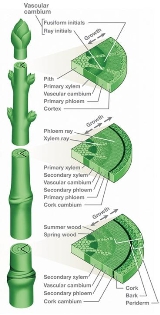
Vascular cambium
Encyclopedia
The vascular cambium is a part of the morphology
of plants. It consists of cells that are partly specialized, for the tissues that transport water solutions, but have not reached any of the final forms that occur in their branch of the specialization graph. When these cells have divided and specialized further they make up the secondary vascular tissues, secondary xylem
and the secondary phloem
.
The vascular cambium is a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue
of plants. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem (inwards, towards the pith) and the secondary phloem
(outwards), and is located between these tissues in the stem and root. A few leaf types also have a vascular cambium.
The vascular cambium usually consists of two types of cells:
The vascular cambium is a type of meristem
- tissue consisting of embryonic (incompletely differentiated) cell
s from which other (more differentiated) plant tissues originate. Primary meristems are the apical meristems on root tips and shoot tips. Another lateral meristem is the cork cambium
, which produces cork, part of the bark
. Together, the secondary vascular tissues (produced by the vascular cambium) and periderm (formed by the cork cambium) makes up the secondary plant body.
Vascular cambia are found in dicots and gymnosperm
s but not monocots, which usually lack secondary growth.
For successful grafting
, the vascular cambia of the stock and scion must be aligned so they can grow together.
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
of plants. It consists of cells that are partly specialized, for the tissues that transport water solutions, but have not reached any of the final forms that occur in their branch of the specialization graph. When these cells have divided and specialized further they make up the secondary vascular tissues, secondary xylem
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue in vascular plants. . The word xylem is derived from the Classical Greek word ξυλον , meaning "wood"; the best-known xylem tissue is wood, though it is found throughout the plant...
and the secondary phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
.
The vascular cambium is a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue
Vascular tissue
Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. There are also two meristems associated with vascular tissue:...
of plants. The vascular cambium is the source of both the secondary xylem (inwards, towards the pith) and the secondary phloem
Phloem
In vascular plants, phloem is the living tissue that carries organic nutrients , in particular, glucose, a sugar, to all parts of the plant where needed. In trees, the phloem is the innermost layer of the bark, hence the name, derived from the Greek word "bark"...
(outwards), and is located between these tissues in the stem and root. A few leaf types also have a vascular cambium.
Origin
Vascular cambium arises from the primary meristem, procambium that remains undifferentiated between the primary xylem and primary phloem. Upon maturity, this region known as the fascicular cambium, and the area of cells between the vascular bundles (fascicles) called pith rays becomes what is called the interfascicular cambium. The fascicular and interfascicular cambiums, therefore, represent a continuous ring which bisects the primary xylem and primary phloem. The vascular cambium then produces secondary xylem on the inside of the ring, and secondary phloem on the outside, pushing the primary xylem and phloem apart.The vascular cambium usually consists of two types of cells:
- Fusiform initials (tall cells, axially oriented)
- Ray initials (almost isodiametric cells - smaller and round to angular in shape)
The vascular cambium is a type of meristem
Meristem
A meristem is the tissue in most plants consisting of undifferentiated cells , found in zones of the plant where growth can take place....
- tissue consisting of embryonic (incompletely differentiated) cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s from which other (more differentiated) plant tissues originate. Primary meristems are the apical meristems on root tips and shoot tips. Another lateral meristem is the cork cambium
Cork cambium
Cork cambium is a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary growth that replaces the epidermis in roots and stems...
, which produces cork, part of the bark
Bark
Bark is the outermost layers of stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines and shrubs. Bark refers to all the tissues outside of the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner...
. Together, the secondary vascular tissues (produced by the vascular cambium) and periderm (formed by the cork cambium) makes up the secondary plant body.
Vascular cambia are found in dicots and gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s but not monocots, which usually lack secondary growth.
For successful grafting
Grafting
Grafting is a horticultural technique whereby tissues from one plant are inserted into those of another so that the two sets of vascular tissues may join together. This vascular joining is called inosculation...
, the vascular cambia of the stock and scion must be aligned so they can grow together.
External links
- Pictures of Vascular cambium
- Detailed description - James D. Mauseth
- Review: Risopatron JPM, Sun YQ, Jones BJ (2010) The vascular cambium: Molecular control of cellular structure. Protoplasma 247 (3-4):145-161. doi:10.1007/s00709-010-0211-z (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20978810)

