
Uvular consonant
Encyclopedia
Uvulars are consonant
s articulated with the back of the tongue
against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonant
s. Uvulars may be plosives
, fricatives
, nasal stops
, trills
, or approximants
, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and the symbol for the voiced fricative is used instead. Uvular affricates
can certainly be made but are rare: they occur in some southern High-German dialects, as well as in a few African and Native American languages. (Ejective uvular affricates occur in as realizations of uvular stops in Lillooet and Georgian
.)
are:
 English
English
has no uvular consonants, and they are unknown in the indigenous languages of Australia and the Pacific
. Uvular consonants are however found in many African and Middle-Eastern languages, most notably Arabic
, and in Native American
languages. In parts of the Caucasus mountains and northwestern North America, nearly every language has uvular stops and fricatives. Two uvular Rs are found in north-western Europe. It was once thought that they spread from northern French
, but some linguists believe that contact does not explain the appearance of all uvular Rs in Europe.
The voiceless uvular plosive is transcribed as [q] in both the IPA and SAMPA
. It is pronounced somewhat like the voiceless velar plosive
[k], but with the middle of the tongue further back on the velum, against or near the uvula. The most familiar use will doubtless be in the transliteration of Arabic place names such as Qatar and Iraq into English, though, since English lacks this sound, this is generally pronounced as [k], the most similar sound that occurs in English.
[ɢ], the voiced equivalent of [q], is much rarer. It is like the voiced velar plosive
[ɡ], but articulated in the same uvular position as [q]. Few languages use this sound, but it is found in some varieties of Persian
and in several Northeast Caucasian languages
, notably Tabasaran
. It may also occur as an allophone of another uvular consonant - in Kazakh
, the voiced uvular plosive is an allophone of the voiced uvular fricative after the velar nasal
.
The voiceless uvular fricative [χ] is similar to the voiceless velar fricative
[x], except that it is articulated near the uvula. It is found instead of [x] in some dialects of German, Spanish and Arabic.
Uvular flaps have been reported for Kube
(Trans–New Guinea) and for the variety of Khmer
spoken in Battambang
.
The Tlingit language
of the Alaskan Panhandle has ten uvular consonants:
and the Ubykh language
of Turkey has 20
.
[ʀ] is used in certain dialect
s (especially those associated with European capitals) of French
, German
, Dutch
, Portuguese
, Danish
, Swedish
and Norwegian
, as well as Hebrew
, for the rhotic
phoneme. In many of these it has a uvular fricative (either voiced [ʁ] or voiceless [χ]) as an allophone
when it follows one of the voiceless
stops
/p/, /t/, or /k/ at the end of a word, as in maître [mɛtχ], or even a uvular approximant.
As with most trills, uvular trills are often reduced to a single contact, especially between vowels.
Unlike other uvular consonants, the uvular trill is articulated without a retraction of the tongue, and therefore doesn't lower neighboring high vowels the way uvular stops commonly do.
Several other languages, including Inuktitut
, Abkhaz
, Uyghur
and some varieties of Arabic, have a voiced uvular fricative but do not treat it as a rhotic consonant
.
In Lakhota
the uvular trill is an allophone of the voiced uvular fricative before /i/.
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s articulated with the back of the tongue
Tongue
The tongue is a muscular hydrostat on the floors of the mouths of most vertebrates which manipulates food for mastication. It is the primary organ of taste , as much of the upper surface of the tongue is covered in papillae and taste buds. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva, and is richly...
against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonant
Velar consonant
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum)....
s. Uvulars may be plosives
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
, fricatives
Fricative consonant
Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or...
, nasal stops
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
, trills
Trill consonant
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the articulator and the place of articulation. Standard Spanish <rr> as in perro is an alveolar trill, while in Parisian French it is almost always uvular....
, or approximants
Approximant consonant
Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough or with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no...
, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and the symbol for the voiced fricative is used instead. Uvular affricates
Affricate consonant
Affricates are consonants that begin as stops but release as a fricative rather than directly into the following vowel.- Samples :...
can certainly be made but are rare: they occur in some southern High-German dialects, as well as in a few African and Native American languages. (Ejective uvular affricates occur in as realizations of uvular stops in Lillooet and Georgian
Georgian language
Georgian is the native language of the Georgians and the official language of Georgia, a country in the Caucasus.Georgian is the primary language of about 4 million people in Georgia itself, and of another 500,000 abroad...
.)
