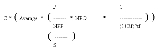
Valuation using multiples
Encyclopedia
Valuation using multiples is a method for determining the current value of a company by examining and comparing the financial ratio
s of relevant peer groups, also often described as comparable company analysis (or comps). The most widely used multiple is the price-earnings ratio
(P/E ratio or PER) of stocks in a similar industry. Using the average of multiple PERs improves reliability but it can still be necessary to correct the PER for current market conditions.
P/E multiples are popular in part due to their wide availability. The value of a business should, however, be reflected in multiples based on enterprise value (EV/EBITDA
, EV/EBIT
, EV/NOPAT
) of a company. These multiples reveal the rating of a business independently of its capital structure, and are the most commonly used in transactions on private companies.
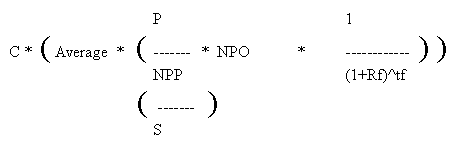
Condition: Peer company is profitable.
Rf = discount rate
during the last forecast year
tf = last year of the forecast period.
C = correction factor
P = current stock Price
NPP = net profit peer company
S = number of shares
NPO = net profit of target company after forecast period
Example:
‘VirusControl’ is an ICT startup that has just finished their business plan. Their goal is to provide professionals with software for simulating virus outbreaks. Their only investor is required to wait for 5 years before making an exit. Therefore VirusControl is using a forecast period of 5 years.
Important characteristics include: operating margin
, company size, products, customer segmentation, growth rate, cash flow
, number of employees, etc.
Example:
VirusControl has identified 4 other companies similar to itself.
Particular attention is paid to companies with P/E ratios substantially higher or lower than the peer group. A P/E far below the average can mean (among other reasons) that the true value of a company has not been identified by the market, that the business model
is flawed, or that the most recent profits include, for example, substantial one-off items. Companies with P/E ratios substantially different from the peers (the outliers) can be removed or other corrective measures used to avoid this problem.
Example:
P/E ratio of companies similar to VirusControl:
One company, PM Software, has substantially lower P/E ratio than the others. Further market research
shows that PM Software has recently acquired a government contract to supply the military with simulating software for the next three years. Therefore VirusControl decides to discard this PER and only use the values of 17.95, 21.7 and 20.8.
Average corrected PER * net profit
at the end of the forecast period.
Example:
VirusControl is expecting a net profit at the end of the fifth year of about € 2.2 million. They use the following calculation to determine their future value:
((17.95 + 21.7 + 20.8) / 3) * 2.200.000 = € 44.3 million
Example:
VirusControl has chosen their discount rate very high as their company is potentially very profitable but also very risky. They calculate their discount factor based on five years.
.
Example:
VirusControl multiplies their future company value with the discount factor:
44,300,000 * 0.1316 = 5,829,880 The company or equity value
of VirusControl : € 5.83 million
Financial ratio
A financial ratio is a relative magnitude of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. Often used in accounting, there are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization...
s of relevant peer groups, also often described as comparable company analysis (or comps). The most widely used multiple is the price-earnings ratio
P/E ratio
The P/E ratio of a stock is a measure of the price paid for a share relative to the annual net income or profit earned by the firm per share...
(P/E ratio or PER) of stocks in a similar industry. Using the average of multiple PERs improves reliability but it can still be necessary to correct the PER for current market conditions.
P/E multiples are popular in part due to their wide availability. The value of a business should, however, be reflected in multiples based on enterprise value (EV/EBITDA
EBITDA
EBITDA is an acronym for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is a non-GAAP metric that is measured exactly as stated. All interest, tax, depreciation and amortization entries in the income statement are reversed out from the bottom-line net income...
, EV/EBIT
Earnings before interest and taxes
In accounting and finance, earnings before interest and taxes is a measure of a firm's profit that excludes interest and income tax expenses. Operating income is the difference between operating revenues and operating expenses...
, EV/NOPAT
NOPAT
In corporate finance, net operating profit after tax or NOPAT is a company's after-tax operating profit for all investors, including shareholders and debt holders. It is equal to NOPLAT and is defined as follows:An alternative formula is as follows...
) of a company. These multiples reveal the rating of a business independently of its capital structure, and are the most commonly used in transactions on private companies.
Mathematics

Condition: Peer company is profitable.
Rf = discount rate
Discount rate
The discount rate can mean*an interest rate a central bank charges depository institutions that borrow reserves from it, for example for the use of the Federal Reserve's discount window....
during the last forecast year
tf = last year of the forecast period.
C = correction factor
P = current stock Price
NPP = net profit peer company
S = number of shares
NPO = net profit of target company after forecast period
Forecast period (finance)
In finance, the forecast period is the time period in which the individual yearly cash flows are input to the discounted cash flow formula. Cash flows after the forecast period can only be represented by a fixed number such as the compound annual growth rate. There are no fixed rules for...
