
VATS lobectomy
Encyclopedia
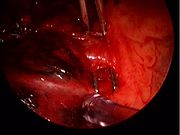
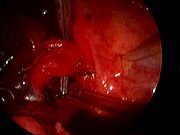
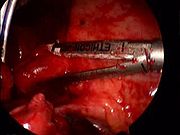
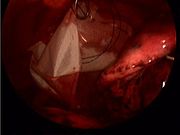
Traditional approach to lung cancer surgery: thoracotomy
Anatomic lung resection, i.e. pulmonary lobectomyLobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
or pneumonectomy
Pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a lung. Removal of just one lobe of the lung is specifically referred to as a lobectomy, and that of a segment of the lung as a wedge resection .-Indications:...
, in conjunction with removal of the lymph nodes from the mediastinum
Mediastinum
The mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
is the treatment modality that provides the greatest chance of long-term survival in patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anatomic lung resections require a dissection of the pulmonary hilum
Hilum of lung
Above and behind the cardiac impression is a triangular depression named the hilum, where the structures which form the root of the lung enter and leave the viscus. These include the pulmonary artery, superiormost on the left lung, the superior and inferior pulmonary veins, lymphatic vessels and...
with individual ligation and division of the pulmonary artery
Pulmonary artery
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
, pulmonary vein
Pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are large blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. In humans there are four pulmonary veins, two from each lung...
, and the bronchus
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The bronchus branches into smaller tubes, which in turn become bronchioles....
where these enter the lung. In the setting of lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
, the rationale for anatomic lung resection is a complete removal of a lung tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
along with the lymphatics that drain that tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
to assure that any tumor cells present in the lymphatics will also be removed; lesser resections have been shown to be associated with a higher risk of local recurrence and diminished long-term survival. A cornerstone of surgical treatment of early stage lung cancer is aggressive removal of lymph nodes from the mediastinum; this enhances the likelihood of removing all cancer cells (complete resection) and identifies patients who will require additional treatment (i.e. adjuvant chemotherapy
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Adjuvant therapy, also called adjuvant care, is treatment that is given in addition to the primary, main or initial treatment. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in cancer therapy have led the term to be used mainly to describe adjuvant cancer treatments...
). An important consideration when performing anatomic lung resection is to spare as much lung tissue as possible; while lobectomy and pneumonectomy are equivalent cancer operations, the risk of complications and morbidity is considerably less with lobectomy.
Traditionally, pulmonary lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
is performed through a thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
incision; over decades, thoracotomy has demonstrated its effectiveness in providing access to structures in the thorax and is in general tolerated by patients. Thoracotomy, as most commonly performed, requires cutting through one or more major muscles of the chest wall including the latissimus dorsi, pectoralis
Pectoralis major muscle
The pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped muscle, situated at the chest of the body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles in the male and lies under the breast in the female...
or serratus
Serratus
-See also:*Serratus anterior muscle*Serratus posterior superior muscle*Serratus posterior inferior muscle...
muscles, and spreading of the ribs with a rib spreader. Because the joints of the ribs with the vertebral bodies have only limited flexibility, the use of a rib spreader usually results in rib fracture
Rib fracture
A rib fracture is a break or fracture in one or more of the bones making up the rib cage.The first rib is rarely fractured because of its protected position behind the clavicle . However, if it is broken serious damage can occur to the brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian vessels...
in the process of rendering the interspace between the ribs wide enough to perform a pulmonary lobectomy. Because of this, thoracic surgeons generally intentionally remove a section of one or more ribs in an effort to prevent splintered rib fracture
Rib fracture
A rib fracture is a break or fracture in one or more of the bones making up the rib cage.The first rib is rarely fractured because of its protected position behind the clavicle . However, if it is broken serious damage can occur to the brachial plexus of nerves and the subclavian vessels...
associated with the use of the rib spreader. There is wide consensus that thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
is one of the most painful incisions that patients can undergo. In the initial post-operative setting after thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
, the use of epidural
Epidural
The term epidural is often short for epidural analgesia, a form of regional analgesia involving injection of drugs through a catheter placed into the epidural space...
