
Viscosity of amorphous materials
Encyclopedia
Viscous flow in amorphous materials
(e.g. in glass
es and melts)
is a thermally activated process:
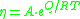
where Q is the activation energy of viscosity, T is temperature, R is the molar gas constant and A is approximately a constant.
The viscous flow in amorphous materials is characterised by a deviation from the Arrhenius-type
behaviour: Q changes from a high value QH at low temperatures (in the glassy state) to a low value QL at high temperatures (in the liquid state). Depending on this change, amorphous materials are classified as either
The fragility of amorphous materials is numerically characterized by the Doremus' fragility ratio:
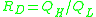
and strong material have ; whereas fragile materials have
The viscosity of amorphous materials is quite exactly described by a two-exponential equation:
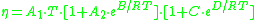
with constants A1, A2, B, C, and D related to thermodynamic parameters of joining bonds of an amorphous material.
Not very far from the glass transition temperature Tg this equation can be approximated by a Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher (VTF) equation or stretched exponent-type equation.
If the temperature is significantly lower than the glass transition temperature , then the two-exponential equation simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation:
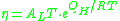
with:
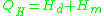
where Hd is the enthalpy of formation of broken bonds (termed configuron s) and Hm is the enthalpy
of their motion.
When the temperature is less than the glass transition temperature,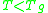 , the activation energy of viscosity is high because the amorphous materials are in the glassy state and most of their joining bonds are intact.
, the activation energy of viscosity is high because the amorphous materials are in the glassy state and most of their joining bonds are intact.
If the temperature is highly above the glass transition temperature,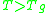 , the two-exponential equation also simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation:
, the two-exponential equation also simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation:
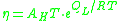
with:
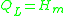
When the temperature is higher than the glass transition temperature , the activation energy of viscosity is low because amorphous materials are melt and have most of their joining bonds broken which facilitates flow.
An example of glass viscosity is given in Calculation of glass properties
, in which the viscosity is around 1012 Pa·s at 400 °C.
Amorphous solid
In condensed matter physics, an amorphous or non-crystalline solid is a solid that lacks the long-range order characteristic of a crystal....
(e.g. in glass
Glass
Glass is an amorphous solid material. Glasses are typically brittle and optically transparent.The most familiar type of glass, used for centuries in windows and drinking vessels, is soda-lime glass, composed of about 75% silica plus Na2O, CaO, and several minor additives...
es and melts)
is a thermally activated process:
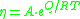
where Q is the activation energy of viscosity, T is temperature, R is the molar gas constant and A is approximately a constant.
The viscous flow in amorphous materials is characterised by a deviation from the Arrhenius-type
Arrhenius equation
The Arrhenius equation is a simple, but remarkably accurate, formula for the temperature dependence of the reaction rate constant, and therefore, rate of a chemical reaction. The equation was first proposed by the Dutch chemist J. H. van 't Hoff in 1884; five years later in 1889, the Swedish...
behaviour: Q changes from a high value QH at low temperatures (in the glassy state) to a low value QL at high temperatures (in the liquid state). Depending on this change, amorphous materials are classified as either
- Strong when:
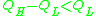 or
or - Fragile when:
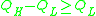
The fragility of amorphous materials is numerically characterized by the Doremus' fragility ratio:
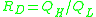
and strong material have ; whereas fragile materials have
The viscosity of amorphous materials is quite exactly described by a two-exponential equation:
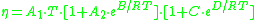
with constants A1, A2, B, C, and D related to thermodynamic parameters of joining bonds of an amorphous material.
Not very far from the glass transition temperature Tg this equation can be approximated by a Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher (VTF) equation or stretched exponent-type equation.
If the temperature is significantly lower than the glass transition temperature , then the two-exponential equation simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation:
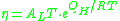
with:
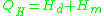
where Hd is the enthalpy of formation of broken bonds (termed configuron s) and Hm is the enthalpy
Enthalpy
Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a...
of their motion.
When the temperature is less than the glass transition temperature,
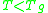 , the activation energy of viscosity is high because the amorphous materials are in the glassy state and most of their joining bonds are intact.
, the activation energy of viscosity is high because the amorphous materials are in the glassy state and most of their joining bonds are intact.If the temperature is highly above the glass transition temperature,
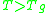 , the two-exponential equation also simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation:
, the two-exponential equation also simplifies to an Arrhenius type equation: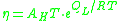
with:
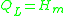
When the temperature is higher than the glass transition temperature , the activation energy of viscosity is low because amorphous materials are melt and have most of their joining bonds broken which facilitates flow.
An example of glass viscosity is given in Calculation of glass properties
Calculation of glass properties
The calculation of glass properties is used to predict glass properties of interest or glass behavior under certain conditions without experimental investigation, based on past data and experience, with the intention to save time, material, financial, and environmental resources, or to gain...
, in which the viscosity is around 1012 Pa·s at 400 °C.

