
Uncanny Valley
Encyclopedia

Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
and 3D
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data that is stored in the computer for the purposes of performing calculations and rendering 2D images...
computer animation
Computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for generating animated images by using computer graphics. The more general term computer generated imagery encompasses both static scenes and dynamic images, while computer animation only refers to moving images....
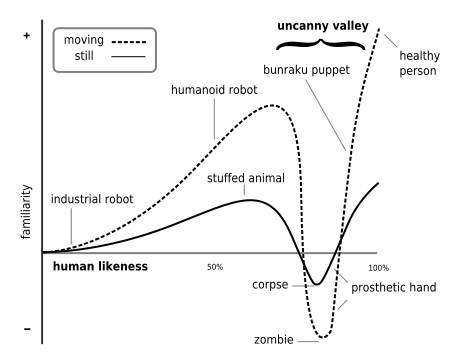
, which holds that when human replicas look and act almost, but not perfectly, like actual human beings, it causes a response of revulsion among human observers. The "valley" in question is a dip in a proposed graph of the positivity of human reaction as a function of a robot's human likeness.
The term was coined by the robotics professor Masahiro Mori
Masahiro Mori
is a Japanese roboticist noted for his pioneering work on the emotional response of humans to non-human entities, as well as for his views on religion and robots. The ASIMO robot was designed by one of Masahiro's students....
as Bukimi no Tani Genshō (不気味の谷現象) in 1970, and has been linked to Ernst Jentsch
Ernst Jentsch
Ernst Jentsch was born in 1867. He is a German psychiatrist and the author of On the Psychology of the Uncanny . "Reference has often been made to Jentsch’s essay on the uncanny, in the vast secondary literature of psychoanalysis after Freud, as if its content were already known, familiar and thus...
's concept of "the uncanny
The Uncanny
The Uncanny is a Freudian concept of an instance where something can be familiar, yet foreign at the same time, resulting in a feeling of it being uncomfortably strange or uncomfortably familiar...
" identified in a 1906 essay, "On the Psychology of the Uncanny." Jentsch's conception was elaborated by Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud , born Sigismund Schlomo Freud , was an Austrian neurologist who founded the discipline of psychoanalysis...
in a 1919 essay entitled "The Uncanny" ("Das Unheimliche").
Hypothesis
Mori's original hypothesis states that as the appearance of a robot is made more human, a human observer's emotional response to the robot will become increasingly positive and empathicEmpathy
Empathy is the capacity to recognize and, to some extent, share feelings that are being experienced by another sapient or semi-sapient being. Someone may need to have a certain amount of empathy before they are able to feel compassion. The English word was coined in 1909 by E.B...
, until a point is reached beyond which the response quickly becomes that of strong revulsion. However, as the robot's appearance continues to become less distinguishable from that of a human being, the emotional response becomes positive once more and approaches human-to-human empathy levels.
This area of repulsive response aroused by a robot with appearance and motion between a "barely human" and "fully human" entity is called the uncanny valley. The name captures the idea that an almost human-looking robot will seem overly "strange" to a human being and thus will fail to evoke the empathic response required for productive human-robot interaction.
Theoretical basis
- Mate selection. Automatic, stimulus-driven appraisals of uncanny stimuli elicit aversion by activating an evolved cognitive mechanism for the avoidance of selecting mates with low fertility, poor hormonal health, or ineffective immune systems based on visible features of the face and body that are predictive of those traits.
- Mortality salienceMortality salience-Potential to cause worldview defense:Mortality salience has the potential to cause worldview defense, a psychological mechanism which strengthens people's connection with their in-group as a defense mechanism. This can lead to feelings of nationalism and racial bigotry being intensified...