catheters, patient-controlled analgesia
Patient-controlled analgesia
Patient-controlled analgesia is any method of allowing a person in pain to administer their own pain relief. The infusion is programmable by the prescriber...
pumps for intravenous narcotic
Narcotic
The term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with any sleep-inducing properties. In the United States of America it has since become associated with opioids, commonly morphine and heroin and their derivatives, such as hydrocodone. The term is, today, imprecisely...
administration, and intravenous ketorolac
Ketorolac
Ketorolac or ketorolac tromethamine is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug in the family of heterocyclic acetic acid derivative, often used as an analgesic...
are commonplace and patients generally require a 7-10 day hospital stay before their pain is adequately controlled with oral opioid
Opioid
An opioid is a psychoactive chemical that works by binding to opioid receptors, which are found principally in the central and peripheral nervous system and the gastrointestinal tract...
analgesics that they can take at home. A great deal of emphasis is placed on post-operative pulmonary toilet
Pulmonary toilet
Pulmonary hygiene, formerly referred to as pulmonary toilet, is a set of methods used to clear mucus and secretions from the airways. The word pulmonary refers to the lungs...
because the incisional pain associated with thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
leads to a decreased ability of patients to cough and clear bronchial secretions, which in turn leads to an increased risk of persistent atelectasis
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is defined as the collapse or closure of alveoli resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It may affect part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation.It is a very common finding in chest x-rays and other...
(collapsed areas of lung) or pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
. Finally, to allow time for the divided muscles and bone fractures to heal, patients must refrain from strenuous activity or lifting greater than 5 lbs for 6 weeks after surgery.
The advent of VATS (video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery)
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgeryVideo-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery is a type of thoracic surgery performed using a small video camera that is introduced into the patient's chest via a scope. The surgeon is able to view the instruments that are being used along with the anatomy on which the surgeon is operating...
, or VATS, came into widespread use in the 1990's and early on in its development practitioners began to perform lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
via VATS incisions. The advantage of VATS over thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
is that major chest wall muscles are not divided and ribs are not spread. This leads to reductions in the intensity and duration of post-operative pain and allows patients to return to full activity more quickly.
VATS for lung cancer surgery
VATS lobectomy is the same as lobectomy performed via thoracotomy in that the pulmonary arteryPulmonary artery
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs. They are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood....
, pulmonary vein
Pulmonary vein
The pulmonary veins are large blood vessels that carry blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. In humans there are four pulmonary veins, two from each lung...
, and bronchus
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The bronchus branches into smaller tubes, which in turn become bronchioles....
to the involved pulmonary lobe
Lobe (anatomy)
In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension that can be determined without the use of a microscope This is in contrast to a lobule, which is a clear division only visible histologically....
are individually dissected, ligated and divided. Generally, endoscopic stapling devices are used to ligate and divide the vessels and the bronchus
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The bronchus branches into smaller tubes, which in turn become bronchioles....
however conventional suture material can also be used. During VATS lobectomy, the structures being operated on are not directly visualized with the naked eye but are visualized solely with a fiberoptic thoracoscope. A camera
Camera
A camera is a device that records and stores images. These images may be still photographs or moving images such as videos or movies. The term camera comes from the camera obscura , an early mechanism for projecting images...
attached to the thoracoscope transmits the image to a video screen, which allows surgeons and assistants to observe the flow of the operation. Surgical specimens are placed into a water-tight bag and removed from the chest without morcellization (i.e. breaking up the specimen into small pieces before removal); this prevents seeding of the VATS incisions with tumor cells and allows for an intact specimen for pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
examination and cancer staging
Cancer staging
The stage of a cancer is a description of the extent the cancer has spread. The stage often takes into account the size of a tumor, how deeply it has penetrated, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many lymph nodes it has metastasized to , and whether it has spread to distant organs...