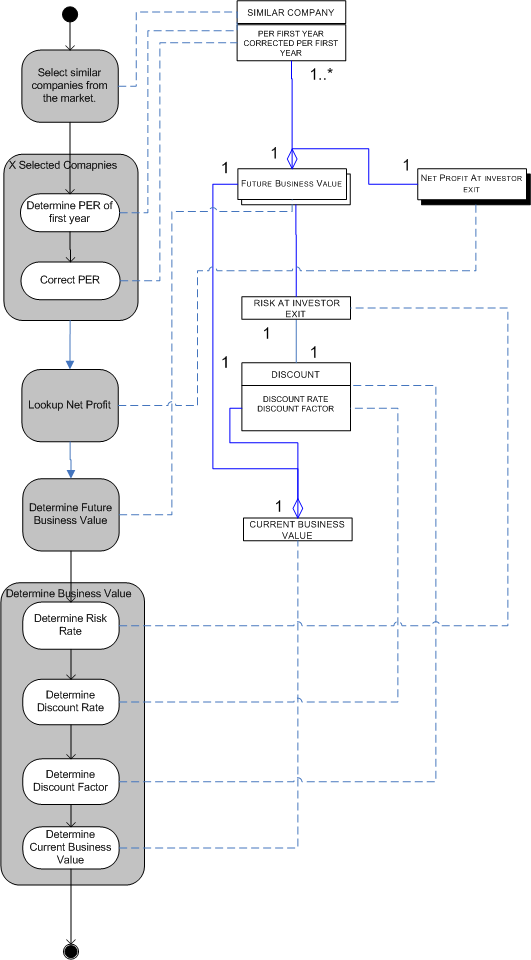
Process Data Diagram
The following diagram shows an overview of the process of company valuation using multiples. All activities in this model are explained in more detail in section 3: Using the Multiples method.
Determine Forecast Period
Determine the year after which the company value is to be known.Example:
‘VirusControl’ is an ICT startup that has just finished their business plan. Their goal is to provide professionals with software for simulating virus outbreaks. Their only investor is required to wait for 5 years before making an exit. Therefore VirusControl is using a forecast period of 5 years.
Identifying peer companies
Search the (stock)market for companies most comparable to the target company. From the investor perspective, a peer universe can also contain companies that are not only direct product competitors but are subject to similar cycles, suppliers and other external factors (e.g. a door and a window manufacturer may be considered peers as well).Important characteristics include: operating margin
Operating margin
In business, operating margin — also known as operating income margin, operating profit margin and return on sales — is the ratio of operating income divided by net sales, usually presented in percent....
, company size, products, customer segmentation, growth rate, cash flow
Cash flow
Cash flow is the movement of money into or out of a business, project, or financial product. It is usually measured during a specified, finite period of time. Measurement of cash flow can be used for calculating other parameters that give information on a company's value and situation.Cash flow...
, number of employees, etc.
Example:
VirusControl has identified 4 other companies similar to itself.
- Medical Sim
- Global Plan
- Virus Solutions
- PM Software
Determining correct Price Earning Ratio (P/E)
The price earnings ratio (P/E) of each identified peer company can be calculated as long as they are profitable. The P/E is calculated as:- P/E = Current Stock Price / (Net Profit / Number of shares)
Particular attention is paid to companies with P/E ratios substantially higher or lower than the peer group. A P/E far below the average can mean (among other reasons) that the true value of a company has not been identified by the market, that the business model
Business model
A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value...
is flawed, or that the most recent profits include, for example, substantial one-off items. Companies with P/E ratios substantially different from the peers (the outliers) can be removed or other corrective measures used to avoid this problem.
Example:
P/E ratio of companies similar to VirusControl:
|
|
Current Stock Price |
Net profit |
Number of Shares |
P/E |
| Medical Sim |
€16.32 |
€1.000.000 |
1.100.000 |
17.95 |
| Global Plan |
€19.50 |
€1.800.000 |
2.000.000 |
21.7 |
| Virus Solutions |
€6.23 |
€3.000.000 |
10.000.000 |
20.8 |
| PM Software |
€12.97 |
€4.000.000 |
2.000.000 |
6.5 |
One company, PM Software, has substantially lower P/E ratio than the others. Further market research
Market research
Market research is any organized effort to gather information about markets or customers. It is a very important component of business strategy...
shows that PM Software has recently acquired a government contract to supply the military with simulating software for the next three years. Therefore VirusControl decides to discard this PER and only use the values of 17.95, 21.7 and 20.8.
Determining future company value
The value of the target company after the forecast period can be calculated by:Average corrected PER * net profit
Net profit
Net profit or net revenue is a measure of the profitability of a venture after accounting for all costs. In a survey of nearly 200 senior marketing managers, 91 percent responded that they found the "net profit" metric very useful...
at the end of the forecast period.
Example:
VirusControl is expecting a net profit at the end of the fifth year of about € 2.2 million. They use the following calculation to determine their future value:
((17.95 + 21.7 + 20.8) / 3) * 2.200.000 = € 44.3 million
Determining discount rate / factor
Determine the appropriate discount rate and factor for the last year of the forecast period based on the risk level associated with the target companyExample:
VirusControl has chosen their discount rate very high as their company is potentially very profitable but also very risky. They calculate their discount factor based on five years.
| Risk Rate |
50% |
| Discount Rate |
50% |
| Discount Factor |
0.1316 |
Determining current company value
Calculate the current value of the future company value by multiplying the future business value with the discount factor. This is known as the time value of moneyTime value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
.
Example:
VirusControl multiplies their future company value with the discount factor:
44,300,000 * 0.1316 = 5,829,880 The company or equity value
Equity value
Equity value is the value of a company available to owners or shareholders. It is the enterprise value plus all cash and cash equivalents, short and long-term investments, and less all short-term debt, long-term debt and minority interests....
of VirusControl : € 5.83 million