. Viewing an "uncanny" robot elicits an innate fear of death and culturally-supported defenses for coping with death’s inevitability.... [P]artially disassembled androids... play on subconscious fears of reduction, replacement, and annihilation: (1) A mechanism with a human facade and a mechanical interior plays on our subconscious fear that we are all just soulless machines. (2) Androids in various states of mutilation, decapitation, or disassembly are reminiscent of a battlefield after a conflict and, as such, serve as a reminder of our mortality. (3) Since most androids are copies of actual people, they are doppelgängerDoppelgängerIn fiction and folklore, a doppelgänger is a paranormal double of a living person, typically representing evil or misfortune...
s and may elicit a fear of being replaced, on the job, in a relationship, and so on. (4) The jerkiness of an android’s movements could be unsettling because it elicits a fear of losing bodily control." - PathogenPathogenA pathogen gignomai "I give birth to") or infectious agent — colloquially, a germ — is a microbe or microorganism such as a virus, bacterium, prion, or fungus that causes disease in its animal or plant host...
avoidance. Uncanny stimuli may activate a cognitive mechanism that originally evolved to motivate the avoidance of potential sources of pathogens by eliciting a disgust response. “The more human an organism looks, the stronger the aversion to its defects, because (1) defects indicate disease, (2) more human-looking organisms are more closely related to human beings genetically, and (3) the probability of contracting disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and other parasites increases with genetic similarity.” Thus, the visual anomalies of android robots and animated human characters have the same effect as those of corpses and visibly diseased individuals: the elicitation of alarm and revulsion. - Sorites paradoxSorites paradoxThe sorites paradox is a paradox that arises from vague predicates. The paradox of the heap is an example of this paradox which arises when one considers a heap of sand, from which grains are individually removed...
es. Stimuli with human and nonhuman traits undermine our sense of human identity by linking qualitatively different categories, human and nonhuman, by a quantitative metric, degree of human likeness. - Violation of human norms. The uncanny valley may "be symptomatic of entities that elicit a model of a human other but do not measure up to it." If an entity looks sufficiently nonhuman, its human characteristics will be noticeable, generating empathy. However, if the entity looks almost human, it will elicit our model of a human other and its detailed normative expectations. The nonhuman characteristics will be noticeable, giving the human viewer a sense of strangeness. In other words, a robot stuck inside the uncanny valley is no longer being judged by the standards of a robot doing a passable job at pretending to be human, but is instead being judged by the standards of a human doing a terrible job at acting like a normal person. This has been linked to perceptual uncertainty and the theory of predictive coding .
- Religious constructions of human identity. The existence of artificial but humanlike entities is viewed by some as a threat to the concept of human identity, as constructed in the West and the Middle East. This is particularly the case with the Abrahamic religions (Christianity, Islam, and Judaism), which emphasize human uniqueness. An example can be found in the theoretical framework of psychiatrist Irvin Yalom. Yalom explains that humans construct psychological defenses in order to avoid existential anxiety stemming from death. One of these defenses is "specialness", the irrational belief that aging and death as central premises of life apply to all others but oneself. The experience of the very humanlike "living" robot can be so rich and compelling that it challenges humans' notions of "specialness" and existential defenses, eliciting existential anxiety.
Research
Research into the evolutionary mechanism behind the aversion associated with the uncanny valley was examined with one recent study. A group of five monkeys were shown three images: two different 3D monkey faces (realistic, unrealistic), and a real photo of a monkey's face. The monkeys' eye-gaze was used as a proxy for preference or aversion. Since the realistic 3D monkey face was looked at less than either the real photo, or the unrealistic 3D monkey face, this was interpreted as an indication that the monkey participants found the realistic 3D face aversive, or otherwise preferred the other two images. As one would expect with the uncanny valley, more realism can lead to less positive reactions, and this study demonstrated that neither human-specific cognitive processes, nor human culture explain the uncanny valley. In other words, this aversive reaction to realism can be said to be evolutionary in origin.Researchers at University of California San Diego and Calit2 are testing human brain activations related to the uncanny valley. . In an fMRI study, a group of cognitive scientists and roboticists found the biggest differences in brain responses for uncanny robots in parietal cortex, on both sides of the brain, specifically in the areas that connect the part of the brain’s visual cortex that processes bodily movements with the section of the motor cortex thought to contain mirror neurons (neurons also known as “monkey-see, monkey-do neurons”). The researchers say they saw, in essence, evidence of mismatch or perceptual conflict. The brain “lit up” when the human-like appearance of the android and its robotic motion “didn’t compute.” Saygin, a professor from UCSD said “The brain doesn’t seem tuned to care about either biological appearance or biological motion per se,” said Saygin, an assistant professor of cognitive science at UC San Diego and alumna of the same department. “What it seems to be doing is looking for its expectations to be met – for appearance and motion to be congruent.”
