
Village Inn (codename)
Encyclopedia

United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
Automatic Gun-Laying
Gun laying
Gun laying is the process of aiming an artillery piece, such as a gun, howitzer or mortar on land or at sea against surface or air targets. It may be laying for direct fire, where the gun is aimed similarly to a rifle, or indirect fire, where firing data is calculated and applied to the sights...
Turret (AGLT) was a radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
-aimed FN121 turret fitted to some Lancaster
Avro Lancaster
The Avro Lancaster is a British four-engined Second World War heavy bomber made initially by Avro for the Royal Air Force . It first saw active service in 1942, and together with the Handley Page Halifax it was one of the main heavy bombers of the RAF, the RCAF, and squadrons from other...
and Halifax
Handley Page Halifax
The Handley Page Halifax was one of the British front-line, four-engined heavy bombers of the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. A contemporary of the famous Avro Lancaster, the Halifax remained in service until the end of the war, performing a variety of duties in addition to bombing...
bombers in 1944. The AGLT system was devised to allow a target to be tracked and fired-on in total darkness
Darkness
Darkness, in contrast with brightness, is a relative absence of visible light. It is the appearance of black in a color space. When light is not present, rod and cone cells within the eye are not stimulated. This lack of stimulation means photoreceptor cells are unable to distinguish color...
, the target's range being accurately computed as well as allowing for lead
Deflection (military)
Deflection is a technique used for effectively firing a ranged weapon at a moving target, that describes "leading the target"; that is, shooting ahead of a moving target so that the target and projectile will collide...
and bullet drop. The system was referred to by the codename Village Inn during development.
The system, known as TR3548, was devised by a team led by Dr Philip Dee
Philip Dee
Philip Ivor Dee was a British physicist. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1941 and won its Hughes Medal in 1952...
and designed under the aegis of Chief Designer Dr Alan Hodgkin
Alan Lloyd Hodgkin
Sir Alan Lloyd Hodgkin, OM, KBE, PRS was a British physiologist and biophysicist, who shared the 1963 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine with Andrew Huxley and John Eccles....
, after receiving a request from the Air Ministry
Air Ministry
The Air Ministry was a department of the British Government with the responsibility of managing the affairs of the Royal Air Force, that existed from 1918 to 1964...
for such a system in early 1943. Village Inn was evaluated and tested by the Telecommunications Research Establishment
Telecommunications Research Establishment
The Telecommunications Research Establishment was the main United Kingdom research and development organization for radio navigation, radar, infra-red detection for heat seeking missiles, and related work for the Royal Air Force during World War II and the years that followed. The name was...
(TRE) at RAF Defford
RAF Defford
RAF Defford was a Royal Air Force station in Worcestershire, England during the Second World War.Construction of RAF Defford was completed in 1941, and for a few months the airfield was used as a satellite station by the Wellington bombers of 23 Operational Training Unit , based a few miles away...
using the Lancaster Mark I ND712
Serial number
A serial number is a unique number assigned for identification which varies from its successor or predecessor by a fixed discrete integer value...
and the Lancaster Mark IIIs JB705 and LL737 and subsequently put into production.
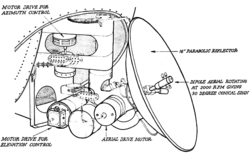
The system consisted of a transmitter
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
/receiver
Receiver (radio)
A radio receiver converts signals from a radio antenna to a usable form. It uses electronic filters to separate a wanted radio frequency signal from all other signals, the electronic amplifier increases the level suitable for further processing, and finally recovers the desired information through...
unit mounted in the navigator's compartment, operating through a conical scanning
Conical scanning
Conical scanning is a system used in early radar units to improve their accuracy, as well as making it easier to steer the antenna properly to point at a target...
parabolic aerial
Antenna (radio)
An antenna is an electrical device which converts electric currents into radio waves, and vice versa. It is usually used with a radio transmitter or radio receiver...
attached to the standard Fraser-Nash turret. It worked on a wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
of 9.1 cm (3 GHz
GHZ
GHZ or GHz may refer to:# Gigahertz .# Greenberger-Horne-Zeilinger state — a quantum entanglement of three particles.# Galactic Habitable Zone — the region of a galaxy that is favorable to the formation of life....
) with a pulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency
Pulse repetition frequency or Pulse repetition rate is the number of pulses per time unit . It is a measure or specification mostly used within various technical disciplines Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) or Pulse repetition rate (PRR) is the number of pulses per time unit (e.g. Seconds). It...
of 660 hertz. The magnetron
Cavity magnetron
The cavity magnetron is a high-powered vacuum tube that generates microwaves using the interaction of a stream of electrons with a magnetic field. The 'resonant' cavity magnetron variant of the earlier magnetron tube was invented by John Randall and Harry Boot in 1940 at the University of...
used was the CV.186 of approx 35kW
Kw
kw or KW may refer to:* Kuwait, ISO 3166-1 country code** .kw, the country code top level domain for Kuwait* Kilowatt* Self-ionization of water Kw* Cornish language's ISO 639 code* Kitchener–Waterloo, Ontario, Canada...
. The electronics sent a signal back to the turret, where it was displayed on a cathode ray tube
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
(CRT) display screen positioned adjacent to the gun sight, the image of which was projected on to the Mark IIC gyro gunsight
Gyro gunsight
A gyro gunsight is a modification of the non-magnifying reflector sight in which target lead and bullet drop are allowed for automatically, the sight incorporating a gyroscopic mechanism that computes the necessary deflections required to ensure a hit on the target...
via a semi-transparent mirror.
Initially, ranging information was provided only at the transmitter situated in the navigator's compartment and was read-off to the gunner over the intercom
Intercom
An intercom , talkback or doorphone is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings, functioning independently of the public telephone network. Intercoms are generally mounted permanently in buildings and vehicles...