. Removal of lymph nodes from the mediastinum
Mediastinum
The mediastinum is a non-delineated group of structures in the thorax, surrounded by loose connective tissue. It is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity...
is not compromised by VATS and remains a cornerstone of the surgical therapy of lung cancer. Visualization is enhanced due to the magnification afforded by the fiberoptic thoracoscope and a 30 degree angle of visualization aids in looking around corners. However, because the incisions are too small to allow passage of the surgeon’s hands into the thorax, the surgeon’s tactile input is compromised. VATS operations rely on a thorough understanding of pulmonary anatomy to allow for strategically placed incisions (usually 3-5 incisions total). The main advantages of VATS over thoracotomy are that major muscles of the chest wall are not divided and rib spreaders that can lead to rib fractures or costovertebral joint pain are not used. This results in a hospital length of stay after VATS lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
generally reported to range from 3–5 days, or roughly half that for lobectomy via thoracotomy.
Candidates for VATS lobectomy
Not all patients are candidates for VATS lobectomy. The classic indication for a VATS approach to lobectomy is early stage lung cancerLung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
in which the primary tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
is 3 cm or less in diameter and located toward the periphery of the lung parenchyma
Parenchyma
Parenchyma is a term used to describe a bulk of a substance. It is used in different ways in animals and in plants.The term is New Latin, f. Greek παρέγχυμα - parenkhuma, "visceral flesh", f. παρεγχεῖν - parenkhein, "to pour in" f. para-, "beside" + en-, "in" + khein, "to pour"...
. Tumors that are located close to the major blood vessels or airway where these enter the lung or larger tumors associated with tumor spread to lymph nodes in the central regions of the lung may require the enhanced tactile input afforded by thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
to make sure the tumors are resected with a negative margin, i.e. that the tumor is surrounded completely by a margin of non-cancerous tissue, and that arteries and airways to portions of the lung that are not being removed are preserved intact. In addition, patients who have had pre-operative chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
or radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
for lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
or previous chest surgeries may not be candidates for VATS due to scarring around the major blood vessels that makes dissection via VATS difficult. Cases in which a lung tumor invades the chest wall and an en bloc resection of ribs must be performed to achieve negative resection margins generally are felt to abrogate the value of VATS. Finally, pneumonectomy
Pneumonectomy
A pneumonectomy is a surgical procedure to remove a lung. Removal of just one lobe of the lung is specifically referred to as a lobectomy, and that of a segment of the lung as a wedge resection .-Indications:...
by VATS, though it has been reported, is generally not performed because the size of the specimen requires a large incision with or without rib spreading for removal, abrogating the value of VATS.
Published benefits of lobectomy performed by VATS versus thoracotomy
Because of the lesser chest wall trauma of VATS compared to thoracotomyThoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
, elderly patients have been shown to tolerate lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
by VATS better than via thoracotomy. Patients who require chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
after surgery have been shown to be more likely to succeed in completing the prescribed course of chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
after VATS lobectomy compared to lobectomy via thoracotomy. Along with the lesser chest wall trauma and improved pulmonary mechanics, a lesser level of cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
disturbance has been reported after VATS lobectomy compared to thoracotomy. From the standpoint of medical economics, VATS lobectomy is less expensive than lobectomy
Lobectomy
Lobectomy means surgical excision of a lobe. This may refer to a lobe of the lung, a lobe of the thyroid , or a lobe of the brain ....
performed via thoracotomy
Thoracotomy
Thoracotomy is an incision into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by a surgeon, and, rarely, by emergency physicians, to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the heart, the lungs, the esophagus or thoracic aorta, or for access to the anterior spine such as is necessary...
because hospital length of stay
Length of stay
Length of stay is a term commonly used to measure the duration of a single episode of hospitalization. Inpatient days are calculated by subtracting day of admission from day of discharge. However, persons entering and leaving a hospital on the same day have a length of stay of one...
and number of days in the intensive care unit
Intensive Care Unit
thumb|220px|ICU roomAn intensive-care unit , critical-care unit , intensive-therapy unit/intensive-treatment unit is a specialized department in a hospital that provides intensive-care medicine...
are significantly reduced.

