in Kufa. Al-Mukhtar hoped to elevate Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah
, another son of Ali, to the caliphate, although Ibn al-Hanafiyyah himself may have had no connection to the revolt. The troops of al-Mukhtar engaged in battles both with the Umayyads, in 686, at the river Khazir near Mosul: an Umayyad defeat, and with Ibn al-Zubayr, in 687, at which time the revolt of al-Mukhtar was crushed. In 691, Umayyad troops reconquered Iraq, and in 692 the same army captured Mecca. Ibn al-Zubayr was killed in the attack.
The second major event of the early reign of Abd al-Malik was the construction of the Dome of the Rock
in Jerusalem. Although the chronology remains somewhat uncertain, the building seems to have been completed in 692, which means that it was under construction during the conflict with Ibn al-Zubayr. This had led some historians, both medieval and modern, to suggest that the Dome of the Rock was built to rival the Kaaba, which was under the control of Ibn al-Zubayr, as a destination for pilgrimage.
Abd al-Malik is credited with centralizing the administration of the caliphate, and with establishing Arabic as its official language. He also introduced a uniquely Muslim coinage, marked by its aniconic decoration, which supplanted the Byzantine and Sasanian coins that had previously been in use.
Following Abd al-Malik's death, his son, Al-Walid I (705–15) became caliph. Al-Walid was also active as a builder, sponsoring the construction of Al-Masjid al-Nabawi
in Medina and the Great Mosque
of Damascus.
A major figure during the reigns of both al-Walid and Abd al-Malik was the Umayyad governor of Iraq, Al-Hajjaj bin Yousef. Many Iraqis remained resistant to Umayyad rule, and al-Hajjaj imported Syrian troops to maintain order, whom he housed in a new garrison town, Wasit. These troops became crucial in the suppression of a revolt led by an Iraqi general, Ibn al-Ash'ath, in the early eighth century.
Al-Walid was succeeded by his brother, Sulayman
(715–17), whose reign was dominated by a protracted siege of Constantinople. The failure of the siege marked the end of serious Arab ambitions against the Byzantine capital. However, the first two decades of the eighth century witnessed the continuing expansion of the caliphate, which pushed into the Iberian Peninsula
in the west, and into Central Asia and northern India
in the east.
Sulayman was succeeded by his cousin, Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz (717–20), whose position among the Umayyad caliphs is somewhat unique. He is the only Umayyad ruler to have been recognized by subsequent Islamic tradition as a genuine caliph (khalifa) and not merely as a worldly king (malik).
Umar is honored for his attempt to resolve the fiscal problems attendant upon conversion to Islam. During the Umayyad period, the majority of people living within the caliphate were not Muslim, but Christian
, Jewish, Zoroastrian, or otherwise. These religious communities were not forced to convert to Islam, but were subject to a tax (jizyah) which was not imposed upon Muslims. This situation may actually have made widespread conversion to Islam undesirable from the point of view of state revenue, and there are reports that provincial governors actively discouraged such conversions. It is not clear how Umar attempted to resolve this situation, but the sources portray him as having insisted on like treatment of Arab and non-Arab (mawali
) Muslims, and on the removal of obstacles to the conversion of non-Arabs to Islam.
After the death of Umar, another son of Abd al-Malik, Yazid II
(720–24) became caliph. Yazid is best known for his "iconoclastic edict", which ordered the destruction of Christian images within the territory of the caliphate. In 720, another major revolt arose in Iraq, this time led by Yazid ibn al-Muhallab
.
(724–43), whose long and eventful reign was above all marked by the curtailment of military expansion.
 Hisham established his court at Resafa
Hisham established his court at Resafa
in northern Syria, which was closer to the Byzantine border than Damascus, and resumed hostilities against the Byzantines, which had lapsed following the failure of the last siege of Constantinople. The new campaigns resulted in a number of successful raids into Anatolia
, but also in a major defeat (the Battle of Akroinon
), and did not lead to any significant territorial expansion.
Hisham's reign furthermore witnessed the end of expansion in the west, following the defeat of the Arab army by the Franks
at the Battle of Tours
in 732. In 739 a major Berber Revolt
broke out in North Africa, which was subdued only with difficulty.
Hisham suffered still worse defeats in the east, where his armies attempted to subdue both Tokharistan, with its center at Balkh
, and Transoxiana
, with its center at Samarkand
. Both areas had already been partially conquered, but remained difficult to govern.
Once again, a particular difficulty concerned the question of the conversion of non-Arabs, especially the Sogdians
of Transoxiana. Ashras ibn 'Abd Allah al-Sulami, governor of Khorasan
, promised tax relief to those Sogdians who converted to Islam, but went back on his offer when it proved too popular and threatened to reduce tax revenues. In 734, al-Harith ibn Surayj led a revolt on behalf of the Sogdians, capturing Balkh but failing to take Merv
. After this defeat, al-Harith's movement seems to have been dissolved, but the problem of the rights of non-Arab Muslims would continue to plague the Umayyads.
 Hisham was succeeded by Al-Walid II
Hisham was succeeded by Al-Walid II
(743–44), the son of Yazid II. Al-Walid is reported to have been more interested in earthly pleasures than in religion, a reputation that may be confirmed by the decoration of the so-called "desert palaces" (including Qusayr Amra
and Khirbat al-Mafjar) that have been attributed to him. He quickly attracted the enmity of many, both by executing a number of those who had opposed his accession, and by persecuting the Qadariyya
.
In 744, Yazid III
, a son of al-Walid I, was proclaimed caliph in Damascus, and his army tracked down and killed al-Walid II. Yazid III has received a certain reputation for piety, and may have been sympathetic to the Qadariyya. He died a mere six months into his reign.
Yazid had appointed his brother, Ibrahim, as his successor, but Marwan II
(744–50), the grandson of Marwan I, led an army from the northern frontier and entered Damascus in December of 744, where he was proclaimed caliph. Marwan immediately moved the capital north to Harran
, in present-day Turkey
. A rebellion soon broke out in Syria, perhaps due to resentment over the relocation of the capital, and in 746 Marwan razed the walls of Homs
and Damascus in retaliation.
Marwan also faced significant opposition from Kharijites in Iraq and Iran, who put forth first Dahhak ibn Qays
and then Abu Dulaf as rival caliphs. In 747, Marwan managed to reestablish control of Iraq, but by this time a more serious threat had arisen in Khorasan
.
 The Hashimiyya movement (a sub-sect of the Kaysanites Shia
The Hashimiyya movement (a sub-sect of the Kaysanites Shia
), led by the Abbasid
family, overthrew the Umayyad caliphate. The Abbasids were members of the Hashim
clan, rivals of the Umayyads, but the word "Hashimiyya" seems to refer specifically to Abu Hashim, a grandson of Ali and son of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya. According to certain traditions, Abu Hashim died in 717 in Humeima in the house of Muhammad ibn Ali, the head of the Abbasid family, and before dying named Muhammad ibn Ali as his successor. This tradition allowed the Abbasids to rally the supporters of the failed revolt of Mukhtar
, who had represented themselves as the supporters of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya.
Beginning around 719, Hashimiyya missions began to seek adherents in Khurasan. Their campaign was framed as one of proselytism (dawah
). They sought support for a "member of the family" of Muhammad, without making explicit mention of the Abbasids. These missions met with success both among Arabs and non-Arabs (mawali
), although the latter may have played a particularly important role in the growth of the movement.
 Around 746, Abu Muslim
Around 746, Abu Muslim
assumed leadership of the Hashimiyya in Khurasan. In 747, he successfully initiated an open revolt against Umayyad rule, which was carried out under the sign of the black flag. He soon established control of Khurasan, expelling its Umayyad governor, Nasr ibn Sayyar
, and dispatched an army westwards. Kufa fell to the Hashimiyya in 749, and in November of the same year Abu al-Abbas
was recognized as the new caliph in the mosque at Kufa.
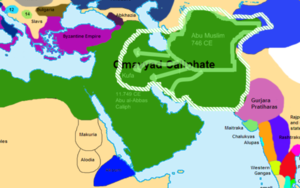 At this point Marwan mobilized his troops from Harran and advanced toward Iraq. In January of 750 the two forces met in the Battle of the Zab
At this point Marwan mobilized his troops from Harran and advanced toward Iraq. In January of 750 the two forces met in the Battle of the Zab
, and the Umayyads were defeated. Damascus fell to the Abbasids in April, and in August Marwan was killed in Egypt.
The victors desecrated the tombs of the Umayyads in Syria, sparing only that of Umar II, and most of the remaining members of the Umayyad family were tracked down and killed. One grandson of Hisham, Abd ar-Rahman I
, survived and established a kingdom in Al-Andalus
(Moorish
Iberia
), proclaiming his family to be the Umayyad Caliphate revived.
Previté-Orton argues that the reasons for the decline of the Umayyads was the rapid expansion of Islam. During Umayyad period, mass conversions brought Persians, Berbers, Copts, and Aramaics to Islam. These mawalis (clients) were often better educated and more civilised than their Arab masters. The new converts, on the basis of equality of all Muslims, transformed the political landscape. Previté-Orton also argues that the feud between Syria and Iraq, further weakened the empire.
On the pattern of the Byzantine system the umayyads reformed their army organization in general and divided it into five corps: the centre, two wings, vanguards and rearguards while on march or in a battle field following the same formation. Marwan II (740–50) abandoned the old division and introduced Kurdus (cohort) a small compact body.
