
Uncial 0308
Encyclopedia
Codex 0308 is one of the recently registered New Testament
Greek uncial
manuscript
s. It consists of only a fragment of a single parchment
leaf of a fourth century codex
, containing portions of the eleventh chapter of the Book of Revelation
.
Uncial 0308 measures 5.9 cm by 4.8 cm (8 x 8 cm) with the surviving leaf having 11 lines out of an original 14 (see reconstruction below). The text was written one column to a page, though line lengths were irregular. The letters Ε (epsilon
) and Θ (theta
) have longer the middle line, and they are similar to those from Codex Washingtonianus
. These characters appear influenced by the shape of Coptic letters.
The nomina sacra
attested in this uncial fragment are ΚΣ (Kurios, Lord) and ΧΡΣ) (Christos, Christ). The number "twenty four" is also written using an abbreviation — ΚΔ. All the abbreviations are marked with the superscript bar.
|-style="background:#FFEBCD"
| ριστουμεν σοι ΚΕ ο
| give thanks to thee Lord
|-style="background:#FFEBCD"
| ΘΣ ο παντοκρατορ
| God Almighty
|}
New Testament
The New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
Greek uncial
Uncial
Uncial is a majuscule script commonly used from the 3rd to 8th centuries AD by Latin and Greek scribes. Uncial letters are written in either Greek, Latin, or Gothic.-Development:...
manuscript
Manuscript
A manuscript or handwrite is written information that has been manually created by someone or some people, such as a hand-written letter, as opposed to being printed or reproduced some other way...
s. It consists of only a fragment of a single parchment
Parchment
Parchment is a thin material made from calfskin, sheepskin or goatskin, often split. Its most common use was as a material for writing on, for documents, notes, or the pages of a book, codex or manuscript. It is distinct from leather in that parchment is limed but not tanned; therefore, it is very...
leaf of a fourth century codex
Codex
A codex is a book in the format used for modern books, with multiple quires or gatherings typically bound together and given a cover.Developed by the Romans from wooden writing tablets, its gradual replacement...
, containing portions of the eleventh chapter of the Book of Revelation
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament. The title came into usage from the first word of the book in Koine Greek: apokalupsis, meaning "unveiling" or "revelation"...
.
Description
The surviving texts of Revelation are verses 11:15-16 and 11:17-18; they are in fragmentary condition.Uncial 0308 measures 5.9 cm by 4.8 cm (8 x 8 cm) with the surviving leaf having 11 lines out of an original 14 (see reconstruction below). The text was written one column to a page, though line lengths were irregular. The letters Ε (epsilon
Epsilon
Epsilon is the fifth letter of the Greek alphabet, corresponding phonetically to a close-mid front unrounded vowel . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 5. It was derived from the Phoenician letter He...
) and Θ (theta
Theta
Theta is the eighth letter of the Greek alphabet, derived from the Phoenician letter Teth...
) have longer the middle line, and they are similar to those from Codex Washingtonianus
Codex Washingtonianus
The Codex Washingtonianus or Codex Washingtonensis, designated by W or 032 , ε 014 , also called the Washington Manuscript of the Gospels, and The Freer Gospel, contains the four biblical gospels and was written in Greek on vellum in the fourth or fifth century...
. These characters appear influenced by the shape of Coptic letters.
The nomina sacra
Nomina sacra
Nomina sacra means "sacred names" in Latin, and can be used to refer to traditions of abbreviated writing of several frequently occurring divine names or titles in early Greek language Holy Scripture...
attested in this uncial fragment are ΚΣ (Kurios, Lord) and ΧΡΣ) (Christos, Christ). The number "twenty four" is also written using an abbreviation — ΚΔ. All the abbreviations are marked with the superscript bar.