Uvular consonants in IPA
The uvular consonants identified by the International Phonetic AlphabetInternational Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
are:
| IPA | Description | Example | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Orthography | IPA | Meaning | ||
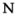 |
uvular nasal | Japanese Japanese language is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an... |
日本 Nihon | [ni.hoɴ] | Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... |
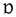 |
voiceless uvular plosive | Kazakh Kazakh language Kazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak.... |
Қазақ Qazaq | [qɑzɑq] | Kazakh Kazakhstan Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe... |
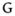 |
voiced uvular plosive | Inuktitut Inuktitut Inuktitut or Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, Eastern Canadian Inuit language is the name of some of the Inuit languages spoken in Canada... |
utirama | [ʔutiɢama] | because I return |
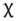 |
voiceless uvular fricative | Castilian Spanish Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... |
enjuto | [ẽ̞ɴˈχut̪o̞] | dry |
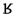 |
voiced uvular fricative | Lakhota Lakota language Lakota is a Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. While generally taught and considered by speakers as a separate language, Lakota is mutually understandable with the other two languages , and is considered by most linguists one of the three major varieties of the Sioux... (LLC orthography) |
aǧúyapi | [ˌʔaˈʁʊjab̥ˑi] | bread |
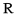 |
uvular trill Uvular trill The uvular trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a small capital R... |
French French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... (Standard Paris Dialect) |
Paris | [paˈʀi] | Paris Paris Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region... |
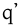 |
uvular ejective Uvular ejective The uvular ejective is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is .-Features:Features of the uvular ejective:-Occurrence:One ejective... |
Quechua Quechua languages Quechua is a Native South American language family and dialect cluster spoken primarily in the Andes of South America, derived from an original common ancestor language, Proto-Quechua. It is the most widely spoken language family of the indigenous peoples of the Americas, with a total of probably... |
q'allu | [ˈqʼaʎu] | tomato sauce |
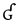 |
voiced uvular implosive Voiced uvular implosive The voiced uvular implosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a small capital letter G with a rightward pointing hook extending from the upper right of the letter.-Occurrence:-Fun Fact:The... |
Mam Mam language Mam is a Mayan language with almost 480,000 speakers as of 2002, spoken in the Mexican state of Chiapas and the Guatemalan departments of Quetzaltenango, Huehuetenango and San Marcos.... |
[ʛa] | fire | |
Descriptions in different languages

English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
has no uvular consonants, and they are unknown in the indigenous languages of Australia and the Pacific
Pacific Islands
The Pacific Islands comprise 20,000 to 30,000 islands in the Pacific Ocean. The islands are also sometimes collectively called Oceania, although Oceania is sometimes defined as also including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago....
. Uvular consonants are however found in many African and Middle-Eastern languages, most notably Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
, and in Native American
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
languages. In parts of the Caucasus mountains and northwestern North America, nearly every language has uvular stops and fricatives. Two uvular Rs are found in north-western Europe. It was once thought that they spread from northern French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, but some linguists believe that contact does not explain the appearance of all uvular Rs in Europe.
The voiceless uvular plosive is transcribed as [q] in both the IPA and SAMPA
SAMPA
The Speech Assessment Methods Phonetic Alphabet is a computer-readable phonetic script using 7-bit printable ASCII characters, based on the International Phonetic Alphabet ....
. It is pronounced somewhat like the voiceless velar plosive
Voiceless velar plosive
The voiceless velar stop or voiceless velar plosive is a type of consonantal sound used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is k....
[k], but with the middle of the tongue further back on the velum, against or near the uvula. The most familiar use will doubtless be in the transliteration of Arabic place names such as Qatar and Iraq into English, though, since English lacks this sound, this is generally pronounced as [k], the most similar sound that occurs in English.
[ɢ], the voiced equivalent of [q], is much rarer. It is like the voiced velar plosive
Voiced velar plosive
The voiced velar plosive is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is g. Strictly, the IPA symbol is the so-called "opentail G" , though the "looptail G" is...
[ɡ], but articulated in the same uvular position as [q]. Few languages use this sound, but it is found in some varieties of Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
and in several Northeast Caucasian languages
Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages constitute a language family spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya, Ingushetia, northern Azerbaijan, and in northeastern Georgia, as well as in diaspora populations in Russia, Turkey, and the Middle East...
, notably Tabasaran
Tabasaran language
Tabasaran is a Northeast Caucasian language of the Lezgic branch. It is spoken by the Tabasaran people in southern part of the Russian Republic of Dagestan. There are two main dialects: North and South Tabasaran. It has a literary language based on the Southern dialect, one of six in the Dagestan...
. It may also occur as an allophone of another uvular consonant - in Kazakh
Kazakh language
Kazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
, the voiced uvular plosive is an allophone of the voiced uvular fricative after the velar nasal
Velar nasal
The velar nasal is the sound of ng in English sing. It is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is N....
.
The voiceless uvular fricative [χ] is similar to the voiceless velar fricative
Voiceless velar fricative
The voiceless velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The sound was part of the consonant inventory of Old English and can still be found in some dialects of English, most notably in Scottish English....
[x], except that it is articulated near the uvula. It is found instead of [x] in some dialects of German, Spanish and Arabic.
Uvular flaps have been reported for Kube
Kube language
Kube , also Mongi, is a Papuan language spoken in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea. Dialects are Kurungtufu, Yoangen ....