The Umayyad troops were divided into three divisions: infantry, cavalry and artillery. Arab troops were dressed and armed in Greek fashion. The Umayyad cavalry used plain and round saddles. The artillery used arradah (ballista), manjaniq (the mangonel) and dabbabah or kabsh (the battering ram). The heavy engines, siege machines and baggage were carried on camels behind the army.
1.Muslim Arabs
2.Muslim non-Arabs (clients of the Muslim Arabs)
3.Non-Muslim free persons (Christians, Jews, Zoroastrians)
4.Slaves
The Muslim Arabs were at the top of the society, and saw it as their duty to rule over the conquered areas. Despite the fact that Islam teaches the equality of all Muslims, the Arab Muslims held themselves in higher esteem than Muslim non-Arabs and generally did not mix with other Muslims.
The inequality of Muslims in the empire led to social unrest. As Islam spread, more and more of the Muslim population became non-Arabs. This caused tension as the new converts were not given the same rights as Muslim Arabs. Also, as conversions increased, tax revenues off non-Muslims decreased to dangerous lows. These issues continued to grow until they helped cause the Abbasid Revolt in the 740s.
According to one common view, the Umayyads transformed the caliphate from a religious institution (during the rashidun
) to a dynastic one. However, the Umayyad caliphs do seem to have understood themselves as the representatives of God on earth, and to have been responsible for the "definition and elaboration of God's ordinances, or in other words the definition or elaboration of Islamic law."
During the period of the Umayyads, Arabic became the administrative language. State documents and currency were issued in the language. Mass conversions brought a large influx of Muslims to the caliphate
. The Umayyads also constructed famous buildings such as the Dome of the Rock
at Jerusalem, and the Umayyad Mosque
at Damascus
.
The Umayyads have met with a largely negative reception from later Islamic historians, who have accused them of promoting a kingship (mulk, a term with connotations of tyranny) instead of a true caliphate (khilafa). In this respect it is notable that the Umayyad caliphs referred to themselves, not as khalifat rasul Allah ("successor of the messenger of God", the title preferred by the tradition) but rather as khalifat Allah ("deputy of God"). The distinction seems to indicate that the Umayyads "regarded themselves as God's representatives at the head of the community and saw no need to share their religious power with, or delegate it to, the emergent class of religious scholars."
In fact, it was precisely this class of scholars, based largely in Iraq, that was responsible for collecting and recording the traditions that form the primary source material for the history of the Umayyad period. In reconstructing this history
, therefore, it is necessary to rely mainly on sources, such as the histories of Tabari
and Baladhuri
, that were written in the Abbasid court at Baghdad.
Modern Arab nationalism
regards the period of the Umayyads as part of the Arab Golden Age which it sought to emulate and restore. This is particularly true of Syrian nationalists and the present-day state of Syria, centered like that of the Umayyads on Damascus. White, one of the four Pan-Arab colors
which appear in various combinations on the flags of most Arab countries, is considered as representing the Umayyads.
. For example, in the section concerning Quran 17:60 in the exegesis
by al-Suyuti entitled Dur al-Manthur
, the author writes that there exist traditions which describe the Umayyads as "the cursed tree". There are some exceptions to this – Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz is commonly praised as one of the greatest Muslim rulers after the four Rightly Guided Caliphs.
described them as the worst Fitna.
In Some Answered Questions
, `Abdu'l-Bahá
asserts that the Umayyad dynasty was the "great red dragon, having seven heads and ten horns, and seven crowns upon his heads" and that the Umayyads "rose against the religion of Prophet Muhammad and against the reality of Ali".
The seven heads of the dragon is symbolic of the seven provinces of the lands dominated by the Umayyads; Damascus, Persia, Arabia, Egypt, Africa, Andalusia, and Transoxania. The ten horns represent the ten names of the leaders of the Umayyad dynasty; Abu Sufyan, Muawiya, Yazid, Marwan, Abd al-Malik, Walid, Sulayman, Umar, Hisham, and Ibrahim. Some names were re-used as in the case of Yazid II and Yazid III were not counted for this interpretation.
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
caliphate
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
s established after the death of Muhammad
Muhammad
Muhammad |ligature]] at U+FDF4 ;Arabic pronunciation varies regionally; the first vowel ranges from ~~; the second and the last vowel: ~~~. There are dialects which have no stress. In Egypt, it is pronounced not in religious contexts...
. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams
Umayya ibn Abd Shams
The clan of Banu Umayyad as well as the dynasty that ruled the Umayyad Caliphate are named after Umayya ibn Abd Shams.Umayya was the son of Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, and the father of Harb ibn Umayya and Abu al-'As....
, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the city of Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
, their capital was Damascus
Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
. At its greatest extent, it covered more than five million square miles (13,000,000 km2), making it one of the largest empires the world had yet seen, and the fifth largest contiguous empire ever to exist. After the Umayyads were overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate, they fled across North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
to Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
(Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
), where they established the Caliphate of Córdoba
Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ruled the Iberian peninsula and part of North Africa, from the city of Córdoba, from 929 to 1031. This period was characterized by remarkable success in trade and culture; many of the masterpieces of Islamic Iberia were constructed in this period, including the famous...
, which lasted until 1031.
Origins


Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
‘Abdu Manāf ibn Quṣayy was a Quraishi and great-great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Ali. His father was Quṣayy ibn Kilāb.-Biography:...
and they are originally from the city of Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
. Muhammad descended from Abd Manāf via his son Hashim
Hashim ibn Abd Manaf
Hashim ibn 'Abd Manaf was the great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the progenitor of the Banu Hashim clan of the distinguished Quraish tribe in Mecca....
, while the Umayyads descended from Abd Manaf via a different son, Abd-Shams
Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf
Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf was a prominent member of the Quraish tribe of Mecca in modern-day Saudi Arabia. The Banu Abd Shams sub-clan of the Quraish tribe and their descendants take its name from him.-Lineage:...
, whose son was Umayya
Umayya ibn Abd Shams
The clan of Banu Umayyad as well as the dynasty that ruled the Umayyad Caliphate are named after Umayya ibn Abd Shams.Umayya was the son of Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, and the father of Harb ibn Umayya and Abu al-'As....
. The two families are therefore considered to be different clans (those of Hashim
Banu Hashim
Banū Hāshim was a clan in the Quraysh tribe. Muhammad, was a member of this clan; his great-grandfather was Hashim, for whom the clan is named. Members of this clan are referred to by the Anglicised version of their name as Hashemites, or Huseini or Hasani...
and of Umayya, respectively) of the same tribe (that of the Quraish). However Muslim Shia historians point out that Umayya
Umayya ibn Abd Shams
The clan of Banu Umayyad as well as the dynasty that ruled the Umayyad Caliphate are named after Umayya ibn Abd Shams.Umayya was the son of Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, and the father of Harb ibn Umayya and Abu al-'As....
was an adopted son of Abd Shams so he was not a blood relative of Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
Abd Manaf ibn Qusai
‘Abdu Manāf ibn Quṣayy was a Quraishi and great-great-grandfather of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Ali. His father was Quṣayy ibn Kilāb.-Biography:...
. Umayya
Umayya ibn Abd Shams
The clan of Banu Umayyad as well as the dynasty that ruled the Umayyad Caliphate are named after Umayya ibn Abd Shams.Umayya was the son of Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, and the father of Harb ibn Umayya and Abu al-'As....
was later discarded from the noble family.
While the Umayyads and the Hashimites may have had bitterness between the two clans before Muhammad
Muhammad
Muhammad |ligature]] at U+FDF4 ;Arabic pronunciation varies regionally; the first vowel ranges from ~~; the second and the last vowel: ~~~. There are dialects which have no stress. In Egypt, it is pronounced not in religious contexts...
, the rivalry turned into a severe case of tribal animosity after the Battle of Badr
Battle of Badr
The Battle of Badr , fought Saturday, March 13, 624 AD in the Hejaz region of western Arabia , was a key battle in the early days of Islam and a turning point in Muhammad's struggle with his opponents among the Quraish in Mecca...
. The battle saw three top leaders of the Umayyad clan (Utba ibn Rabi'ah
Utba ibn Rabi'ah
Utbah ibn Rabi'ah was one of the prominent Leaders of Quraish during the era of Muhammad.-Family:Utba's father was Rabi'ah ibn Abd Shams. Utba's daughter, Hind bint Utbah, married Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, another of the Leaders of the Quraish and Muhammad's arch-enemy...
, Walid ibn Utbah and Shaybah) killed by Hashmites (Ali, Hamza ibn ‘Abd al-Muttalib
Hamza ibn ‘Abd al-Muttalib
Hamza ibn ‘Abdul-Muttalib [b.568-d.625] was the paternal uncle of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and his foster-brother. He and Muhammad were raised together as they were almost the same age. With excellence in the arts of wrestling and swordsmanship...
and Ubaydah ibn al-Harith
Ubaydah ibn al-Harith
Ubaydah ibn al-Harith is the son of Harith ibn Abd al-Muttalib and one of the sahaba of MuhammadObaidah ibn al-Harith ibn Abdul-Muttalib, was the first Muslim to be killed in battle. He was a cousin of Muhammad and Ali, and he was the first Martyr of the battle of Badr...