Viewer perception of facial expression and speech and the Uncanny Valley in realistic, humanlike characters intended for 3D immersive environments and video games is also being investigated by Tinwell et al., 2011. Building on the body of work already undertaken in android science, this research intends to build a conceptual framework of the Uncanny Valley using 3D characters generated in a real-time gaming engine analysing how cross modal factors of facial expression, and speech may exaggerate the uncanny.
Design principles
A number of design principles have been proposed for avoiding the uncanny valley:- Design elements should match in human realism. A robot may look uncanny when human and nonhuman elements are mixed. For example, both a robot with a human voice or a human being with a synthetic voice have been found to be eerier than a robot with a synthetic voice or a human being with a human voice. For a robot to give a more positive impression, its degree of human realism in appearance should also match its degree of human realism in behavior. If an animated character looks more human than its movement, this gives a negative impression. Human neuroimaging studies also indicate matching appearance and motion kinematics are important.
- Reducing conflict and uncertainty by matching appearance, behaviour and ability In terms of performance, if a robot looks too appliance-like, people will expect little from it; if it looks too human, people will expect too much from it. A highly humanlike appearance leads to an expectation that certain behaviors will be present, such as humanlike motion dynamics. This likely operates at a sub-conscious level and may have a biological basis. Neuroscientists have noted "when the brain's expectations are not met, the brain.. generates a "prediction error"... As human-like artificial agents become more commonplace, perhaps our perceptual systems will be re-tuned to accommodate these new social partners. Or perhaps, we will decide it is not a good idea to make [robots] so clearly in our image after all."
- Human facial proportions and photorealistic texture should only be used together. A photorealistic human texture demands human facial proportions, or the computer generated character can fall into the uncanny valley. Abnormal facial proportions, including those typically used by artists to enhance attractiveness (e.g., larger eyes), can look eerie with a photorealistic human texture. Avoiding a photorealistic texture can permit more leeway.
Criticism
A number of criticisms have been raised concerning whether the uncanny valley exists as a unified phenomenon amenable to scientific scrutiny:- Good design can lift human-looking entities out of the valley. David Hanson has criticized Mori's hypothesis that entities approaching human appearance will necessarily be evaluated negatively. He has shown that the uncanny valley that Karl MacDorman and Hiroshi Ishiguro generated – by having participants rate photographs that morphed from humanoid robots to android robots to human beings – could be flattened out by adding neotenousNeotenyNeoteny , also called juvenilization , is one of the two ways by which paedomorphism can arise. Paedomorphism is the retention by adults of traits previously seen only in juveniles, and is a subject studied in the field of developmental biology. In neoteny, the physiological development of an...
, cartoonish features to the entities that had formerly fallen into the valley. - The uncanny appears at any degree of human likeness. Hanson has also pointed out that uncanny entities may appear anywhere in a spectrum ranging from the abstract (e.g., MIT's robot Lazlo) to the perfectly human (e.g., cosmetically atypical people). Capgras syndrome is a relatively rare condition in which the sufferer believes that people (or, in some cases, things) have been replaced with duplicates. These duplicates are rationally accepted to be identical in physical properties, but the irrational belief is held that the "true" entity has been replaced with something else. Some sufferers of Capgras syndrome claim that the duplicate is a robot. Ellis and Lewis argue that the syndrome arises from an intact system for overt recognition coupled with a damaged system for covert recognition, which leads to conflict over an individual being identifiable but not familiar in any emotional sense. This supports the view that the uncanny valley could arise due to issues of categorical perception that are particular to the manner in which the social brain processes information.
