
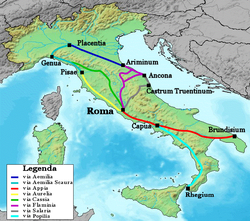
Via Cassia
Encyclopedia
Roman road
The Roman roads were a vital part of the development of the Roman state, from about 500 BC through the expansion during the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. Roman roads enabled the Romans to move armies and trade goods and to communicate. The Roman road system spanned more than 400,000 km...
striking out of the Via Flaminia
Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to Ariminum on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had for travel between Etruria, Latium and Campania and the Po Valley...
near the Milvian Bridge in the immediate vicinity of Rome and, passing not far from Veii
Veii
Veii was, in ancient times, an important Etrurian city NNW of Rome, Italy; its site lies in Isola Farnese, a village of Municipio XX, an administrative subdivision of the comune of Rome in the Province of Rome...
traversed Etruria
Etruria
Etruria—usually referred to in Greek and Latin source texts as Tyrrhenia—was a region of Central Italy, an area that covered part of what now are Tuscany, Latium, Emilia-Romagna, and Umbria. A particularly noteworthy work dealing with Etruscan locations is D. H...
. The Via Cassia passed through Baccanae, Sutrium
Sutri
Sutri is a town and comune in the province of Viterbo, about 50 km from Rome, and about 30 km south of Viterbo. It is picturesquely situated on a narrow tuff hill, surrounded by ravines, a narrow neck on the west alone connecting it with the surrounding country.thumb|220px|Entrance to the...
, Vulsinii
Bolsena
Bolsena is a town and comune of Italy, in the province of Viterbo in northern Lazio on the eastern shore of Lake Bolsena. It is 10 km north-north west of Montefiascone and 36 km north-west of Viterbo...
, Clusium
Clusium
Clusium was an ancient city in Italy, one of several found at the site. The current municipality of Chiusi partly overlaps this Roman walled city. The Roman city remodeled an earlier Etruscan city, Clevsin, found in the territory of a prehistoric culture, possibly also Etruscan or proto-Etruscan...
, Arretium
Arezzo
Arezzo is a city and comune in Central Italy, capital of the province of the same name, located in Tuscany. Arezzo is about 80 km southeast of Florence, at an elevation of 296 m above sea level. In 2011 the population was about 100,000....
, Florentia
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
, Pistoria
Pistoia
Pistoia is a city and comune in the Tuscany region of Italy, the capital of a province of the same name, located about 30 km west and north of Florence and is crossed by the Ombrone Pistoiese, a tributary of the River Arno.-History:...
, and Luca
Lucca
Lucca is a city and comune in Tuscany, central Italy, situated on the river Serchio in a fertile plainnear the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Lucca...
, joining the Via Aurelia
Via Aurelia
The Via Aurelia was a Roman road in Italy constructed around the year 241 BC. The project was undertaken by C. Aurelius Cotta, who at that time was censor...
at Luna
Luni
Luni can refer to:* Luni, Italy, a town in Liguria* Luni, Pakistan, village in Pakistan* Luni, Rajasthan, village in Rajasthan, India* Luni River, in Rajasthan, India* Luni Coleone, a rapper from California...
.
Via Amerina
The Via Amerina was a road that broke off from the Via Cassia near Baccanae, and held north through Falerii, TuderTodi
Todi is a town and comune of the province of Perugia in central Italy. It is perched on a tall two-crested hill overlooking the east bank of the river Tiber, commanding distant views in every direction.In the 1990s, Richard S...
, and Perusia
Perugia
Perugia is the capital city of the region of Umbria in central Italy, near the River Tiber, and the capital of the province of Perugia. The city is located about north of Rome. It covers a high hilltop and part of the valleys around the area....
, rejoining the Via Cassia at Clusium
Clusium
Clusium was an ancient city in Italy, one of several found at the site. The current municipality of Chiusi partly overlaps this Roman walled city. The Roman city remodeled an earlier Etruscan city, Clevsin, found in the territory of a prehistoric culture, possibly also Etruscan or proto-Etruscan...
. When the incursions of Faroald, the Lombard Duke of Spoleto, cut the Via Flaminia
Via Flaminia
The Via Flaminia was an ancient Roman road leading from Rome over the Apennine Mountains to Ariminum on the coast of the Adriatic Sea, and due to the ruggedness of the mountains was the major option the Romans had for travel between Etruria, Latium and Campania and the Po Valley...
, the lifeline between Rome and Ravenna, the Via Amerina was improved and fortified at intervals, works that represented some of the last road-building carried out in Italy in Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity is a periodization used by historians to describe the time of transition from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages, in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world. Precise boundaries for the period are a matter of debate, but noted historian of the period Peter Brown proposed...
. As the new military and strategic route, the Via Amerina "became the communications core of Imperial Italy and the chief support to the claim that imperial Italy was still extant."
Bridges
- For an overview of the location of Roman bridges, see List of Roman bridges.
There are the remains of several Roman bridge
Roman bridge
Roman bridges, built by ancient Romans, were the first large and lasting bridges built. Roman bridges were built with stone and had the arch as its basic structure....
s along the road, including the Ponte San Lorenzo and Ponte San Nicolao.
Sport
The road was used as part of the individual road race cyclingCycling at the 1960 Summer Olympics
The cycling competition at the 1960 Summer Olympics consisted of two road cycling events and four track cycling events, all for men only.-Medal table:-Medal summary:-References:*...
route for the 1960 Summer Olympics
1960 Summer Olympics
The 1960 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVII Olympiad, was an international multi-sport event held from August 25 to September 11, 1960 in Rome, Italy...
in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
.
External links
- 1960 Summer Olympics official report. Volume 1. p. 84.
- 1960 Summer Olympics official report. Volume 2. Part 2. p. 319.
- LacusCurtius - "Viae" (Smith's Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities 1875)