) in a three-on-three melee. This fueled the opposition of Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
Abu Sufyan ibn Harb
Sakhr ibn Harb , more commonly known as Abu Sufyan was a leading man of the Quraish of Mecca. He was a staunch opponent of the Islamic prophet Muhammad before accepting Islam later in his life.-Opposition to Islam:...
, the grandson of Umayya, to Muhammad and to Islam. Abu Sufyan sought to exterminate the adherents of the new religion by waging another battle with Muslims based in Medina only a year after the Battle of Badr
Battle of Badr
The Battle of Badr , fought Saturday, March 13, 624 AD in the Hejaz region of western Arabia , was a key battle in the early days of Islam and a turning point in Muhammad's struggle with his opponents among the Quraish in Mecca...
. He did this to avenge the defeat at Badr. The Battle of Uhud
Battle of Uhud
The Battle of Uhud was fought on March 19, 625 at the valley located in front of Mount Uhud, in what is now northwestern Arabia. It occurred between a force from the Muslim community of Medina led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a force led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb from Mecca, the town from...
is generally believed by scholars to be the first defeat for the Muslims, as they had incurred greater losses than the Meccans. After the battle, Abu Sufyan's wife Hind, who was also the daughter of Utba ibn Rabi'ah
Utba ibn Rabi'ah
Utbah ibn Rabi'ah was one of the prominent Leaders of Quraish during the era of Muhammad.-Family:Utba's father was Rabi'ah ibn Abd Shams. Utba's daughter, Hind bint Utbah, married Abu Sufyan ibn Harb, another of the Leaders of the Quraish and Muhammad's arch-enemy...
is reported to have cut open the corpse of Hamza, taking out his liver which she then attempted to eat. Within five years after his defeat in the Battle of Uhud
Battle of Uhud
The Battle of Uhud was fought on March 19, 625 at the valley located in front of Mount Uhud, in what is now northwestern Arabia. It occurred between a force from the Muslim community of Medina led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a force led by Abu Sufyan ibn Harb from Mecca, the town from...
however, Muhammad took control of Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
and announced a general amnesty for all. Scared for their lives and the hatred from Muslims, Abu Sufyan and his wife Hind embraced Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
on the eve of the conquest of Mecca, as did their son (the future caliph Muawiyah I
Muawiyah I
Muawiyah I was the first Caliph of the Umayyad Dynasty. After the conquest of Mecca by the Muslims, Muawiyah's family converted to Islam. Muawiyah is brother-in-law to Muhammad who married his sister Ramlah bint Abi-Sufyan in 1AH...
). The Conquest of Mecca
Conquest of Mecca
Mecca was conquered by the Muslims in January 630 AD .-Background:In 628 the Meccan tribe of Quraysh and the Muslim community in Medina signed a 10 year truce called the Treaty of Hudaybiyyah....
while overwhelming for the Umayyads for the time being, further fueled their hatred towards the Hashmites; this would later result in battles between Muawiyah I
Muawiyah I
Muawiyah I was the first Caliph of the Umayyad Dynasty. After the conquest of Mecca by the Muslims, Muawiyah's family converted to Islam. Muawiyah is brother-in-law to Muhammad who married his sister Ramlah bint Abi-Sufyan in 1AH...
and Ali
Ali
' |Ramaḍān]], 40 AH; approximately October 23, 598 or 600 or March 17, 599 – January 27, 661).His father's name was Abu Talib. Ali was also the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and ruled over the Islamic Caliphate from 656 to 661, and was the first male convert to Islam...
and then killing of Husayn ibn Ali
Husayn ibn Ali
Hussein ibn ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib was the son of ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Fātimah Zahrā...
along with his family and a few friends on the orders of Yazid ibn Muawiyah at the Battle of Karbala
Battle of Karbala
The Battle of Karbala took place on Muharram 10, in the year 61 of the Islamic calendar in Karbala, in present day Iraq. On one side of the highly uneven battle were a small group of supporters and relatives of Muhammad's grandson Husain ibn Ali, and on the other was a large military detachment...
.
Most historians consider Caliph Muawiyah (661–80) to have been the second ruler of the Umayyad dynasty, even though he was the first to assert the Umayyads' right to rule on a dynastic principle. It was really the caliphate of Uthman Ibn Affan (644–656), a member of Umayyad clan himself, that witnessed the revival and then the ascendancy of the Umayyad clan to the corridors of power. Uthman, during his reign, placed some of the trusted members of his clan at prominent and strong positions throughout the state. Most notable was the appointment of Marwan ibn al-Hakam, Uthman's first cousin, as his top advisor, which created a stir amongst the Hashmite companions of Muhammad, as Marwan along with his father Al-Hakam ibn Abi al-'As had been permanently exiled from Medina by Muhammad during his lifetime. Uthman also appointed Walid ibn Uqba
Walid ibn Uqba
Walid ibn Uqba was one of the companions of Muhammad.-Family:He was the son of Uqbah ibn Abu Mu'ayt, a man who tried to kill Muhammad and finally died as a non-Muslim, and thus the brother of Umm Kulthum bint Uqba...
, Uthman's half-brother, as the governor of Kufah
Kufah
Kufah may refer to:* Ovophis okinavensis, a.k.a. the Okinawa pitviper, a venomous pitviper species found in the Ryukyu Islands of Japan.* Alternative English spelling for Kufa, a city in modern Iraq....
, who was accused, by Hashmites, of leading prayer while under the influence of alcohol. Uthman also consolidated Muawiyah's Governorship of Syria by granting him control over a larger area and appointed his foster brother Abdullah ibn Saad
Abdullah ibn Saad
‘Abdullāh ibn Sa‘ad ibn Abī as-Sarḥ was the foster brother of Uthman. His father was Saad ibn Abi Sarh. Abdullah bin Sa'ad bin Abi'l Sarh built a strong Egyptian Arab navy. Under him the Muslim navy won a number of naval victories including its first major naval battle against Constans II at...
as the Governor of Egypt. However, since Uthman never named an heir, he cannot be considered the founder of a dynasty.
After the assassination of Uthman in 656
656
Year 656 was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 656 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* The Battle of Bassorah between Ali and Aisha,...
, Ali
Ali
' |Ramaḍān]], 40 AH; approximately October 23, 598 or 600 or March 17, 599 – January 27, 661).His father's name was Abu Talib. Ali was also the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and ruled over the Islamic Caliphate from 656 to 661, and was the first male convert to Islam...
, a member of the Hashimite clan and a cousin of Muhammad, was elected as the caliph. He soon met with resistance from several factions, owing to his relative political inexperience. Fearing a danger to his life, Ali moved his capital from Medina
Medina
Medina , or ; also transliterated as Madinah, or madinat al-nabi "the city of the prophet") is a city in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia, and serves as the capital of the Al Madinah Province. It is the second holiest city in Islam, and the burial place of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, and...
to Kufa
Kufa
Kufa is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000....
. The resulting conflict, which lasted from 656 until 661, is known as the First Fitna
First Fitna
The First Islamic Civil War , also called the First Fitna , was the first major civil war within the Islamic Caliphate. It arose as a struggle over who had the legitimate right to become the ruling Caliph...
("civil war").
Ali was first opposed by an alliance led by Aisha
Aisha
Aisha bint Abu Bakr also transcribed as was Muhammad's favorite wife...
, the wife of Muhammad, and Talhah and Al-Zubayr, two of the companions of Muhammad. The two sides clashed at the Battle of the Camel in 656, where Ali won a decisive victory.
Following this battle, Ali fought a battle against Muawiyah, known as the Battle of Siffin. For reasons that remain obscure, the battle was stopped before either side had achieved victory, and the two parties agreed to arbitrate their dispute. Both the terms and the result of the arbitration, however, are subjects of contradictory and sometimes confused reports.
Following the battle, a large group of Ali's soldiers, who resented his decision to submit the dispute to arbitration, broke away from Ali's force, rallying under the slogan, "arbitration belongs to God alone." This group came to be known as the Kharijites
Kharijites
Kharijites is a general term embracing various Muslims who, while initially supporting the authority of the final Rashidun Caliph Ali ibn Abi Talib, the son-in-law and cousin of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, then later rejected his leadership...
("those who leave").
In 659 Ali's forces and the Kharijites met in the Battle of Nahrawan
Battle of Nahrawan
The Battle of Nahrawan was a battle between Ali ibn Abi Talib and the Kharijites.After the unsatisfactory conclusion to the Battle of Siffin, Imam Ali ibn Abi Talib returned with his army back to Kufa on the 13th of Safar 37 A.H...
. Although Ali won the battle, the constant conflict had begun to affect his standing, and in the following years some Syrians seem to have acclaimed Muawiyah as a rival caliph.
Ali was assassinated in 661, apparently by a Kharijite partisan. Muawiyah marched to Kufa, where he persuaded a number of Ali's supporters to acclaim him as caliph instead of Ali's son, Hasan
Hasan ibn Ali
Al-Hasan ibn ‘Alī ibn Abī Tālib is an important figure in Islam, the son of Fatimah the daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and of the fourth Caliph Ali ibn Abi Talib. Hasan is a member of the Ahl al-Bayt and Ahl al-Kisa...