- The uncanny valley is a heterogeneous group of phenomena. Phenomena labeled as being in the uncanny valley can be diverse, involve different sense modalities, and have multiple, possibly overlapping causes, which can range from evolved or learned circuits for early face perception to culturally-shared psychological constructs. People's cultural backgrounds may have a considerable influence on how androids are perceived with respect to the uncanny valley.
History
An effect similar to the uncanny valley was noted by Charles DarwinCharles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory...
in 1839:
Transhumanism
According to writer Jamais CascioJamais Cascio
Jamais Cascio is a San Francisco Bay Area-based writer and ethical futurist specializing in design strategies and possible outcomes for future scenarios...
, a similar "uncanny valley" effect could show up when humans begin modifying themselves with transhuman
Transhuman
Transhuman or trans-human is a term that has been defined and redefined many times in history. In its contemporary usage, “transhuman” refers to an intermediary form between the human and the hypothetical posthuman.-History of hypotheses:...
enhancements (cf. body modification
Body modification
Body modification is the deliberate altering of the human body for any non-medical reason, such as aesthetics, sexual enhancement, a rite of passage, religious reasons, to display group membership or affiliation, to create body art, shock value, or self expression...
), which aim to improve the abilities of the human body beyond what would normally be possible, be it eyesight, muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
strength, or cognition
Cognition
In science, cognition refers to mental processes. These processes include attention, remembering, producing and understanding language, solving problems, and making decisions. Cognition is studied in various disciplines such as psychology, philosophy, linguistics, and computer science...
. So long as these enhancements remain within a perceived norm of human behavior, a negative reaction is unlikely, but once individuals supplant normal human variety, revulsion can be expected. However, according to this theory, once such technologies gain further distance from human norms, "transhuman" individuals would cease to be judged on human levels and instead be regarded as separate entities altogether (this point is what has been dubbed "posthuman
Posthuman
Posthuman may refer to:*Posthuman, a hypothetical future being whose basic capacities so radically exceed those of present humans as to be no longer human by our current standards...
"), and it is here that acceptance would rise once again out of the uncanny valley. Another example comes from "pageant retouching" photos, especially of children, which some find disturbingly doll-like.
Film and television
Roboticist Dario FloreanoDario Floreano
Dario Floreano is director of the Laboratory of Intelligent Systems at the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne in Switzerland. He is one of the pioneers in evolutionary robotics, a research field in which robots are evolved using artificial evolution.Floreano received an M.A. in visual...
stated that the concept of the uncanny valley is taken seriously by the film industry
Film industry
The film industry consists of the technological and commercial institutions of filmmaking: i.e. film production companies, film studios, cinematography, film production, screenwriting, pre-production, post production, film festivals, distribution; and actors, film directors and other film crew...
due to negative audience reactions to the animated baby in Pixar
Pixar
Pixar Animation Studios, pronounced , is an American computer animation film studio based in Emeryville, California. The studio has earned 26 Academy Awards, seven Golden Globes, and three Grammy Awards, among many other awards and acknowledgments. Its films have made over $6.3 billion worldwide...
's 1988 short film Tin Toy
Tin Toy
Tin Toy is a 1988 short film using computer animation. It was directed by John Lasseter and produced by Pixar. It was the first testing of PhotoRealistic RenderMan...
.
In the 2008 30 Rock
30 Rock
30 Rock is an American television comedy series created by Tina Fey that airs on NBC. The series is loosely based on Fey's experiences as head writer for Saturday Night Live...
episode "Succession
Succession (30 Rock)
"Succession" is the thirteenth episode of NBC's second season of 30 Rock and the thirty-fourth episode overall. It was written by Andrew Guest and one of the seasons' co-executive producers, John Riggi; it was directed by Gail Mancuso. It first aired on April 24, 2008 in the United States...
