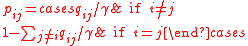Uniformization (probability theory)
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
, uniformization method, (also known as Jensen's method or the randomization method) is a method to transient solutions of continuous-time Markov chains. The word uniformization in its narrower sense involves the transformation of a continuous time Markov chain to an analgous discrete time Markov chain.. This chain is then randomized, that is, the times between changes are no longer constant, but exponential. The method is simple to program and efficiently calculates the transient distribution..
For a continuous time Markov chain with transition rate matrix Q, the uniformized discrete time Markov chain has probability transition matrix P calculated by
with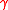 chosen such that
chosen such that 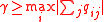 .
.
Randomizing the discrete-time Markov chain now results in the following formula for the solution of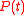 , the transient solution of the continuous-time Markov chain
, the transient solution of the continuous-time Markov chain
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
, uniformization method, (also known as Jensen's method or the randomization method) is a method to transient solutions of continuous-time Markov chains. The word uniformization in its narrower sense involves the transformation of a continuous time Markov chain to an analgous discrete time Markov chain.. This chain is then randomized, that is, the times between changes are no longer constant, but exponential. The method is simple to program and efficiently calculates the transient distribution..
For a continuous time Markov chain with transition rate matrix Q, the uniformized discrete time Markov chain has probability transition matrix P calculated by
with
 chosen such that
chosen such that 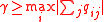 .
.Randomizing the discrete-time Markov chain now results in the following formula for the solution of
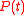 , the transient solution of the continuous-time Markov chain
, the transient solution of the continuous-time Markov chain