Text
| God, saying, we|-style="background:#FFEBCD"
| ριστουμεν σοι ΚΕ ο
| give thanks to thee Lord
|-style="background:#FFEBCD"
| ΘΣ ο παντοκρατορ
| God Almighty
|}
| |
|
| ο ων και ο ην και οτι ει | who art and who wast |
| ληφας την δυναμιν | that you taken thy power |
| σου την μεγαλην και | great and |
| εβασιλευσας και | begun to reign |
| τα εθνη ωργισθησαν | The nations raged |
| και ηλθην η οργη σου | but thy wrath came |
| και ο καιρος των νε | and the time for the |
| κρων κριθηναι και | dead to be judged |
| δουναι τον μισθον | for rewarding |
| τοις δουλοις σου και | thy servants and |
| τοις προφηταις και | the prophets |
| τοις αγιοις και | and saints |
| τοις φοβουμενοις | and those who fear |
| το ονομα σου | thy name |
Although the text of the codex is too brief to determine its textual character, it concurs with both Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
and with
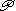 47 (Papyrus 47), with one exception.
47 (Papyrus 47), with one exception.In Rev 11:16 it has the textual variant κα]θημενο[ι, agreeing with Codex Alexandrinus
Codex Alexandrinus
The Codex Alexandrinus is a 5th century manuscript of the Greek Bible,The Greek Bible in this context refers to the Bible used by Greek-speaking Christians who lived in Egypt and elsewhere during the early history of Christianity...
, Uncial 051
Uncial 051
Uncial 051 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Book of Revelation, dated paleographically to the 10th century.- Description :...
and
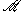 A against καθηνται—
A against καθηνται—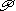 47 and Codex Ephraemi—also οι καθηνται—Sinaiticus and
47 and Codex Ephraemi—also οι καθηνται—Sinaiticus and 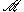 K.
K.In Rev 11:17 it has και οτι, a variant supported by:
 47, א
47, אCodex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
, C and 2344
Minuscule 2344
Minuscule 2344 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament.- Description :The codex contains the text of the Acts, CE, Paul, Rev, on 61 parchment leaves...
.
In Re 11:18 it has textual variant "τοις δουλοις σου και τοις προφηταις" (like: Sinaiticus and
 47), Textus Receptus
47), Textus ReceptusTextus Receptus
Textus Receptus is the name subsequently given to the succession of printed Greek texts of the New Testament which constituted the translation base for the original German Luther Bible, the translation of the New Testament into English by William Tyndale, the King James Version, and for most other...
and NA27 have: "τοις δουλοις σου τοις προφηταις".
It differs two times with NA27 (και used 2 times more). The text of the codex was published by W. E. H. Cockle in 1999.
It is cataloged among the Oxyrhynchus Papyri
Oxyrhynchus Papyri
The Oxyrhynchus Papyri are a very numerous group of manuscripts discovered by archaeologists including Bernard Pyne Grenfell and Arthur Surridge Hunt at an ancient rubbish dump near Oxyrhynchus in Egypt . The manuscripts date from the 1st to the 6th century AD. They include thousands of Greek and...
as P. Oxy. 4500, and is now part of the Sackler Library
Sackler Library
The Sackler Library holds a large portion of the classical, art historical, and archaeological works belonging to the University of Oxford, England.- History :...
collection in Oxford
Oxford
The city of Oxford is the county town of Oxfordshire, England. The city, made prominent by its medieval university, has a population of just under 165,000, with 153,900 living within the district boundary. It lies about 50 miles north-west of London. The rivers Cherwell and Thames run through...
.
Further reading
- W. E. H. Cockle, "4500. Revelation XI 15–16; 17–18", The Oxyrhynchus Papyri LXVI (London: Egypt Exploration SocietyEgypt Exploration SocietyThe Egypt Exploration Society is the foremost learned society in the United Kingdom promoting the field of Egyptology....
, 1999).
Images
- P.Oxy. LXVI 4500 from Oxford University's official papyrologyPapyrologyPapyrology is the study of ancient literature, correspondence, legal archives, etc., as preserved in manuscripts written on papyrus, the most common form of writing material in the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, and Rome...
website "POxy: Oxyrhynchus Online"
Official registration
- "Continuation of the Manuscript List", Institute for New Testament Textual ResearchInstitute for New Testament Textual ResearchThe Institute for New Testament Textual Research at the University of Münster, Westphalia, Germany, is an institute for the investigation of the text of the New Testament. The INTF was founded in Münster in 1959 by Professor Kurt Aland , the first director of the Institute...
, University of MünsterUniversity of MünsterThe University of Münster is a public university located in the city of Münster, North Rhine-Westphalia in Germany. The WWU is part of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, a society of Germany's leading research universities...
. Retrieved April 9, 2008

