Visual appearance
Encyclopedia
The visual appearance of objects is given by the way in which they reflect and transmit light
. The color
of objects is determined by the parts of the spectrum
of (incident white) light that are reflected or transmitted without being absorbed. Additional appearance attributes are based on the directional distribution of reflected (BRDF) or transmitted light (BTDF) described by attributes like glossy
, shiny versus dull, matte, clear, turbid
, distinct, etc.
. The reflective properties of the surface can be characterized by a closer look at the (micro)-topography
of that surface.
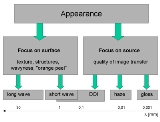
Structures on the surface and the texture of the surface are determined by typical dimensions between some 10 mm and 0.1 mm (the detection limit of the human eye is at ~0.07 mm). Smaller structures and features of the surface cannot be directly detected by the unaided eye, but their effect becomes apparent in objects or images reflected in the surface. Structures at and below 0.1 mm reduce the distinctness of image (DOI), structures in the range of 0.01 mm induce haze and even smaller structures affect the gloss
of the surface.
Transmissive objects
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
. The color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
of objects is determined by the parts of the spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of (incident white) light that are reflected or transmitted without being absorbed. Additional appearance attributes are based on the directional distribution of reflected (BRDF) or transmitted light (BTDF) described by attributes like glossy
Gloss (material appearance)
Gloss is an optical property, which is based on the interaction of light with physical characteristics of a surface. It is actually the ability of a surface to reflect light into the specular direction. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident...
, shiny versus dull, matte, clear, turbid
Turbidity
Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality....
, distinct, etc.
Appearance of reflective objects
The appearance of reflecting objects is determined by the way the surface reflects incident lightLight
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
. The reflective properties of the surface can be characterized by a closer look at the (micro)-topography
Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
of that surface.
Structures on the surface and the texture of the surface are determined by typical dimensions between some 10 mm and 0.1 mm (the detection limit of the human eye is at ~0.07 mm). Smaller structures and features of the surface cannot be directly detected by the unaided eye, but their effect becomes apparent in objects or images reflected in the surface. Structures at and below 0.1 mm reduce the distinctness of image (DOI), structures in the range of 0.01 mm induce haze and even smaller structures affect the gloss
Gloss (material appearance)
Gloss is an optical property, which is based on the interaction of light with physical characteristics of a surface. It is actually the ability of a surface to reflect light into the specular direction. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident...
of the surface.
-
- Definition
diffusion, scatteringScatteringScattering is a general physical process where some forms of radiation, such as light, sound, or moving particles, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by one or more localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of...
: process by which the spatial distribution of a beam of radiation is changed in many directions when it is deviated by a surface or by a medium, without change of frequency of its monochromatic components.
- Definition
| Appearance of Reflective Objects | |
|---|---|
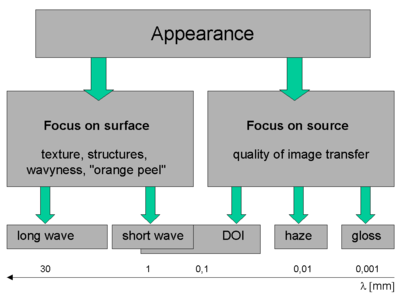 |
Figure 1:Manifestation of surface properties upon reflection of light. Structures with dimensions, λ, above 0,1 mm can be seen directly by the unaided eye (focus on surface), smaller structures become manifest by their effect on the directional distribution of the reflected light (focus on source). Structures at and below 0,1 mm reduce the distinctness of image (DOI), structures in the range of 0,01 mm induce haze and even smaller structures affect the gloss Gloss (material appearance) Gloss is an optical property, which is based on the interaction of light with physical characteristics of a surface. It is actually the ability of a surface to reflect light into the specular direction. The factors that affect gloss are the refractive index of the material, the angle of incident... of the surface. |
Basic types of light reflection
 |
 |
 |
|
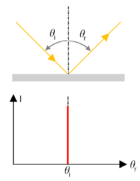
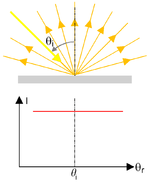
