
Ventilation (physiology)
Encyclopedia
In respiratory physiology
, ventilation (or ventilation rate) is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung
. It is categorized under the following definitions:
Pulmonary ventilation may be evaluated using a breathing tube or spirometer
, measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal walls using respiratory inductance plethysmography
or by isolating the subject in an enclosed metabolic chamber.
Respiratory physiology
Respiratory physiology is the branch of human physiology focusing upon respiration.Topics include:-Volumes:* lung volumes* vital capacity* functional residual capacity* dead space* spirometry* body plethysmography* peak flow meter-Mechanics:...
, ventilation (or ventilation rate) is the rate at which gas enters or leaves the lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
. It is categorized under the following definitions:
| Measurement | Symbol | Equation | Description >- | Minute ventilation |
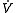 |
= tidal volume Tidal volume Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:... * respiratory rate Respiratory rate Respiratory rate is also known by respiration rate, pulmonary ventilation rate, ventilation rate, or breathing frequency is the number of breaths taken within a set amount of time, typically 60 seconds.... |
>- | 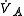 |
= (tidal volume Tidal volume Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:... - dead space) * respiratory rate Respiratory rate Respiratory rate is also known by respiration rate, pulmonary ventilation rate, ventilation rate, or breathing frequency is the number of breaths taken within a set amount of time, typically 60 seconds.... |
>- |  |
= dead space * respiratory rate Respiratory rate Respiratory rate is also known by respiration rate, pulmonary ventilation rate, ventilation rate, or breathing frequency is the number of breaths taken within a set amount of time, typically 60 seconds.... |
is the volume of gas per unit time that does not reach these respiratory portions, but instead remains in the airways (trachea Vertebrate trachea In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus... , bronchi, etc.). |
Sample values
| Measure | Sample value at rest | Sample value moderate exercise |
|---|---|---|
| Tidal volume Tidal volume Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:... |
0.5 L | 3.0 L |
| Respiratory rate Respiratory rate Respiratory rate is also known by respiration rate, pulmonary ventilation rate, ventilation rate, or breathing frequency is the number of breaths taken within a set amount of time, typically 60 seconds.... |
12 breaths/minute | 30 breaths/minute |
| Minute ventilation Respiratory minute volume Respiratory minute volume is the volume of gas inhaled or exhaled from a person's lungs in one minute. It is an important parameter in respiratory medicine due to its relationship with blood carbon dioxide levels... |
6.0 L/min | 90 L/min |
| Dead space Dead space In physiology, dead space is air that is inhaled by the body in breathing, but does not take part in gas exchange. Not all the air in each breath is able to be used for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. About a third of every resting breath has no change in O2 and CO2 levels... |
0.15 L | 0.15 L |
| Dead space ventilation | 1.8 L/min | 4.5 L/min |
| Alveolar ventilation | 4.2 L/min | 85.5 L/min |
Pulmonary ventilation may be evaluated using a breathing tube or spirometer
Spirometer
A spirometer is an apparatus for measuring the volume of air inspired and expired by the lungs. It is a precision differential pressure transducer for the measurements of respiration flow rates. The spirometer records the amount of air and the rate of air that is breathed in and out over a...
, measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal walls using respiratory inductance plethysmography
Respiratory inductance plethysmography
Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography is a method of evaluating pulmonary ventilation by measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal wall....
or by isolating the subject in an enclosed metabolic chamber.
External links
- RT Corner (Educational Site for RT's and Nurses) at rtcorner.net