, the gunner using foot pedals to set the target range on the sight. In production equipment the process was made automatic, the range information being fed electronically directly into the gunsight, with the navigator's "running commentary" only being retained for the benefit of the rest of the crew. The gunner simply maneuvered his guns to place the "blip" in the center of the gunsight's reticle, and opened fire when the range was appropriate. Windage, bullet drop and other factors were already calculated by the gunsight.
No. 101 Squadron RAF
No. 101 Squadron of the Royal Air Force operates the Vickers VC10 C1K, K3 and K4 from RAF Brize Norton, Oxfordshire. Since 10 Squadron disbanded in 2005, the squadron is the only operator of the VC10.-Formation and early years:...
, based at Ludford Magna
RAF Ludford Magna
RAF Ludford Magna was a Royal Air Force airfield operated by Bomber Command during World War II and the Cold War. The station lay on agricultural farmland immediately south of the village of Ludford, Lincolnshire and was sited 21.4 miles north east of the county town of Lincoln, Lincolnshire...
, in the autumn of 1944, followed soon afterwards by No. 49
No. 49 Squadron RAF
No. 49 Squadron was a bomber squadron of the Royal Air Force from 1938 to 1965. They received their first Hampdens in September 1938.They were a famous Hampden squadron; with the only Victoria Cross awarded Rod Learoyd amongst the ones who served on the type....
in the attack on Darmstadt
Bombing of Darmstadt in World War II
Darmstadt was bombed a number of times during World War II. The most devastating air raid on Darmstadt occurred on the night of 11/12 September 1944 when No. 5 Group the Royal Air Force bombed the city....
on September 11/12, 156
No. 156 Squadron RAF
No. 156 Squadron RAF was a Royal Air Force Squadron that was active as a bomber unit in World War II.-Formation and World War I:No. 156 Squadron Royal Air Force was first formed on 12 October 1918 at RAF Wyton and equipped with DH 9 aircraft, but was disbanded on 9 December 1918 without becoming...
and 635
No. 635 Squadron RAF
No. 635 Squadron RAF was a heavy bomber squadron of the Royal Air Force during the Second World War.-History:635 squadron was formed at RAF Downham Market in Norfolk on 20 March 1944 from two flights drawn from No. 35 Squadron and No. 97 Squadron, equipped with Lancaster Mk.I bombers, as part of...
Squadrons.
Village Inn was eventually produced in four Marks:
AGLT Mark I - initial design - Airborne Radio Installation (ARI) 5559.
AGLT Mark II - modified, improved, Mark I - soon discontinued - ARI 5561.
AGLT Mark III - scanning aerial mounted remotely from turret. Scan independent of turret's movements - ARI 5562.
AGLT Mark IV - ARI 5632
The system was also fitted to the Rose Rice twin gun 0.5in turret on at least one Avro Lincoln B.Mk II
Avro Lincoln
The Avro Type 694, better known as the Avro Lincoln, was a British four-engined heavy bomber, which first flew on 9 June 1944. Developed from the Avro Lancaster, the first Lincoln variants were known initially as the Lancaster IV and V, but were renamed Lincoln I and II...
, although how many so-fitted is not known at present. Some Lincolns fitted with the Boulton Paul Type D tail turret also incorporated the equipment.
A similar type of system was produced in the US
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
by the Emerson
Emerson Electric Company
Emerson Electric Company is a major multinational corporation headquartered in Ferguson, Missouri, United States. This Fortune 500 company manufactures products and provides engineering services for a wide range of industrial, commercial, and consumer markets.Emerson is one of the largest...
Company, St Louis
St. Louis, Missouri
St. Louis is an independent city on the eastern border of Missouri, United States. With a population of 319,294, it was the 58th-largest U.S. city at the 2010 U.S. Census. The Greater St...
, when an Emerson Model III tail turret was equipped with the Emerson APG8 Blind Tracking Radar and fitted to the Canadian-built Lancaster KB805. The system was found to have no advantages over the British system and the project was subsequently dropped.
See also
- Telecommunications Research EstablishmentTelecommunications Research EstablishmentThe Telecommunications Research Establishment was the main United Kingdom research and development organization for radio navigation, radar, infra-red detection for heat seeking missiles, and related work for the Royal Air Force during World War II and the years that followed. The name was...
- RAF DeffordRAF DeffordRAF Defford was a Royal Air Force station in Worcestershire, England during the Second World War.Construction of RAF Defford was completed in 1941, and for a few months the airfield was used as a satellite station by the Wellington bombers of 23 Operational Training Unit , based a few miles away...
- List of World War II electronic warfare equipment
External links
- A photograph of a Village Inn-equipped 635 Sqn Lancaster
- Illustration of a 460 Sqn Lancaster I/III fitted with Village Inn
- http://1000aircraftphotos.com/Contributions/7800L-4.jpgA photograph of a Village Inn-equipped Rose Rice turret on an Avro LincolnAvro LincolnThe Avro Type 694, better known as the Avro Lincoln, was a British four-engined heavy bomber, which first flew on 9 June 1944. Developed from the Avro Lancaster, the first Lincoln variants were known initially as the Lancaster IV and V, but were renamed Lincoln I and II...
] - http://www.wolverhamptonhistory.org.uk/people/at_war/ww2/production/turretA photograph of a Village Inn-equipped twin .5 in turret on a Handley Page HalifaxHandley Page HalifaxThe Handley Page Halifax was one of the British front-line, four-engined heavy bombers of the Royal Air Force during the Second World War. A contemporary of the famous Avro Lancaster, the Halifax remained in service until the end of the war, performing a variety of duties in addition to bombing...
] - Village Inn (PDF)
- Eyewitness account of Village Inn testing on 460 Squadron