. Following his elevation, Muawiyah moved the capital of the caliphate to Damascus
Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
. Syria would remain the base of Umayyad power until the end of the dynasty in 750 AD. However, this Dynasty became reborn in Cordoba (Al Andalus, today's Portugal and Spain) in the form of an Emirate and then a Caliphate, lasting until 1031 AD. Muslim rule continued in Iberia for another 500 years in several forms: Taifas, Berber kingdoms, and under the Kingdom of Granada until the 16th century AD.
In the year 712, Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi was a Umayyad general who, at the age of 17, began the conquest of the Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River for the Umayyad Caliphate. He was born in the city of Taif...
, an Umayyad general sailed from the khaleej into Sindh and conquered both the Sindh and the Punjab regions along the Indus river. The conquest of Sindh and Punjab in modern day Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, although costly, were major gains for the Umayyad Caliphate. However, further gains were halted by Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
Kingdoms in North India.
During the later period of its existence and particularly from 1031 AD under the Ta'ifa system of Islamic Emirates (Princedoms) in the southern half of Iberia, the Emirate/Sultanate of Granada maintained its independence largely due to the payment of Tributes to the northern Christian Kingdoms which began to gradually expand south at its expense from 1031.
Muslim rule in Iberia came to an end on January 2, 1492 with the conquest of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada. The last Muslim ruler of Granada, Muhammad XII, better known as Boabdil, surrendered his kingdom to Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile, the Catholic Monarchs, los Reyes Católicos.
Sufyanids

661
Year 661 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 661 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Europe :* Perctarit and Godepert become co-rulers of...
to 684
684
Year 684 was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 684 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.- Asia :* Wu Ze Tian takes power in China.* The Ummayad...
, until his grandson Muawiya II
Muawiya II
Muawiyah II was an Umayyad caliph for about four months after the death of his father Yazīd...
. The reign of Muawiyah I was marked by internal security and external expansion. On the internal front, only one major rebellion is recorded, that of Hujr ibn Adi
Hujr ibn Adi
Hujr ibn Adi was a supporter of Ali ibn Abi talib, he and his companions were killed by Muawiya I for refusing to Curse Ali. Hujr asked that his son be killed before he did so that he will be sure that his son stayed on the love of Ali and will not be affected by his death.-Character and...
in Kufa. Hujr ibn Adi supported the claims of the descendants of Ali to the caliphate, but his movement was easily suppressed by the governor of Iraq, Ziyad ibn Abi Sufyan
Ziyad ibn Abi Sufyan
Ziyad ibn Abeeh where 'Abeeh' means 'his father' since his ancestry is disputed. was a Muslim general and administrator and a member of the clan of the Umayyads.-Biography:...
.
Muawiyah also encouraged peaceful coexistence with the Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
communities of Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, and one of his closest advisers was Sarjun, the father of John of Damascus
John of Damascus
Saint John of Damascus was a Syrian monk and priest...
. At the same time, he waged unceasing war against the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. During his reign, Rhodes
Rhodes
Rhodes is an island in Greece, located in the eastern Aegean Sea. It is the largest of the Dodecanese islands in terms of both land area and population, with a population of 117,007, and also the island group's historical capital. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within...
and Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
were occupied, and several assaults were launched against Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
. Muawiyah also oversaw military expansion in North Africa (the foundation of Kairouan
Kairouan
Kairouan , also known as Kirwan or al-Qayrawan , is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia. Referred to as the Islamic Cultural Capital, it is a UNESCO World Heritage site. The city was founded by the Arabs around 670...
) and in Central Asia (the conquest of Kabul
Kabul
Kabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
, Bukhara
Bukhara
Bukhara , from the Soghdian βuxārak , is the capital of the Bukhara Province of Uzbekistan. The nation's fifth-largest city, it has a population of 263,400 . The region around Bukhara has been inhabited for at least five millennia, and the city has existed for half that time...
, and Samarkand
Samarkand
Although a Persian-speaking region, it was not united politically with Iran most of the times between the disintegration of the Seleucid Empire and the Arab conquest . In the 6th century it was within the domain of the Turkic kingdom of the Göktürks.At the start of the 8th century Samarkand came...
).
Following Muawiyah's death in 680, he was succeeded by his son, Yazid I
Yazid I
Yazīd ibn Mu‘āwiya ibn Abī Sufyān , commonly known as Yazid I, was the second Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate . He ruled for three years from 680 CE until his death in 683 CE. Many Muslims condemn Yazid's rule as contentious and unjust...
. The hereditary accession of Yazid was opposed by a number of prominent Muslims, most notably Abd-Allah ibn al-Zubayr
Abd-Allah ibn al-Zubayr
`Abd Allah al-Zubayr or ibn Zubayr 624 - 692) was an Arab sahabi whose father was Zubayr ibn al-Awwam, and whose mother was Asma bint Abi Bakr, daughter of the first Caliph Abu Bakr. He was the nephew of Aisha, Prophet Muhammad's third wife....
, son of one of the companions of Muhammad, and Husayn ibn Ali
Husayn ibn Ali
Hussein ibn ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib was the son of ‘Alī ibn Abī Ṭālib and Fātimah Zahrā...
, grandson of Muhammad and younger son of Ali
Ali
' |Ramaḍān]], 40 AH; approximately October 23, 598 or 600 or March 17, 599 – January 27, 661).His father's name was Abu Talib. Ali was also the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and ruled over the Islamic Caliphate from 656 to 661, and was the first male convert to Islam...
. The resulting conflict is known as the Second Fitna
Second Fitna
The Second Fitna, or Second Islamic Civil War, was a period of general political and military disorder that afflicted the Islamic empire during the early Umayyad dynasty, following the death of the first Umayyad caliph Muawiyah I...
.
In 680 Ibn al-Zubayr and Husayn fled Medina for Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
. While Ibn al-Zubayr would stay in Mecca until his death, Husayn decided to travel on to Kufa to rally support. However, on the instructions of Yazid, a large Umayyad army (traditions mention 70,000) intercepted and mercilessly slaughtered Husayn, his family members and companions at the Battle of Karbala
Battle of Karbala
The Battle of Karbala took place on Muharram 10, in the year 61 of the Islamic calendar in Karbala, in present day Iraq. On one side of the highly uneven battle were a small group of supporters and relatives of Muhammad's grandson Husain ibn Ali, and on the other was a large military detachment...
. Husayn and his party numbered 128 including women, children and the elderly. 72 were killed including Husayn and his infant son of six months.
Following the death of Husayn, Ibn al-Zubayr, although remaining in Mecca, was associated with two opposition movements, one centered in Medina and the other around Kharijites in Basra
Basra
Basra is the capital of Basra Governorate, in southern Iraq near Kuwait and Iran. It had an estimated population of two million as of 2009...
and Arabia. In 683, Yazid dispatched an army to subdue both. This army suppressed the Medinese opposition at the Battle of al-Harra, and continued on to lay siege to Mecca. At some point during the siege, the Kaaba
Kaaba
The Kaaba is a cuboid-shaped building in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, and is the most sacred site in Islam. The Qur'an states that the Kaaba was constructed by Abraham, or Ibraheem, in Arabic, and his son Ishmael, or Ismaeel, as said in Arabic, after he had settled in Arabia. The building has a mosque...
was badly damaged in a fire. The destruction of the Kaaba became a major cause for censure of the Umayyads in later histories of the period.
Yazid died while the siege was still in progress, and the Umayyad army returned to Damascus, leaving Ibn al-Zubayr in control of Mecca. Yazid was succeeded at first by his son, Muawiya II
Muawiya II
Muawiyah II was an Umayyad caliph for about four months after the death of his father Yazīd...
(683–84), but he seems never to have been recognized as caliph outside of Syria. Two factions developed within Syria: the Confederation of Qays, who supported Ibn al-Zubayr, and the Quda'a, who supported Marwan
Marwan I
Marwan ibn al-Hakam was the fourth Umayyad Caliph, who took over the dynasty after Muawiya II abdicated in 684. Marwan's ascension pointed to a shift in the lineage of the Umayyad dynasty from descendants of Abu Sufyan to those of Hakam, both of whom were grandsons of Umayya...
, a descendant of Umayya via Wa'il ibn Umayyah
Wa'il ibn Umayyah
Abu al'As ibn Umayya was the son of Umayya ibn Abd Shams.As his sons are mentioned:*Uthman ibn Abi al-'As, a companion of Muhammad.*Affan, father of Uthman.*al-Hakam, the father of Marwan I, an Umayyad Caliph.He also had a daughter:...
. The partisans of Marwan triumphed at a battle at Marj Rahit, near Damascus, in 684, and Marwan became caliph shortly thereafter.
First Marwanids
Marwan's first task was to assert his authority against the rival claims of Ibn al-Zubayr, who was at this time recognized as caliph throughout most of the Islamic world. Marwan recaptured EgyptEgypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
for the Umayyads, but died in 685, having reigned for only nine months.
Marwan was succeeded by his son, Abd al-Malik (685–705), who reconsolidated Umayyad control of the caliphate. The early reign of Abd al-Malik was marked by the revolt of Al-Mukhtar
Al-Mukhtar
al-Mukhtār ibn Abī ‘Ubayd Allah al-Thaqafī was an early Islamic revolutionary who led an abortive rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphs after the death of Husayn ibn Ali at the Battle of Karbala.-Life:...
