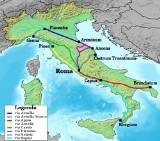
Via Aemilia
Encyclopedia
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
in the north Italian plain, running from Ariminum (Rimini
Rimini
Rimini is a medium-sized city of 142,579 inhabitants in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy, and capital city of the Province of Rimini. It is located on the Adriatic Sea, on the coast between the rivers Marecchia and Ausa...
), on the Adriatic coast, to Placentia (Piacenza
Piacenza
Piacenza is a city and comune in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Piacenza...
) on the river Padus (Po
Po River
The Po |Ligurian]]: Bodincus or Bodencus) is a river that flows either or – considering the length of the Maira, a right bank tributary – eastward across northern Italy, from a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face...
). It was completed in 187 BC
187 BC
Year 187 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lepidus and Flaminius...
. The Via Aemilia connected at Rimini with the Via Flaminia
Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to Ariminum on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had for travel between Etruria, Latium and Campania and the Po Valley...
to Rome, which had been completed 33 years earlier.
History
The land today known as northern Italy (Italia settentrionale) was known to the ancient Romans during the republican period (to 44 BC44 BC
Year 44 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Friday or Saturday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
) as Gallia Cisalpina (literally: Gaul on the near - i.e. southern - side of the Alps). This is because it was then inhabited by Celtic tribes from Gaul, who had colonised the area in the 5th and 4th centuries BC. Italia meant the area inhabited by Italic tribes: the border between Italia and Gallia Cisalpina was roughly a line between Pisae (Pisa) and Ariminum.
Gallia Cisalpina contained the Pianura padana (Po river plain). This vast country, by far the largest fertile plain in the mountainous peninsula, contained potentially its best agricultural land, and offered the Romans the opportunity to expand enormously their population and economic resources by mass colonisation.

220 BC
Year 220 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Laevinus/Catulus and Scaevola/Philo...
, the Via Flaminia was completed, providing the Romans with ready access to the region. The Via Aemilia would probably have followed within the next century.
However, Roman expansion was delayed for some twenty years by the Second Punic War
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War, also referred to as The Hannibalic War and The War Against Hannibal, lasted from 218 to 201 BC and involved combatants in the western and eastern Mediterranean. This was the second major war between Carthage and the Roman Republic, with the participation of the Berbers on...
. During the Carthaginian general Hannibal's invasion of Italy (218 BC
218 BC
Year 218 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Scipio and Longus...
-203 BC
203 BC
Year 203 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caepio and Geminus...
), Roman military control of the Pianura Padana was temporarily overthrown. Many of the recently defeated tribes (such as the Insubres
Insubres
The Insubres were a Gaulish population settled in Insubria, in what is now Lombardy . They were the founders of Milan . Though ethnically Celtic at the time of Roman conquest , they were most likely the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian, Celtic and "Italic" population strata with Gaulish...
and the Boii
Boii
The Boii were one of the most prominent ancient Celtic tribes of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul , Pannonia , in and around Bohemia, and Transalpine Gaul...
) rebelled and joined forces with Hannibal in the hope of regaining their independence. It was not until 189 BC
189 BC
Year 189 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Nobilior and Vulso...
that the rebel tribes had been pacified sufficiently to allow work on the Via Aemilia to begin.
The time-tested Roman method of expansion was to build a brand new road straight through the newly-conquered territory, and then establish a string of colonies, either of civilian settlers or of military veterans along its route. The settlers would be allocated fertile plots from lands confiscated from the defeated native peoples. This was the precise function of the Via Aemilia: its period of construction also saw the foundation of Roman colonies along its whole length at Bononia (Bologna
Bologna
Bologna is the capital city of Emilia-Romagna, in the Po Valley of Northern Italy. The city lies between the Po River and the Apennine Mountains, more specifically, between the Reno River and the Savena River. Bologna is a lively and cosmopolitan Italian college city, with spectacular history,...
) (founded 189 BC), Mutina (Modena
Modena
Modena is a city and comune on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy....
), Regium (Reggio Emilia
Reggio Emilia
Reggio Emilia is an affluent city in northern Italy, in the Emilia-Romagna region. It has about 170,000 inhabitants and is the main comune of the Province of Reggio Emilia....
) and Parma
Parma
Parma is a city in the Italian region of Emilia-Romagna famous for its ham, its cheese, its architecture and the fine countryside around it. This is the home of the University of Parma, one of the oldest universities in the world....
(all founded in 183 BC
183 BC
Year 183 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcellus and Labeo...
).


Rubicon
The Rubicon is a shallow river in northeastern Italy, about 80 kilometres long, running from the Apennine Mountains to the Adriatic Sea through the southern Emilia-Romagna region, between the towns of Rimini and Cesena. The Latin word rubico comes from the adjective "rubeus", meaning "red"...
crossed by Julius Caesar in 49 BC
49 BC
Year 49 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Lentulus and Marcellus...
; and the river Trebbia near Piacenza, site of the first of Hannibal's three major victories over the Romans during his invasion of Italy.