", Frank Rossitano explains the uncanny valley concept, using a graph and Star Wars
Star Wars
Star Wars is an American epic space opera film series created by George Lucas. The first film in the series was originally released on May 25, 1977, under the title Star Wars, by 20th Century Fox, and became a worldwide pop culture phenomenon, followed by two sequels, released at three-year...
examples, to try to convince Tracy Jordan
Tracy Jordan
Ogbert Jordan, better known by his stage name, Tracy, is a fictional character on the American television series 30 Rock, based on and played by Tracy Morgan.-Brief overview:...
that his dream of creating a pornographic video game is impossible. He also references The Polar Express.
In the Doctor Who
Doctor Who
Doctor Who is a British science fiction television programme produced by the BBC. The programme depicts the adventures of a time-travelling humanoid alien known as the Doctor who explores the universe in a sentient time machine called the TARDIS that flies through time and space, whose exterior...
serial The Robots of Death
The Robots of Death
The Robots of Death is a serial in the British science fiction television series Doctor Who, which was first broadcast in four weekly parts from 29 January to 19 February 1977.-Synopsis:...
, a similar concept is referred to as "Grimwade's Syndrome" which is described as a psychological condition among people with frequent contact with robots, attributed to the robots moving like humans, but without any of the characteristic human body language. In the mind of those afflicted, they appear to be, in the words of the Doctor, "surrounded by walking, talking dead men."
Episode 12 (season 5) of Criminal Minds
Criminal Minds
Criminal Minds is an American police procedural drama that premiered September 22, 2005, on CBS. The series follows a team of profilers from the FBI's Behavioral Analysis Unit based in Quantico, Virginia. The BAU is part of the FBI National Center for the Analysis of Violent Crime...
is titled "The Uncanny Valley" and explores the theme through the lens of a serial abductress (and murderess) who chemically paralyzes the women she abducts and treats them like dolls.
In the season 6 episode of Red Dwarf
Red Dwarf
Red Dwarf is a British comedy franchise which primarily comprises eight series of a television science fiction sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999 and Dave from 2009–present. It gained cult following. It was created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, who also wrote the first six series...
, "Out of Time", Kryten
Kryten
Kryten is a fictional character in the British science fiction situation comedy Red Dwarf. Kryten's registration code on Red Dwarf is "Kryten additional 001". The name Kryten is a reference to the head butler in the J.M...
mentions the Uncanny Valley (though not by name) as the reason his faceted head was designed to look so inhuman. The series of Mechanoids that preceded his were hyper-realistic, and people's natural revulsion to such realistic-appearing machines severely hurt their sales.
The 1972 satirical thriller The Stepford Wives
The Stepford Wives
The Stepford Wives is a 1972 satirical thriller novel by Ira Levin. The story concerns Joanna Eberhart, a photographer and young mother who begins to suspect that the frighteningly submissive housewives in her new idyllic Connecticut neighborhood may be robots created by their husbands.Two films of...
and its 1975 and 2004 movie adaptations feature, though unmentioned and unexplored, the concept of the uncanny valley. As the story's protagonist moves to a suburban residence, she notices increasingly uncharacteristic behavior by the women in her community. As they become more and more docile and subject their behavior and ambitions to the needs of their partners, this leads to the protagonist beginning to see a conspiracy where the women are replaced by "gynoid
Gynoid
A gynoid is anything which resembles or pertains to the female human form. It is also used in American English medical terminology as a shortening of the term Gynecoid ....
".
In the 2010 film The Last Airbender
The Last Airbender
The Last Airbender is a 2010 American fantasy adventure film written and directed by M. Night Shyamalan. It is a live-action film adaptation of the first season to the Nickelodeon animated series Avatar: The Last Airbender....