, which was based in Kufa. Al-Mukhtar hoped to elevate Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah
Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah
Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah surnamed Abu'l-Qasim was an early Muslim leader. He was a son of Ali ibn Abi Talib, the first Shi'ite Imam and the fourth Sunni Caliph.-Biography:...
, another son of Ali, to the caliphate, although Ibn al-Hanafiyyah himself may have had no connection to the revolt. The troops of al-Mukhtar engaged in battles both with the Umayyads, in 686, at the river Khazir near Mosul: an Umayyad defeat, and with Ibn al-Zubayr, in 687, at which time the revolt of al-Mukhtar was crushed. In 691, Umayyad troops reconquered Iraq, and in 692 the same army captured Mecca. Ibn al-Zubayr was killed in the attack.
The second major event of the early reign of Abd al-Malik was the construction of the Dome of the Rock
Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock is a shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. The structure has been refurbished many times since its initial completion in 691 CE at the order of Umayyad Caliph Abd al-Malik...
in Jerusalem. Although the chronology remains somewhat uncertain, the building seems to have been completed in 692, which means that it was under construction during the conflict with Ibn al-Zubayr. This had led some historians, both medieval and modern, to suggest that the Dome of the Rock was built to rival the Kaaba, which was under the control of Ibn al-Zubayr, as a destination for pilgrimage.
Abd al-Malik is credited with centralizing the administration of the caliphate, and with establishing Arabic as its official language. He also introduced a uniquely Muslim coinage, marked by its aniconic decoration, which supplanted the Byzantine and Sasanian coins that had previously been in use.
Following Abd al-Malik's death, his son, Al-Walid I (705–15) became caliph. Al-Walid was also active as a builder, sponsoring the construction of Al-Masjid al-Nabawi
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi , often called the Prophet's Mosque, is a mosque situated in the city of Medina. As the final resting place of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, it is considered the second holiest site in Islam by Muslims and is one of the largest mosques in the world...
in Medina and the Great Mosque
Umayyad Mosque
The Umayyad Mosque, also known as the Great Mosque of Damascus or formerly the Basilica of Saint John the Baptist , is located in the old city of Damascus, is one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world...
of Damascus.
A major figure during the reigns of both al-Walid and Abd al-Malik was the Umayyad governor of Iraq, Al-Hajjaj bin Yousef. Many Iraqis remained resistant to Umayyad rule, and al-Hajjaj imported Syrian troops to maintain order, whom he housed in a new garrison town, Wasit. These troops became crucial in the suppression of a revolt led by an Iraqi general, Ibn al-Ash'ath, in the early eighth century.
Al-Walid was succeeded by his brother, Sulayman
Sulayman ibn Abd al-Malik
Sulayman bin Abd al-Malik was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 715 until 717. His father was Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan, and he was a younger brother of the previous caliph, al-Walid I.-Early years:...
(715–17), whose reign was dominated by a protracted siege of Constantinople. The failure of the siege marked the end of serious Arab ambitions against the Byzantine capital. However, the first two decades of the eighth century witnessed the continuing expansion of the caliphate, which pushed into the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
in the west, and into Central Asia and northern India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
in the east.
Sulayman was succeeded by his cousin, Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz (717–20), whose position among the Umayyad caliphs is somewhat unique. He is the only Umayyad ruler to have been recognized by subsequent Islamic tradition as a genuine caliph (khalifa) and not merely as a worldly king (malik).
Umar is honored for his attempt to resolve the fiscal problems attendant upon conversion to Islam. During the Umayyad period, the majority of people living within the caliphate were not Muslim, but Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
, Jewish, Zoroastrian, or otherwise. These religious communities were not forced to convert to Islam, but were subject to a tax (jizyah) which was not imposed upon Muslims. This situation may actually have made widespread conversion to Islam undesirable from the point of view of state revenue, and there are reports that provincial governors actively discouraged such conversions. It is not clear how Umar attempted to resolve this situation, but the sources portray him as having insisted on like treatment of Arab and non-Arab (mawali
Mawali
Mawali or mawālá is a term in Classical Arabic used to address non-Arab Muslims.The term gained prominence in the centuries following the early Arab Muslim conquests in the 7th century, as many non-Arabs such as Persians, Egyptians, and Turks converted to Islam...
) Muslims, and on the removal of obstacles to the conversion of non-Arabs to Islam.
After the death of Umar, another son of Abd al-Malik, Yazid II
Yazid II
Yazid bin Abd al-Malik or Yazid II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 720 until his death in 724.According to the medieval Persian historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, Yazid came to power on the death of Umar II on February 10, 720. His forces engaged in battle the Kharijites with whom Umar...
(720–24) became caliph. Yazid is best known for his "iconoclastic edict", which ordered the destruction of Christian images within the territory of the caliphate. In 720, another major revolt arose in Iraq, this time led by Yazid ibn al-Muhallab
Yazid ibn al-Muhallab
Yazid ibn al-Muhallab was a provincial governor in the time of the Umayyad dynasty.In A.H. 78 Al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf appointed al-Muhallab Khurasan's governor. In A.H. 82 al-Muhallab's son Mughirah died and al-Muhallab sent Yazid to replace him. Soon afterwards al-Muhallab died and al-Hajjaj...
.
Hisham and the limits of military expansion
The final son of Abd al-Malik to become caliph was HishamHisham ibn Abd al-Malik
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik 10th Umayyad caliph who ruled from 723 until his death in 743. When he was born in 691 his mother named him after her father....
(724–43), whose long and eventful reign was above all marked by the curtailment of military expansion.

Resafa
Resafa , known in Roman times as Sergiopolis, was a city located in what is now modern-day Syria. It is an archaeological site situated south-west of the city of Ar Raqqah and the Euphrates.-History:...
in northern Syria, which was closer to the Byzantine border than Damascus, and resumed hostilities against the Byzantines, which had lapsed following the failure of the last siege of Constantinople. The new campaigns resulted in a number of successful raids into Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
, but also in a major defeat (the Battle of Akroinon
Battle of Akroinon
The Battle of Akroinon was fought at Akroinon or Akroinos in Phrygia, on the western edge of the Anatolian plateau, in 740 between an Umayyad Arab army and the Byzantine forces. The Arabs had been conducting regular raids into Anatolia for the past century, and the 740 expedition was the largest...
), and did not lead to any significant territorial expansion.
Hisham's reign furthermore witnessed the end of expansion in the west, following the defeat of the Arab army by the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
at the Battle of Tours
Battle of Tours
The Battle of Tours , also called the Battle of Poitiers and in Battle of the Court of the Martyrs, was fought in an area between the cities of Poitiers and Tours, located in north-central France, near the village of Moussais-la-Bataille, about northeast of Poitiers...
in 732. In 739 a major Berber Revolt
Berber Revolt
The Great Berber Revolt of 739/740-743 AD took place during the reign of the Umayyad Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik and marked the first successful secession from the Arab caliphate...
broke out in North Africa, which was subdued only with difficulty.
Hisham suffered still worse defeats in the east, where his armies attempted to subdue both Tokharistan, with its center at Balkh
Balkh
Balkh , was an ancient city and centre of Zoroastrianism in what is now northern Afghanistan. Today it is a small town in the province of Balkh, about 20 kilometers northwest of the provincial capital, Mazar-e Sharif, and some south of the Amu Darya. It was one of the major cities of Khorasan...
, and Transoxiana
Transoxiana
Transoxiana is the ancient name used for the portion of Central Asia corresponding approximately with modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, southern Kyrgystan and southwest Kazakhstan. Geographically, it is the region between the Amu Darya and Syr Darya rivers...
, with its center at Samarkand
Samarkand
Although a Persian-speaking region, it was not united politically with Iran most of the times between the disintegration of the Seleucid Empire and the Arab conquest . In the 6th century it was within the domain of the Turkic kingdom of the Göktürks.At the start of the 8th century Samarkand came...
. Both areas had already been partially conquered, but remained difficult to govern.
Once again, a particular difficulty concerned the question of the conversion of non-Arabs, especially the Sogdians
Sogdiana
Sogdiana or Sogdia was the ancient civilization of an Iranian people and a province of the Achaemenid Empire, eighteenth in the list on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great . Sogdiana is "listed" as the second of the "good lands and countries" that Ahura Mazda created...
of Transoxiana. Ashras ibn 'Abd Allah al-Sulami, governor of Khorasan
Greater Khorasan
Greater Khorasan or Ancient Khorasan is a historical region of Greater Iran mentioned in sources from Sassanid and Islamic eras which "frequently" had a denotation wider than current three provinces of Khorasan in Iran...
, promised tax relief to those Sogdians who converted to Islam, but went back on his offer when it proved too popular and threatened to reduce tax revenues. In 734, al-Harith ibn Surayj led a revolt on behalf of the Sogdians, capturing Balkh but failing to take Merv
Merv
Merv , formerly Achaemenid Satrapy of Margiana, and later Alexandria and Antiochia in Margiana , was a major oasis-city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, located near today's Mary in Turkmenistan. Several cities have existed on this site, which is significant for the interchange of...
. After this defeat, al-Harith's movement seems to have been dissolved, but the problem of the rights of non-Arab Muslims would continue to plague the Umayyads.
Third Fitna

Al-Walid II
Walid ibn Yazid or Walid II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 743 until 744. He succeeded his uncle, Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik....
