
Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
Encyclopedia
The Uralic Phonetic Alphabet (UPA) or Finno-Ugric transcription system is a phonetic transcription
or notational system used predominantly for the transcription
and reconstruction
of Uralic languages
. It was first published in 1901 by Eemil Nestor Setälä
, a Finnish
linguist.
Phonetic transcription
Phonetic transcription is the visual representation of speech sounds . The most common type of phonetic transcription uses a phonetic alphabet, e.g., the International Phonetic Alphabet....
or notational system used predominantly for the transcription
Transcription (linguistics)
Transcription in the linguistic sense is the systematic representation of language in written form. The source can either be utterances or preexisting text in another writing system, although some linguists only consider the former as transcription.Transcription should not be confused with...
and reconstruction
Linguistic reconstruction
Linguistic reconstruction is the practice of establishing the features of the unattested ancestor of one or more given languages. There are two kinds of reconstruction. Internal reconstruction uses irregularities in a single language to make inferences about an earlier stage of that language...
of Uralic languages
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
. It was first published in 1901 by Eemil Nestor Setälä
Eemil Nestor Setälä
Eemil Nestor Setälä, was a Finnish politician and once the Chairman of the Senate of Finland, from September 1917 to November 1917....
, a Finnish
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
linguist.
Unlike the International Phonetic Alphabet
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
(IPA) notational standard which concentrates on accurately and uniquely transcribing the phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
s of a language, the UPA is also used to denote the functional categories of a language, as well as their phonetic
Phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that comprises the study of the sounds of human speech, or—in the case of sign languages—the equivalent aspects of sign. It is concerned with the physical properties of speech sounds or signs : their physiological production, acoustic properties, auditory...
quality. For this reason, it is not possible to automatically convert a UPA transcription into an IPA one.
The basic UPA characters are based on the Finnish alphabet
Finnish alphabet
The Finnish alphabet is based on the Latin script, and especially the Swedish alphabet. Officially it comprises 28 letters:A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, X, Y, Z, Å, Ä, Ö...
where possible, with extensions taken from Cyrillic and Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
orthographies
Orthography
The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
. Small-capital letters and some novel diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
s are also used.
General
Unlike the IPA, which is usually transcribed with uprightRoman type
In typography, roman is one of the three main kinds of historical type, alongside blackletter and italic. Roman type was modelled from a European scribal manuscript style of the 1400s, based on the pairing of inscriptional capitals used in ancient Rome with Carolingian minuscules developed in the...
characters, the UPA is usually transcribed with italic
Italic type
In typography, italic type is a cursive typeface based on a stylized form of calligraphic handwriting. Owing to the influence from calligraphy, such typefaces often slant slightly to the right. Different glyph shapes from roman type are also usually used—another influence from calligraphy...
characters. Although many of its characters are also used in standard Latin
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
, Cyrillic
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
orthographies or the IPA, and are found in the corresponding Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
blocks, many are not. These have been encoded in the Phonetic Extensions and Phonetic Extensions Supplement blocks. Font support for these extended characters is very rare; Code2000
Code2000
Code2000 is a pan-Unicode digital font, which includes characters and symbols from a very large range of writing systems. As of the current final version 1.171 released in 2008, Code2000 is designed and implemented by James Kass to include as much of the Unicode 5.2 standard as practical , and to...
and Fixedsys Excelsior
Fixedsys Excelsior
Fixedsys Excelsior is an unofficial pan-Unicode extension of the popular Microsoft font Fixedsys. The current version, last updated in 2007, is 3.01....
are two fonts that do support them. A professional font containing them is Andron Mega, it supports UPA characters in Regular and Italics.
Vowels
A vowelVowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
to the left of a dot is illabial (unrounded); to the right is labial (rounded).
Other vowels are denoted using diacritics; see the section below.
The UPA also uses three characters to denote a vowel of uncertain quality:
- denotes a vowel of uncertain quality;
- denotes a back vowel of uncertain quality;
- denotes a front vowel of uncertain quality
If a distinction between close-mid vowel
Close-mid vowel
A close-mid vowel is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a close-mid vowel is that the tongue is positioned two-thirds of the way from a close vowel to a mid vowel...
s and open-mid vowels is needed, the IPA symbols for the open-mid basic front illabial and back labial vowels, ⟨ɛ⟩ and ⟨ɔ⟩, can be used. However, in keeping with the principles of the UPA, the open-mid front labial and back illabial vowels are still transcribed with the addition of diacritics, as and .
Consonants
The following table describes the consonants of the UPA. Note that the UPA does not distinguish voiced fricatives from approximates, and does not contain many characters of the IPA such as [ɹ].| Stop | Fricative | Lateral | Trill | Nasal | Click | |||||||||||||
| Bilabial | ||||||||||||||||||
| Labiodental | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dental | ||||||||||||||||||
| Alveolar | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dentipalatal (palatalised) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Prepalatal (palatalised and/or anterior) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Velar | ||||||||||||||||||
| Postvelar | ||||||||||||||||||
| Uvular | ||||||||||||||||||
When there are two or more consonants in a column, the rightmost one is voiced; when there are three, the centre one is partially devoiced.
Modifiers
| Character | Unicode | Image | Description | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| U+0308 | - | umlaut above | Palatal (fully front) vowel | |
| U+0323 |  |
dot below | Palatal (fronted) variant of vowel | |
| U+032E | 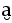 |
breve below | Velar (fully back or backed) vowel or variant of vowel | |
| U+0304 | 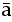 |
macron | Long form of a vowel; also by duplication | |
| U+0354 | 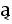 |
left arrowhead below | Advanced form of a vowel or consonant | |
| U+0355 | 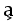 |
right arrowhead below | Retracted form of a vowel or consonant | |
| U+032D | 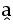 |
circumflex below | Raised variant of a vowel | |
| U+032C |  |
caron below | Lowered variant of a vowel | |
| U+0306 | 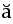 |
breve | Shorter or reduced vowel | |
| U+032F |  |
inverted breve below | Non-syllabic, glide or semi-vowel | |
| U+0280 | 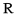 |
small capital | Unvoiced or partially voiced version of voiced sound | |
| superscripted character | Very short sound | |||
| subscripted character | Coarticulation due to surrounding sounds | |||
| U+1D1E |  |
Rotated (180°) or sideways (−90°) | Reduced form of sound |
Sample use of UPA
This section contains some sample words from both Uralic languages and English (using Australian EnglishAustralian English phonology
Australian English is a non-rhotic variety of English spoken by most native-born Australians. Phonologically, it is one of the most regionally homogeneous language varieties in the world...
) along with comparisons to the IPA transcription.
| English | Language | UPA | IPA |
|---|---|---|---|
| ship | English | ʃɪp | |
| ran | English | ræn or ɹæn | |
| bored | English | boːd | |
| I sow | Moksha Moksha language The Moksha language is a member of the Finno-Volgaic subdivision of the Uralic languages with about 500,000 native speakers. Moksha is the majority language in the western part of Mordovia.... |
vɤ̈dʲæn |

