Vega
Overview
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
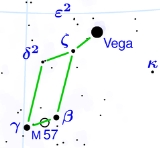
Lyra
Lyra
Lyra is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Its principal star, Vega — a corner of the Summer Triangle — is one of the brightest...
, the fifth brightest star in the night sky and the second brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere
Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an imaginary sphere of arbitrarily large radius, concentric with the Earth and rotating upon the same axis. All objects in the sky can be thought of as projected upon the celestial sphere. Projected upward from Earth's equator and poles are the...
, after Arcturus. It is a relatively close star at only 25 light-years from Earth, and, together with Arcturus and Sirius
Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
, one of the most luminous stars in the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
's neighborhood.
Vega has been extensively studied by astronomers, leading it to be termed "arguably the next most important star in the sky after the Sun." Vega was the northern pole star
Pole star
The term "Pole Star" usually refers to Polaris, which is the current northern pole star, also known as the North Star.In general, however, a pole star is a visible star, especially a prominent one, that is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation; that is, a star whose apparent...
around 12,000 BC and will be so again around AD 13,727 when the declination will be +86°14'.