(743–44), the son of Yazid II. Al-Walid is reported to have been more interested in earthly pleasures than in religion, a reputation that may be confirmed by the decoration of the so-called "desert palaces" (including Qusayr Amra
Qasr Amra
Qasr Amra , often Quseir Amra or Qusayr Amra, is the best-known of the desert castles located in present-day eastern Jordan. It was built early in the 8th century by the Umayyad caliph Walid I whose dominance of the region was rising at the time...
and Khirbat al-Mafjar) that have been attributed to him. He quickly attracted the enmity of many, both by executing a number of those who had opposed his accession, and by persecuting the Qadariyya
Al-Qadariyya
Qadariyya was a theological movement in early Islam which held that man was endowed by God with free will. Qadariyya resisted the Umayyad Caliphs' claims to be ordained rulers of all Muslims by God himself, and for that reason its proponents, the Qadarites, supported the Abbasid revolution...
.
In 744, Yazid III
Yazid III
Yazid ibn al-Walid ibn 'Abd al-Malik or Yazid III was an Umayyad caliph. He reigned for six months, from April 15 to October 3 or 4, 744; and died in that office....
, a son of al-Walid I, was proclaimed caliph in Damascus, and his army tracked down and killed al-Walid II. Yazid III has received a certain reputation for piety, and may have been sympathetic to the Qadariyya. He died a mere six months into his reign.
Yazid had appointed his brother, Ibrahim, as his successor, but Marwan II
Marwan II
Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan or Marwan II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 744 until 750 when he was killed. He was the last Umayyad ruler to rule from Damascus.In A.H. 114 Caliph Hisham appointed Marwan governor of Armenia and Azerbaijan. In A.H...
(744–50), the grandson of Marwan I, led an army from the northern frontier and entered Damascus in December of 744, where he was proclaimed caliph. Marwan immediately moved the capital north to Harran
Harran
Harran was a major ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia whose site is near the modern village of Altınbaşak, Turkey, 24 miles southeast of Şanlıurfa...
, in present-day Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
. A rebellion soon broke out in Syria, perhaps due to resentment over the relocation of the capital, and in 746 Marwan razed the walls of Homs
Homs
Homs , previously known as Emesa , is a city in western Syria and the capital of the Homs Governorate. It is above sea level and is located north of Damascus...
and Damascus in retaliation.
Marwan also faced significant opposition from Kharijites in Iraq and Iran, who put forth first Dahhak ibn Qays
Al-Dahhak ibn Qays al-Shaybani
Al-Dahhak ibn Qays al-Shaybani was the leader of a widespread but unsuccessful Kharijite rebellion in Iraq against the Umayyad Caliph Marwan II from 745 until his death in battle in 746....
and then Abu Dulaf as rival caliphs. In 747, Marwan managed to reestablish control of Iraq, but by this time a more serious threat had arisen in Khorasan
Greater Khorasan
Greater Khorasan or Ancient Khorasan is a historical region of Greater Iran mentioned in sources from Sassanid and Islamic eras which "frequently" had a denotation wider than current three provinces of Khorasan in Iran...
.
Insurrection

Kaysanites Shia
The Kaysanites were a once dominant Shi'a Ghulat sect that formed from the followers of Al-Mukhtar. They believed in the Imamate of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah. Following the death of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyyah the sect split up into numerous sub-sects, each with their own Imam and unique beliefs...
), led by the Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
family, overthrew the Umayyad caliphate. The Abbasids were members of the Hashim
Banu Hashim
Banū Hāshim was a clan in the Quraysh tribe. Muhammad, was a member of this clan; his great-grandfather was Hashim, for whom the clan is named. Members of this clan are referred to by the Anglicised version of their name as Hashemites, or Huseini or Hasani...
clan, rivals of the Umayyads, but the word "Hashimiyya" seems to refer specifically to Abu Hashim, a grandson of Ali and son of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya. According to certain traditions, Abu Hashim died in 717 in Humeima in the house of Muhammad ibn Ali, the head of the Abbasid family, and before dying named Muhammad ibn Ali as his successor. This tradition allowed the Abbasids to rally the supporters of the failed revolt of Mukhtar
Mukhtar
Mukhtar meaning "chosen" in Arabic, refers to the head of a village or mahalle in many Arab countries as well as in Turkey and Cyprus. The name refers to the fact that mukhtars are usually selected by some consensual or participatory method, often involving an election. Mukhtar is also a common...
, who had represented themselves as the supporters of Muhammad ibn al-Hanafiyya.
Beginning around 719, Hashimiyya missions began to seek adherents in Khurasan. Their campaign was framed as one of proselytism (dawah
Dawah
Da‘wah or Dawah usually denotes the preaching of Islam. Da‘wah literally means "issuing a summons" or "making an invitation", being the active participle of a verb meaning variously "to summon" or "to invite"...
). They sought support for a "member of the family" of Muhammad, without making explicit mention of the Abbasids. These missions met with success both among Arabs and non-Arabs (mawali
Mawali
Mawali or mawālá is a term in Classical Arabic used to address non-Arab Muslims.The term gained prominence in the centuries following the early Arab Muslim conquests in the 7th century, as many non-Arabs such as Persians, Egyptians, and Turks converted to Islam...
), although the latter may have played a particularly important role in the growth of the movement.

Abu Muslim
- External links :* *...
assumed leadership of the Hashimiyya in Khurasan. In 747, he successfully initiated an open revolt against Umayyad rule, which was carried out under the sign of the black flag. He soon established control of Khurasan, expelling its Umayyad governor, Nasr ibn Sayyar
Nasr ibn Sayyar
Nasr ibn Sayyar was an Arab general and the last Umayyad governor of Khurasan in 738–748. An experienced commander in the wars against the Turgesh, as governor he introduced tax reforms in his province and stabilized Umayyad control beyond the Oxus...
, and dispatched an army westwards. Kufa fell to the Hashimiyya in 749, and in November of the same year Abu al-Abbas
As-Saffah
Abu al-`Abbās `Abdu'llāh ibn Muhammad as-Saffāh, or Abul `Abbas al-Saffah , was the first Abbasid caliph .As-Saffah was the head of one branch of the Banu Hashim, who traced their lineage to Hashim, a great-grandfather of...
was recognized as the new caliph in the mosque at Kufa.

Battle of the Zab
The Battle of the Zab took place on the banks of the Great Zab river in what is now Iraq on January 25, 750. It spelled the end of the Umayyad Caliphate and the rise of the Abbasids, a dynasty that would last until the 13th century.-Background:A serious rebellion had broken out in 747 against...
, and the Umayyads were defeated. Damascus fell to the Abbasids in April, and in August Marwan was killed in Egypt.
The victors desecrated the tombs of the Umayyads in Syria, sparing only that of Umar II, and most of the remaining members of the Umayyad family were tracked down and killed. One grandson of Hisham, Abd ar-Rahman I
Abd ar-Rahman I
Abd al-Rahman I, or, his full name by patronymic record, Abd al-Rahman ibn Mu'awiya ibn Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan was the founder of the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba , a Muslim dynasty that ruled the greater part of Iberia for nearly three centuries...
, survived and established a kingdom in Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
(Moorish
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
Iberia
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
), proclaiming his family to be the Umayyad Caliphate revived.
Previté-Orton argues that the reasons for the decline of the Umayyads was the rapid expansion of Islam. During Umayyad period, mass conversions brought Persians, Berbers, Copts, and Aramaics to Islam. These mawalis (clients) were often better educated and more civilised than their Arab masters. The new converts, on the basis of equality of all Muslims, transformed the political landscape. Previté-Orton also argues that the feud between Syria and Iraq, further weakened the empire.
Central diwans
To assist the Caliph in administration there were six Boards at the Centre: Diwan al-Kharaj (the Board of Revenue), Diwan al-Rasa'il (the Board of Correspondence), Diwan al-Khatam (the Board of Signet), Diwan al-Barid (the Board of Posts), Diwan al-Qudat (the Board of Justice) and Diwan al-Jund (the Military Board)Diwan al-Kharaj
The Central Board of Revenue administered the entire finance of the empire, it also imposed and collected taxes and disbursed revenue.Diwan al-Rasa'il
A regular Board of Correspondence was established under the Umayyads. It issued state missives and circulars to the Central and Provincial Officers. It co-ordinated the work of all Boards and dealt with all correspondence as the chief secretariat.Diwan al-Khatam
In order to check forgery Diwan al-Khatam (Bureau of Registry) a kind of state chancellery was instituted by Mu'awiyah. It used to make and preserve a copy of each official document before sealing and despatching the original to its destination. Thus in the course of time a state archive developed in Damascus by the Umayyads under Abd al-Malik. This department survived till the middle of the Abbasid period.Diwan al-Barid
Mu'awiyah introduced postal service. Abd al-Malik extended it throughout his empire and Walid made full use of it. The Umayyad Caliph Abd al-Malik developed a regular postal service. Umar bin Abdul-Aziz developed it further by building caravanserais at stages along the Khurasan highway. Relays of horses were used for the conveyance of dispatches between the caliph and his agents and officials posted in the provinces. The main highways were divided into stages of 12 miles (19.3 km) each and each stage had horses, donkeys or camels ready to carry the post. Primarily the service met the needs of Government officials but travellers and their important dispatches were also benefitted by the system. For swift transport of troops also the postal carriages were used. They were able to carry fifty to a hundred men at a time. Under it Governor Yusuf bin Umar, the postal department of Iraq cost 4,000,000 dirhams a year.Diwan al-Qudat
In the early period of Islam justice was administered by Muhammad and the orthodox Caliphs in person. After the expansion of the Islamic State Umar al-Faruq had to separate judiciary from the general administration and appointed the first qadi in Egypt as early as 23H/643AD. After 661AD a series of judges succeeded one after another in Egypt under the Umayyad Caliphs, Hisham and Walid II.Diwan al-Jund
The Diwan of Umar(rali) assigning annuities to all Arabs and to the Muslim soldiers of other races underwent a change in the hands of the Umayyads. The Umayyads meddled with the register and the recipients regarded pensions as the subsistence allowance even without being in active service. Hisham reformed it and paid only to those who participated in battle.On the pattern of the Byzantine system the umayyads reformed their army organization in general and divided it into five corps: the centre, two wings, vanguards and rearguards while on march or in a battle field following the same formation. Marwan II (740–50) abandoned the old division and introduced Kurdus (cohort) a small compact body.
