.gif)
Upstream and downstream (DNA)
Encyclopedia
In molecular biology
and genetics
, upstream and downstream both refer to a relative position in DNA
or RNA
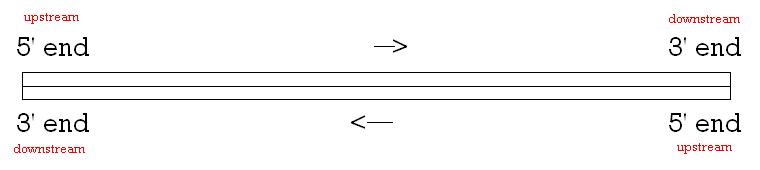
. Each strand of DNA or RNA has a 5' end and a 3' end, so named for the carbons on the deoxyribose
(or ribose
) ring. Relative to the position on the strand, downstream is the region towards the 3' end of the strand. Since DNA strands run in opposite directions, downstream on one strand is upstream on the other strand.
and translation of DNA and mRNA, respectively, have their direction defined by the newly synthesized strand, that is, in downstream direction (5' --> 3'). However, it is in the upstream direction (3' --> 5') for the copied template strand.
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
and genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, upstream and downstream both refer to a relative position in DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
or RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
. Each strand of DNA or RNA has a 5' end and a 3' end, so named for the carbons on the deoxyribose
Deoxyribose
Deoxyribose, more, precisely 2-deoxyribose, is a monosaccharide with idealized formula H---3-H. Its name indicates that it is a deoxy sugar, meaning that it is derived from the sugar ribose by loss of an oxygen atom...
(or ribose
Ribose
Ribose is an organic compound with the formula C5H10O5; specifically, a monosaccharide with linear form H––4–H, which has all the hydroxyl groups on the same side in the Fischer projection....
) ring. Relative to the position on the strand, downstream is the region towards the 3' end of the strand. Since DNA strands run in opposite directions, downstream on one strand is upstream on the other strand.

Examples
TranscriptionTranscription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
and translation of DNA and mRNA, respectively, have their direction defined by the newly synthesized strand, that is, in downstream direction (5' --> 3'). However, it is in the upstream direction (3' --> 5') for the copied template strand.