(Trans–New Guinea) and for the variety of Khmer
Khmer language
Khmer , or Cambodian, is the language of the Khmer people and the official language of Cambodia. It is the second most widely spoken Austroasiatic language , with speakers in the tens of millions. Khmer has been considerably influenced by Sanskrit and Pali, especially in the royal and religious...
spoken in Battambang
Battambang
Battambang is the capital city of Battambang province in northwestern Cambodia.Battambang is the second-largest city in Cambodia with a population of over 250,000. Founded in the 11th century by the Khmer Empire, Battambang is well known for being the leading rice-producing province of the country...
.
The Tlingit language
Tlingit language
The Tlingit language ) is spoken by the Tlingit people of Southeast Alaska and Western Canada. It is a branch of the Na-Dené language family. Tlingit is very endangered, with fewer than 140 native speakers still living, all of whom are bilingual or near-bilingual in English...
of the Alaskan Panhandle has ten uvular consonants:
| tenuis plosive | qákʷ | tree spine |
| aspirated plosive | qʰákʷ | basket |
| ejective stop | qʼakʷ | screech owl |
| labialized tenuis plosive | náaqʷ | octopus |
| labialized aspirated plosive | qʷʰáan | people, tribe |
| labialized ejective stop | qʷʼátɬ | cooking pot |
| voiceless fricative | χaakʷ | fingernail |
| ejective fricative | χʼáakʷ | freshwater sockeye salmon |
| labialized voiceless fricative | χʷastáa | canvas, denim |
| labialized ejective fricative | χʷʼáaɬʼ | down (feathers) |
and the Ubykh language
Ubykh language
Ubykh or Ubyx is an extinct language of the Northwestern Caucasian group, spoken by the Ubykh people...
of Turkey has 20
Ubykh phonology
Ubykh, a North-West Caucasian language, has the largest consonant inventory of all documented languages that do not use clicks, and also has the most disproportional ratio of phonemic consonants to vowels. It also possesses consonants in at least eight, perhaps nine, basic places of articulation...
.
Uvular Rhotics
The uvular trillTrill consonant
In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the articulator and the place of articulation. Standard Spanish <rr> as in perro is an alveolar trill, while in Parisian French it is almost always uvular....
[ʀ] is used in certain dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s (especially those associated with European capitals) of French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
, German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
, Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
, Danish
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
, Swedish
Swedish language
Swedish is a North Germanic language, spoken by approximately 10 million people, predominantly in Sweden and parts of Finland, especially along its coast and on the Åland islands. It is largely mutually intelligible with Norwegian and Danish...
and Norwegian
Norwegian language
Norwegian is a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Norway, where it is the official language. Together with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional variants .These Scandinavian languages together with the Faroese language...
, as well as Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, for the rhotic
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
phoneme. In many of these it has a uvular fricative (either voiced [ʁ] or voiceless [χ]) as an allophone
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
when it follows one of the voiceless
Voiceless
In linguistics, voicelessness is the property of sounds being pronounced without the larynx vibrating. Phonologically, this is a type of phonation, which contrasts with other states of the larynx, but some object that the word "phonation" implies voicing, and that voicelessness is the lack of...
stops
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
/p/, /t/, or /k/ at the end of a word, as in maître [mɛtχ], or even a uvular approximant.
As with most trills, uvular trills are often reduced to a single contact, especially between vowels.
Unlike other uvular consonants, the uvular trill is articulated without a retraction of the tongue, and therefore doesn't lower neighboring high vowels the way uvular stops commonly do.
Several other languages, including Inuktitut
Inuktitut
Inuktitut or Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, Eastern Canadian Inuit language is the name of some of the Inuit languages spoken in Canada...
, Abkhaz
Abkhaz language
Abkhaz is a Northwest Caucasian language spoken mainly by the Abkhaz people. It is the official language of Abkhazia where around 100,000 people speak it. Furthermore, it is spoken by thousands of members of the Abkhazian diaspora in Turkey, Georgia's autonomous republic of Adjara, Syria, Jordan...
, Uyghur
Uyghur language
Uyghur , formerly known as Eastern Turk, is a Turkic language with 8 to 11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur-speakers are located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and various other...
and some varieties of Arabic, have a voiced uvular fricative but do not treat it as a rhotic consonant
Rhotic consonant
In phonetics, rhotic consonants, also called tremulants or "R-like" sounds, are liquid consonants that are traditionally represented orthographically by symbols derived from the Greek letter rho, including "R, r" from the Roman alphabet and "Р, p" from the Cyrillic alphabet...
.
In Lakhota
Lakota language
Lakota is a Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. While generally taught and considered by speakers as a separate language, Lakota is mutually understandable with the other two languages , and is considered by most linguists one of the three major varieties of the Sioux...
the uvular trill is an allophone of the voiced uvular fricative before /i/.