The Umayyad troops were divided into three divisions: infantry, cavalry and artillery. Arab troops were dressed and armed in Greek fashion. The Umayyad cavalry used plain and round saddles. The artillery used arradah (ballista), manjaniq (the mangonel) and dabbabah or kabsh (the battering ram). The heavy engines, siege machines and baggage were carried on camels behind the army.
Social Organization
The Umayyad Caliphate exhibited four main social classes:1.Muslim Arabs
2.Muslim non-Arabs (clients of the Muslim Arabs)
3.Non-Muslim free persons (Christians, Jews, Zoroastrians)
4.Slaves
The Muslim Arabs were at the top of the society, and saw it as their duty to rule over the conquered areas. Despite the fact that Islam teaches the equality of all Muslims, the Arab Muslims held themselves in higher esteem than Muslim non-Arabs and generally did not mix with other Muslims.
The inequality of Muslims in the empire led to social unrest. As Islam spread, more and more of the Muslim population became non-Arabs. This caused tension as the new converts were not given the same rights as Muslim Arabs. Also, as conversions increased, tax revenues off non-Muslims decreased to dangerous lows. These issues continued to grow until they helped cause the Abbasid Revolt in the 740s.
Historical significance
The Umayyad caliphate was marked both by territorial expansion and by the administrative and cultural problems that such expansion created. Despite some notable exceptions, the Umayyads tended to favor the rights of the old Arab families, and in particular their own, over those of newly converted Muslims (mawali). Therefore they held to a less universalist conception of Islam than did many of their rivals. As G.R. Hawting has written, "Islam was in fact regarded as the property of the conquering aristocracy."According to one common view, the Umayyads transformed the caliphate from a religious institution (during the rashidun
Rashidun
The Rightly Guided Caliphs or The Righteous Caliphs is a term used in Sunni Islam to refer to the first four Caliphs who established the Rashidun Caliphate. The concept of "Rightly Guided Caliphs" originated with the Abbasid Dynasty...
) to a dynastic one. However, the Umayyad caliphs do seem to have understood themselves as the representatives of God on earth, and to have been responsible for the "definition and elaboration of God's ordinances, or in other words the definition or elaboration of Islamic law."
During the period of the Umayyads, Arabic became the administrative language. State documents and currency were issued in the language. Mass conversions brought a large influx of Muslims to the caliphate
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
. The Umayyads also constructed famous buildings such as the Dome of the Rock
Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock is a shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem. The structure has been refurbished many times since its initial completion in 691 CE at the order of Umayyad Caliph Abd al-Malik...
at Jerusalem, and the Umayyad Mosque
Umayyad Mosque
The Umayyad Mosque, also known as the Great Mosque of Damascus or formerly the Basilica of Saint John the Baptist , is located in the old city of Damascus, is one of the largest and oldest mosques in the world...
at Damascus
Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
.
The Umayyads have met with a largely negative reception from later Islamic historians, who have accused them of promoting a kingship (mulk, a term with connotations of tyranny) instead of a true caliphate (khilafa). In this respect it is notable that the Umayyad caliphs referred to themselves, not as khalifat rasul Allah ("successor of the messenger of God", the title preferred by the tradition) but rather as khalifat Allah ("deputy of God"). The distinction seems to indicate that the Umayyads "regarded themselves as God's representatives at the head of the community and saw no need to share their religious power with, or delegate it to, the emergent class of religious scholars."
In fact, it was precisely this class of scholars, based largely in Iraq, that was responsible for collecting and recording the traditions that form the primary source material for the history of the Umayyad period. In reconstructing this history
Historiography of early Islam
The historiography of early Islam refers to the study of the early origins of Islam based on a critical analysis, evaluation, and examination of authentic primary source materials and the organization of these sources into a narative timeline....
, therefore, it is necessary to rely mainly on sources, such as the histories of Tabari
Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari
Abu Ja'far Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari was a prominent and influential Sunni scholar and exegete of the Qur'an from Persia...
and Baladhuri
Ahmad Ibn Yahya al-Baladhuri
Ahmad Ibn Yahya al-Baladhuri Arabic was a 9th century Persian historian. One of the eminent middle-eastern historians of his age , he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-Mutawakkil. He traveled in Syria and Iraq, compiling information for his...
, that were written in the Abbasid court at Baghdad.
Modern Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism is a nationalist ideology celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language and literature of the Arabs, calling for rejuvenation and political union in the Arab world...
regards the period of the Umayyads as part of the Arab Golden Age which it sought to emulate and restore. This is particularly true of Syrian nationalists and the present-day state of Syria, centered like that of the Umayyads on Damascus. White, one of the four Pan-Arab colors
Pan-Arab colors
The Pan-Arab colors are black, white, green, and red. They were first combined in the flag of the Arab Revolt in 1916. They are used currently in the flags of Jordan, Kuwait, Palestinian Authority, Sahrawi Republic, Sudan, Libya and the United Arab Emirates. A sub-set of the Pan-Arab colors are...
which appear in various combinations on the flags of most Arab countries, is considered as representing the Umayyads.
Sunni opinions
Sunni opinions of the Umayyad dynasty after Muawiyah are typically dim, viewing many of the rulers as sinners and the cause of great tribulation in the UmmahUmmah
Ummah is an Arabic word meaning "community" or "nation." It is commonly used to mean either the collective nation of states, or the whole Arab world...
. For example, in the section concerning Quran 17:60 in the exegesis
Tafsir
Tafseer is the Arabic word for exegesis or commentary, usually of the Qur'an. Ta'wīl is a subset of tafsir and refers to esoteric or mystical interpretation. An author of tafsir is a mufassir .- Etymology :...
by al-Suyuti entitled Dur al-Manthur
Dur al-Manthur
Al-Durr Al-Manthur Fi Tafsir Bil-Ma'thur , The Scattered Pearls: Intertextual Exegesis, is an authoritatve Sunni tafsir , written by the prominent Imam Jalal al-Din al- Suyuti d. 911H...
, the author writes that there exist traditions which describe the Umayyads as "the cursed tree". There are some exceptions to this – Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz is commonly praised as one of the greatest Muslim rulers after the four Rightly Guided Caliphs.
Shi'a opinions
The negative view of the Umayyads of Shias is briefly expressed in the Shi'a book "Sulh al-Hasan". According to some sources AliAli
' |Ramaḍān]], 40 AH; approximately October 23, 598 or 600 or March 17, 599 – January 27, 661).His father's name was Abu Talib. Ali was also the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and ruled over the Islamic Caliphate from 656 to 661, and was the first male convert to Islam...
described them as the worst Fitna.
Bahá'í standpoint
In Some Answered Questions
Some Answered Questions
Some Answered Questions was first published in 1908. It contains questions asked to `Abdu'l-Bahá, son of the founder of the Bahá'í Faith, by Laura Clifford Barney, during several of her visits to Haifa between 1904 and 1906, and `Abdu'l-Bahá's answers to these questions.Prominent among the topics...
, `Abdu'l-Bahá
`Abdu'l-Bahá
‘Abdu’l-Bahá , born ‘Abbás Effendí, was the eldest son of Bahá'u'lláh, the founder of the Bahá'í Faith. In 1892, `Abdu'l-Bahá was appointed in his father's will to be his successor and head of the Bahá'í Faith. `Abdu'l-Bahá was born in Tehran to an aristocratic family of the realm...
asserts that the Umayyad dynasty was the "great red dragon, having seven heads and ten horns, and seven crowns upon his heads" and that the Umayyads "rose against the religion of Prophet Muhammad and against the reality of Ali".
The seven heads of the dragon is symbolic of the seven provinces of the lands dominated by the Umayyads; Damascus, Persia, Arabia, Egypt, Africa, Andalusia, and Transoxania. The ten horns represent the ten names of the leaders of the Umayyad dynasty; Abu Sufyan, Muawiya, Yazid, Marwan, Abd al-Malik, Walid, Sulayman, Umar, Hisham, and Ibrahim. Some names were re-used as in the case of Yazid II and Yazid III were not counted for this interpretation.