| Figures 2: Illustration of the basic types of reflection – specular (mirror like, left), haze (center) and Lambertian diffuse Diffuse reflection Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light from a surface such that an incident ray is reflected at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection... (right). The geometry is shown in the upper part, the intensity versus angle of inclination of a detector is shown in the lower part of the diagrams. |
|||
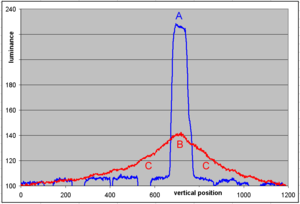
| Figure 3 (left): Light source (fluorescent tube) reflected by a smooth glass surface (left half) and a scattering surface with micro-structures (frosted glass Frosted glass Frosted glass is produced by the sandblasting or acid etching of clear sheet glass. It has the effect of rendering the glass translucent by scattering of light during transmission, thus blurring images while still transmitting light.Applications:... , right half). A distinct image of the lamp is only provided via reflection without scattering. The scattering of the frosted glass Frosted glass Frosted glass is produced by the sandblasting or acid etching of clear sheet glass. It has the effect of rendering the glass translucent by scattering of light during transmission, thus blurring images while still transmitting light.Applications:... slightly increases the reflected luminance in the areas above and below the position of the lamp (indicated by the arrows). This additional luminance is called haze or veiling glare. Figure 4 (right): Profile of reflected luminance from the photo in fig. 3 (top to bottom). The scattering of the frosted glass Frosted glass Frosted glass is produced by the sandblasting or acid etching of clear sheet glass. It has the effect of rendering the glass translucent by scattering of light during transmission, thus blurring images while still transmitting light.Applications:... reduces the luminance reflected in the specular direction (A, peaked blue curve vs. B, red curve), but outside the specular direction (at locations C) the luminance is increased by veiling glare. |
 |
|
Appearance of transmissive objects
| Appearance of Transmissive Objects | |
|---|---|
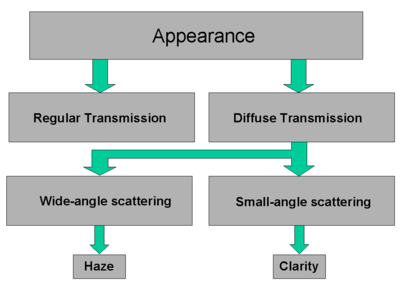 |
Figure 5: Scattering of light during transmission with classification of diffuse transmission into wide and small-angle scattering domains, resulting in haze and reduction of clarity, respectively. |
| Appearance of a Transmissive Object | |
|---|---|
 |
Figure 6: graduation of a ruler as seen through a translucent scattering layer (frosted glass). The original distinctness of image can be seen in the center of the lower graduation (around 0). On the left side the frosted glass is in contact with the ruler surface and it is 4 cm above the ruler surface at the right side of the image. With increasing distance between ruler graduation and scattering layer the blur (haze, also see turbidity Turbidity Turbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality.... ) increases and the distinctness of image Distinctness of image * See alsoVisual_appearanceDistinctness of image, DOI, is a quantification of the deviation of the direction of light propagation from the regular direction by scattering during transmission or reflection... (clarity) decreases. |
Terminology
Reflective objects- Reflectance Factor, R
- Gloss Reflectance Factor, Rs
- Gloss (at least six types of gloss may be observed depending upon the character of the surface and the spatial (directional) distribution of the reflected light.)
- Specular Gloss
- Distinctness of imageDistinctness of image* See alsoVisual_appearanceDistinctness of image, DOI, is a quantification of the deviation of the direction of light propagation from the regular direction by scattering during transmission or reflection...
Gloss - Sheen
- Reflection Haze, H (for a specified specular angle), the ratio of (lightLightLight or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
) fluxFluxIn the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
reflected at a specified angle (or angles) from the specular direction to the flux similarly reflected at the specular angle by a specified gloss standard.
Transmissive objects
- TransmittanceTransmittanceIn optics and spectroscopy, transmittance is the fraction of incident light at a specified wavelength that passes through a sample. A related term is absorptance, or absorption factor, which is the fraction of radiation absorbed by a sample at a specified wavelength...
, T - Haze (turbidityTurbidityTurbidity is the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid caused by individual particles that are generally invisible to the naked eye, similar to smoke in air. The measurement of turbidity is a key test of water quality....
) - Clarity