, Appa the flying bison, which is a CGI character based on a character of the same name in the television series, Avatar: The Last Airbender
Avatar: The Last Airbender
Avatar: The Last Airbender is an American animated television series that aired for three seasons on Nickelodeon from 2005 to 2008. The series was created and produced by Michael Dante DiMartino and Bryan Konietzko, who served as executive producers along with Aaron Ehasz...
, has been called "uncanny." Geekosystem's Susana Polo found the CGI version of Appa "really quite creepy," noting "that prey animals (like bison) have eyes on the sides of their heads, and so moving them to the front without changing rest of the facial structure tips us right into the Uncanny Valley."
The television show Courage the Cowardly Dog
Courage the Cowardly Dog
Courage the Cowardly Dog is an American animated television series created by John R. Dilworth for Cartoon Network. Its central plot revolves around a somewhat anthropomorphic dog named Courage who lives with his owners, Muriel and Eustace Bagge, an elderly, married farming couple in the "Middle of...
has been noted by TV Tropes
TV Tropes
TV Tropes is a wiki which collects and expands on various conventions and devices found within creative works. Since its establishment in 2004, the site has gone from covering only television and film tropes to also covering those in a number of other media such as literature, comics, video-games,...
to have some uncanny valley elements, including King Ramses from the "King Ramses' Curse" episode, the girl with a violin from "Courage in the Big, Stinkin' City", and a hazy, blue, warped bugle of Courage's master Eustace, with a whispery voice and human face. The latter of these three has been called the scariest moment in the series, due to the bugle's freaky appearance, not to mention the background music, the whispery voice, and the bugle has warped parts, sometimes mistaken to be a fetus.
In reviewing the aforementioned Polar Express in 2004, CNN.com reviewer Paul Clinton references his uncanny valley response directly: "Those human characters in the film come across as downright... well, creepy. So The Polar Express is at best disconcerting, and at worst, a wee bit horrifying."
External links
- IEEE Spectrum article "Who's Afraid of the Uncanny Valley," April 2, 2010 A compilation of images of humanoid robots, lifelike mannequins and CGI humans, and a discussion of origins and scientific foundations of the uncanny valley hypothesis.
- Your Brain on Androids UCSD news release about human brain and the uncanny valley.
- On The Media Transcript and audio archive of their story, "The Uncanny Valley", March 5, 2010.
- IEEE-RAS Humanoids-2005 Workshop: Views on the Uncanny Valley. Was held in Tsukuba, Japan, near Tokyo on December 5, 2005.
- The Uncanny Valley (Dave Bryant)
- Almost too human and lifelike for comfort - research journal for an uncanny valley PhD project
- Relation between motion and appearance is communication between androids and humans
- Android Science video, the Discovery ChannelDiscovery ChannelDiscovery Channel is an American satellite and cable specialty channel , founded by John Hendricks and distributed by Discovery Communications. It is a publicly traded company run by CEO David Zaslav...
, 24 March 2005, discusses android science, the uncanny valley and features an Actroid. - Wired article: "Why is this man smiling?", June 2002.
- The Polar Express: A Virtual Train Wreck, Part 1 - Animation Director Ward Jenkins discusses in length about the use of motion capture in the film. In Part 2, he tries to "fix" the uncanny valley problem by using Photoshop to tweak some of the characters in the film.
- This robotic mouth, apparently designed to help hearing-impaired people learn to enunciate vowels correctly, is an example of the uncanny valley
- The Uncanny Valley (in On The MediaOn the MediaOn the Media is an hour-long weekly radio program, hosted by Bob Garfield and Brooke Gladstone, covering journalism, technology, and First Amendment issues. It is produced by WNYC in New York City...
) - Androids Are the Future: Scenes From Vanguard, even more disturbing than Repliee.
- The Uncanny valley- a visual explanation of the hypothesis with the application in gaming.