Leaders
Political
| Ruler | Reign |
|---|---|
| Caliphs of Damascus | |
| Muawiyah I Muawiyah I Muawiyah I was the first Caliph of the Umayyad Dynasty. After the conquest of Mecca by the Muslims, Muawiyah's family converted to Islam. Muawiyah is brother-in-law to Muhammad who married his sister Ramlah bint Abi-Sufyan in 1AH... ibn Abi Sufyan |
661 – 680 |
| Yazid I Yazid I Yazīd ibn Mu‘āwiya ibn Abī Sufyān , commonly known as Yazid I, was the second Caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate . He ruled for three years from 680 CE until his death in 683 CE. Many Muslims condemn Yazid's rule as contentious and unjust... ibn Muawiyah |
680 – 683 |
| Muawiyah II ibn Yazid | 683 – 684 |
| Marwan I Marwan I Marwan ibn al-Hakam was the fourth Umayyad Caliph, who took over the dynasty after Muawiya II abdicated in 684. Marwan's ascension pointed to a shift in the lineage of the Umayyad dynasty from descendants of Abu Sufyan to those of Hakam, both of whom were grandsons of Umayya... ibn al-Ḥakam |
684 – 685 |
| Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan | 685 – 705 |
| al-Walid I ibn Abd al-Malik | 705 – 715 |
| Suleiman ibn Abd al-Malik | 715 – 718 |
| Umar ibn Abd al-Aziz | 717 – 720 |
| Yazid II Yazid II Yazid bin Abd al-Malik or Yazid II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 720 until his death in 724.According to the medieval Persian historian Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari, Yazid came to power on the death of Umar II on February 10, 720. His forces engaged in battle the Kharijites with whom Umar... ibn Abd al-Malik |
720 – 724 |
| Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik 10th Umayyad caliph who ruled from 723 until his death in 743. When he was born in 691 his mother named him after her father.... |
724 – 743 |
| al-Walid II Al-Walid II Walid ibn Yazid or Walid II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 743 until 744. He succeeded his uncle, Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik.... ibn Yazid II |
743 – 744 |
| Yazid III Yazid III Yazid ibn al-Walid ibn 'Abd al-Malik or Yazid III was an Umayyad caliph. He reigned for six months, from April 15 to October 3 or 4, 744; and died in that office.... ibn al-Walid |
744 |
| Ibrahim ibn al-Walid | 744 |
| Marwan II Marwan II Marwan ibn Muhammad ibn Marwan or Marwan II was an Umayyad caliph who ruled from 744 until 750 when he was killed. He was the last Umayyad ruler to rule from Damascus.In A.H. 114 Caliph Hisham appointed Marwan governor of Armenia and Azerbaijan. In A.H... ibn Muhammad (ruled from Harran Harran Harran was a major ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia whose site is near the modern village of Altınbaşak, Turkey, 24 miles southeast of Şanlıurfa... in the Jazira Al-Jazira, Mesopotamia Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq and northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey which is known by the traditional Arabic name of Al-Jazira , variously transliterated into Roman script as Djazirah, Djezirah and Jazirah... ) |
744 – 750 |
| Emirs of Cordoba | |
| Abd ar-Rahman I Abd ar-Rahman I Abd al-Rahman I, or, his full name by patronymic record, Abd al-Rahman ibn Mu'awiya ibn Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ibn Marwan was the founder of the Umayyad Emirate of Córdoba , a Muslim dynasty that ruled the greater part of Iberia for nearly three centuries... |
756 – 788 |
| Hisham I Hisham I Hisham I or Hisham Al-Reda was the second Umayyad Emir of Cordoba, ruling from 788 to 796 in the Al-Andalus .Hisham was born in Cordoba. He was the 1st son of Abd ar-Rahman I and his wife, Halul and the younger half brother of Suleiman. He built many mosques and completed the Mezquita. In 792 he... |
788 – 796 |
| al-Hakam I Al-Hakam I Al-Hakam Ibn Hisham Ibn Abd-ar-Rahman I was Umayyad Emir of Cordoba from 796 until 822 in the Al-Andalus .Al-Hakam was the second son of his father, his older brother having died at an early age. When he came to power, he was challenged by his uncles Sulayman and Abdallah, sons of Abd ar-Rahman I... |
796 – 822 |
| Abd ar-Rahman II Abd ar-Rahman II Abd ar-Rahman II was Umayyad Emir of Córdoba in the Al-Andalus from 822 until his death.He was born in Toledo, the son of Emir Al-Hakam I... |
822 – 852 |
| Muhammad I of Córdoba Muhammad I of Córdoba Muhammad I was the Umayyad emir of Córdoba from 852 to 886 in the Al-Andalus .-Biography:Muhammad was born in Córdoba... |
852 – 886 |
| Al-Mundhir Al-Mundhir Al-Mundhir was Emir of Córdoba from 886 to 888. He was a member of the Umayyad dynasty of Al-Andalus , the son of Muhamad bin Abd al-Rahman.-Biography:... |
886 – 888 |
| Abdallah ibn Muhammad | 888 – 912 |
| Abd ar-Rahman III | 912 – 929 |
| Caliphs of Cordoba | |
| Abd ar-Rahman III, as caliph | 929 – 961 |
| Al-Hakam II Al-Hakam II Al-Hakam II was the second Caliph of Cordoba, in Al-Andalus , and son of Abd-ar-rahman III . He ruled from 961 to 976.... |
961 – 976 |
| Hisham II Hisham II Hisham II was the third Caliph of Cordoba, of the Umayyad dynasty. He ruled 976–1009, and 1010–1013 in the Al-Andalus .... |
976 – 1008 |
| Mohammed II | 1008 – 1009 |
| Suleiman | 1009 – 1010 |
| Hisham II Hisham II Hisham II was the third Caliph of Cordoba, of the Umayyad dynasty. He ruled 976–1009, and 1010–1013 in the Al-Andalus .... , restored |
1010 – 1012 |
| Suleiman, restored | 1012 – 1017 |
| Abd ar-Rahman IV Abd ar-Rahman IV Abd ar-Rahman IV Mortada was the Caliph of Cordoba in the Umayyad dynasty of the Al-Andalus , succeeding Suleiman II, in 1018. That same year, he was murdered at Cadiz while fleeing from a battle in which he had been deserted by the very supporters which had brought him into power... |
1021 – 1022 |
| Abd ar-Rahman V Abd ar-Rahman V Abd ar-Rahman V was an Umayyad Caliph of Córdoba.In the agony of the Umayyad dynasty in the Al-Andalus , two princes of the house were proclaimed Caliph of Cordoba for a very short time, Abd-ar-Rahman IV Mortada , and Abd-ar-Rahman V Mostadir . Both were the mere puppets of factions, who deserted... |
1022 – 1023 |
| Muhammad III | 1023 – 1024 |
| Hisham III Hisham III Hisham III was the last Umayyad ruler in the Al-Andalus , and the last person to hold the title Caliph of Cordoba.... |
1027 – 1031 |
Religious Umayyad
- Marwan ibn al-HakamMarwan IMarwan ibn al-Hakam was the fourth Umayyad Caliph, who took over the dynasty after Muawiya II abdicated in 684. Marwan's ascension pointed to a shift in the lineage of the Umayyad dynasty from descendants of Abu Sufyan to those of Hakam, both of whom were grandsons of Umayya...
- Muawiyah ibn Abi SufyanMuawiyah IMuawiyah I was the first Caliph of the Umayyad Dynasty. After the conquest of Mecca by the Muslims, Muawiyah's family converted to Islam. Muawiyah is brother-in-law to Muhammad who married his sister Ramlah bint Abi-Sufyan in 1AH...
- Abu Sufiyan ibn Harb
See also
- Timeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsulaTimeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsulaThis is a timeline of notable events in the Muslim presence in Iberia, which started with the Umayyad conquest in the 8th century.-Conquest :...
- al-AndalusAl-AndalusAl-Andalus was the Arabic name given to a nation and territorial region also commonly referred to as Moorish Iberia. The name describes parts of the Iberian Peninsula and Septimania governed by Muslims , at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries...
- Umayya ibn Abd ShamsUmayya ibn Abd ShamsThe clan of Banu Umayyad as well as the dynasty that ruled the Umayyad Caliphate are named after Umayya ibn Abd Shams.Umayya was the son of Abd Shams ibn Abd Manaf, and the father of Harb ibn Umayya and Abu al-'As....
- Caliphate of CórdobaCaliphate of CórdobaThe Caliphate of Córdoba ruled the Iberian peninsula and part of North Africa, from the city of Córdoba, from 929 to 1031. This period was characterized by remarkable success in trade and culture; many of the masterpieces of Islamic Iberia were constructed in this period, including the famous...
- History of Islam
- CaliphateCaliphateThe term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
- List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
Further reading
- A. Bewley, Mu'awiya, Restorer of the Muslim Faith (London, 2002)
- P. Crone, Slaves on horses (Cambridge, 1980).
- P. Crone and M.A. Cook, Hagarism (Cambridge, 1977).
- F.M. Donner, The early Islamic conquests (Princeton, 1981).
- G.R. Hawting, The first dynasty of Islam: the Umayyad caliphate, AD 661–750 Rutledge Eds. (London, 2000]
- H. Kennedy, The Prophet and the age of the caliphates: the Islamic Near East from the sixth to the eleventh century (London, 1986).
- Previté-Orton, C. W (1971). The Shorter Cambridge Medieval History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- J. Wellhausen, The Arab Kingdom and its fall (London, 2000).

