
Utilization
Encyclopedia
Utilization is a statistical concept (Queueing Theory) as well as a primary business measure for the rental industry.
, utilization is the proportion of the system's resources which is used by the traffic which arrives at it. It should be strictly less than one for the system to function well. It is usually represented by the symbol . If
. If 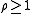 then the queue will continue to grow as time goes on. In the simplest case of an M/M/1 queue
then the queue will continue to grow as time goes on. In the simplest case of an M/M/1 queue
(Poisson
arrivals and a single Poisson server) then it is given by the mean arrival rate over the mean service rate, that is,

where is the mean arrival rate and
is the mean arrival rate and 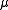 is the mean service rate. More generally:
is the mean service rate. More generally:

where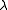 is the mean arrival rate,
is the mean arrival rate, 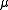 is the mean service rate, and M is the number of servers.
is the mean service rate, and M is the number of servers.
In most cases a lower utilization will mean less queuing for customers but will mean that the system is idle more (which could be considered inefficient)...
, utilization is the primary method by which asset performance is measured and business success determined. In basic terms it is a measure of the actual revenue earned by assets against the potential revenue they could have earned. Rental utilization is divided into a number of different calculations, and not all companies work precisely the same way. In general terms however there are 2 key calculations: the physical utilization on the asset, which is measured based on the number of available days for rental against the number of days actually rented. (This may also be measured in hours for certain types of equipment), and the financial utilization on the asset (referred to in North America as $ Utilization) which is measured as the rental revenue achieved over a period of time against the potential revenue that could have been achieved based on a target or standard, non-discounted rate.
Physical utilization is also sometimes referred to as spot utilization, where a rental company looks at its current utilization of assets based on a single moment in time (e.g. now, 9 am today, etc).
, each product is produced in one area or cell, sometimes requiring more machines and lower utilizations.
Queueing theory
In queueing theoryQueueing theory
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of waiting lines, or queues. The theory enables mathematical analysis of several related processes, including arriving at the queue, waiting in the queue , and being served at the front of the queue...
, utilization is the proportion of the system's resources which is used by the traffic which arrives at it. It should be strictly less than one for the system to function well. It is usually represented by the symbol
 . If
. If 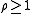 then the queue will continue to grow as time goes on. In the simplest case of an M/M/1 queue
then the queue will continue to grow as time goes on. In the simplest case of an M/M/1 queueM/M/1 model
In queueing theory, a discipline within the mathematical theory of probability, a M/M/1 queue represents the queue length in a system having a single server, where arrivals are detemined by a Poisson process and job service times have an exponential distribution. The model name is written in...
(Poisson
Poisson process
A Poisson process, named after the French mathematician Siméon-Denis Poisson , is a stochastic process in which events occur continuously and independently of one another...
arrivals and a single Poisson server) then it is given by the mean arrival rate over the mean service rate, that is,

where
 is the mean arrival rate and
is the mean arrival rate and 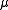 is the mean service rate. More generally:
is the mean service rate. More generally:
where
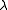 is the mean arrival rate,
is the mean arrival rate, 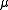 is the mean service rate, and M is the number of servers.
is the mean service rate, and M is the number of servers.In most cases a lower utilization will mean less queuing for customers but will mean that the system is idle more (which could be considered inefficient)...
Rental equipment utilization
In equipment and tool rental companiesRental management software
The rental industry spans many different types of equipment from tools to heavy construction equipment, aerial to vehicles, party and event to computers and test and measurement equipment and highly specialized areas such as Crane and Temporary Accommodation rental...
, utilization is the primary method by which asset performance is measured and business success determined. In basic terms it is a measure of the actual revenue earned by assets against the potential revenue they could have earned. Rental utilization is divided into a number of different calculations, and not all companies work precisely the same way. In general terms however there are 2 key calculations: the physical utilization on the asset, which is measured based on the number of available days for rental against the number of days actually rented. (This may also be measured in hours for certain types of equipment), and the financial utilization on the asset (referred to in North America as $ Utilization) which is measured as the rental revenue achieved over a period of time against the potential revenue that could have been achieved based on a target or standard, non-discounted rate.
Physical utilization is also sometimes referred to as spot utilization, where a rental company looks at its current utilization of assets based on a single moment in time (e.g. now, 9 am today, etc).
Variations in rental utilization calculations
Utilization calculations may be varied based on many different factors. For example:- a company with equipment which requires preventative maintenance activities every 2 weeks, may decide that the number of available days in the month is decreased as it will unavailable due to maintenance for 2 days out of each month.
- Some rental businesses give "free days" on rental contract billing processes, for example on a national or public holiday, and therefor the equipment does not earn any money on those days, even though it is physically on rent.
- Some companies charge minimum rates, for example you may rent an excavator for 1 day, but be charged a three-day minimum. The Physical utilization will therefore be 100% on the day, but the financial utilization is actually 300% as you've earned 3 days revenue for 1 day's work.
- Rental SoftwareRental management softwareThe rental industry spans many different types of equipment from tools to heavy construction equipment, aerial to vehicles, party and event to computers and test and measurement equipment and highly specialized areas such as Crane and Temporary Accommodation rental...
is normally required to assist management teams in measuring and calculating utilization figures. - Asset Tracking softwareMobile asset managementMobile asset management is managing availability and serviceability of assets used to move, store, secure, protect and control inventory within the enterprise and along the supply chain or in conjunction with service providing.Mobile assets are e.g...
may also be important in increasing or managing utilization figures.
Profitability in relation to rental utilization
Utilization in this context is heavily linked to profitability. Low physical utilization may be mitigated by keeping rental rates high, high physical utilization normally justifies keeping rental rates lower. Different types of equipment may also alter the relationship between rates and utilization .Equipment or machine utilization
In production, an increase of utilisation will require more preventative maintenance and more wear and tear on the machine. Sometimes it is more economical to buy new equipment, but increasing the utilisation of the current equipment is usually the most practical. In the case of cellular manufacturingCellular manufacturing
Cellular Manufacturing is a model for workplace design, and has become an integral part of lean manufacturing systems. Cellular Manufacturing is based upon the principals of Group Technology, which seeks to take full advantage of the similarity between parts, through standardisation and common...
, each product is produced in one area or cell, sometimes requiring more machines and lower utilizations.