In the century following the construction of the Via Aemilia, Piacenza became the key Roman road hub in the pianura padana. In 148 BC
148 BC
Year 148 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magnus and Caesoninus...
, the Via Postumia
Via Postumia
The Via Postumia was an ancient Roman road of northern Italy constructed in 148 BC by the consul Spurius Postumius Albinus Magnus.It ran from the coast at Genua through the mountains to Dertona, Placentia and Cremona, just east of the point where it crossed the Po River...
linked Piacenza to Aquileia
Aquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in what is now Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about 10 km from the sea, on the river Natiso , the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times...
on the north Adriatic coast. In 109 BC
109 BC
Year 109 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Numidicus and Silanus...
, the consul Marcus Aemilius Scaurus completed the Via Aemilia Scaura to Genua (Genoa) and Pisae (Pisa).
Remains
At Rimini, the starting point of the Via Aemilia, the road's first bridge still exists, a massive structure spanning the MarecchiaMarecchia
The Marecchia is a river in eastern Italy. In ancient times it was known as the Ariminus which was from the Greek Ariminos, Αριμινος . The source of the river is east of Pieve Santo Stefano and southwest of Badia Tedalda in the province of Arezzo in Tuscany...
River, started by the Emperor Augustus and completed by his successor Tiberius. It still bears its twin dedicatory inscriptions. At Bologna, milestone 78 was found in the bed of the river Reno
Reno
Reno is the fourth most populous city in Nevada, US.Reno may also refer to:-Places:Italy*The Reno River, in Northern ItalyCanada*Reno No...
. It records Augustus' reconstruction of the Aemilia, in 2 BC
2 BC
Year 2 BC was a common year starting on Thursday or Friday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
, from Rimini as far as the river Trebbia. Remains of the Aemilia bridge over the Reno were found in the 1890s, consisting of parts of the parapets from each side. These were originally 38.75 feet apart, of Veronese red marble. The bed of the river was found to have risen at least 20 feet since this bridge collapsed in the 9th century. Ruins of some of the other ancient Roman bridges still exist. At Savignano sul Rubicone
Savignano sul Rubicone
Savignano sul Rubicone is a comune in the Province of Forlì-Cesena in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about 90 km southeast of Bologna and about 30 km southeast of Forlì....
a Roman bridge survived until it was demolished as recently as World War II. The current bridge is a reconstruction.
Legacy
The construction of the Via Aemilia launched the intensive Roman colonisation of the Pianura Padana. The vast agricultural potential of this region soon rendered it the most populous and economically important part of Italy, overshadowing Central Italy, Rome and the South. The area remains economically preeminent in modern Italy. By the time of the Second Triumvirate (44 BC-30 BC30 BC
Year 30 BC was either a common year starting on Wednesday, Thursday or Friday or a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Wednesday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
), Romanisation of this formerly Celtic country was so complete that the province of Gallia Cisalpina was abolished and its territory incorporated into the heartland province of Italia
Italia (Roman province)
Italia was the name of the Italian peninsula of the Roman Empire.-Under the Republic and Augustan organization:During the Republic and the first centuries of the empire, Italia was not a province, but rather the territory of the city of Rome, thus having a special status: for example, military...
.
The road gave its name to that part of Gallia Cisalpina through which it ran. This area was, before the Roman conquest, the territory of the Gallic tribes Boii
Boii
The Boii were one of the most prominent ancient Celtic tribes of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul , Pannonia , in and around Bohemia, and Transalpine Gaul...
(who gave their name to the city of Bologna) and Senones
Senones
The Senones were an ancient Gaulish tribe.In about 400 BC they crossed the Alps and, having driven out the Umbrians settled on the east coast of Italy from Forlì to Ancona, in the so-called ager Gallicus, and founded the town of Sena Gallica , which became their capital. In 391 BC they invaded...
. It was already commonly referred to as Aemilia by the time the Emperor Augustus assumed sole power. In around 7 BC
7 BC
Year 7 BC was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Thursday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
, when Augustus divided the provincia of Italia into 11 regiones (administrative districts), the area became the eighth regio. This initially had the official name of Padus, but was later changed to Aemilia.
The western part of this area is still known as Emilia today. The boundaries of the Roman VIII regio roughly corresponded to those of the modern Italian administrative region of Emilia-Romagna
Emilia-Romagna
Emilia–Romagna is an administrative region of Northern Italy comprising the two historic regions of Emilia and Romagna. The capital is Bologna; it has an area of and about 4.4 million inhabitants....
. Its inhabitants are today known as Emiliani. The modern Italian State Road 9 is still officially called Via Emilia and follows the Roman route over much of its length. Indeed, the modern road in many parts lies directly above the Roman road.
Bridges
- For an overview of the location of Roman bridges, see List of Roman bridges.
There are the remains of several Roman bridges along the road, including the Ponte d’Augusto
Pons Augustus
The Ponte d'Augusto or Bridge of Tiberius is a Roman bridge in Rimini, Italy. The bridge features five semicircular arches with an average span length of ca. 8 m...
, Ponte di Sant’Arcangelo di Romagna, Ponte San Vito, Ponte sul Reno and Ponte sul Rubicone.

