Vocal registration
Encyclopedia
A vocal register is a particular series of tones in the human voice that are produced by one particular vibratory pattern of the vocal folds and therefore possess a common quality.
Registers originate in laryngeal
function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches
and produces certain characteristic sounds.
In speech pathology, the vocal register has three components: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Although this view is also adopted by many vocal pedagogists
, others define vocal registration more loosely than in the sciences, using the term to denote various theories of how the human voice changes, both subjectively and objectively, as it moves through its pitch range. There are many divergent theories on vocal registers within vocal pedagogy
, making the term somewhat confusing and at times controversial within the field of singing
. Vocal pedagogists may use the term vocal register to refer to any of the following :
, a term currently widely used in both speech pathology and vocal pedagogy publications. In this usage, modal refers to the natural disposition or manner of action of the vocal cords. The other three vibratory forms are known as vocal fry, falsetto, and whistle. Each of these four registers has its own vibratory pattern, its own pitch area (although there is some overlapping), and its own characteristic sound. Arranged by the pitch areas covered, vocal fry is the lowest register, modal voice
is next, then falsetto
, and finally the whistle register
.
While speech pathologists and scholars of phonetics consistently divide the voice into these four registers, vocal pedagogists are divided on this issue. Indiscriminate use of the word register has led to much confusion and controversy about the number of registers in the human voice within vocal pedagogical circles. This controversy does not exist within speech pathology and the other sciences as vocal registers are viewed from a purely physiological standpoint that is concerned with laryngeal function. Various writers concerned with the art of singing state that there are from anywhere from one to seven registers present. The diversity of opinion in this area is quite wide and there is no one consensus or point of view.
One prevailing practice within vocal pedagogy is to divide both men and women's voices into three registers. Men's voices are designated "chest," "head," and "falsetto" and woman's voices are "chest," "middle," and "head." This way of classifying registers, however, is not universally accepted. Many vocal pedagogists partially blame this confusion on the incorrect use of the terms "chest register" and "head register". These professionals argue that since all registers originate in laryngeal function, it is meaningless to speak of registers being produced in the chest or head. The vibratory sensations which are felt in these areas are resonance
phenomena and should be described in terms related to resonance, not to registers. These vocal pedagogists prefer the terms "chest voice
" and "head voice
" over the term register. Many of the problems which people identify as register problems are really problems of resonance adjustment. This helps to explain the multiplicity of registers which some vocal pedagogists advocate. For the purposes of this article, resonance problems are relegated to their own area since their usage here is controversial and without an overall supporting consensus. For more information on resonance see Vocal resonation
.
The confusion which exists concerning what a register is, and how many registers there are, is due in part to what takes place in the modal register when a person sings from the lowest pitches
of that register to the highest pitches. The frequency of vibration of the vocal folds is determined by their length, tension, and mass. As pitch rises, the vocal folds are lengthened, tension increases, and their thickness decreases. In other words, all three of these factors are in a state of flux in the transition from the lowest to the highest tones.
If a singer holds any of these factors constant and interferes with their progressive state of change, his laryngeal
function tends to become static and eventually breaks occur, with obvious changes of tone quality. These breaks are often identified as register boundaries or as transition areas between registers. The distinct change or break between registers is called a passaggio
or a ponticello. Vocal pedagogists teach that with study a singer can move effortlessly from one register to the other with ease and consistent tone. Registers can even overlap while singing. Teachers who like to use this theory of "blending registers" usually help students through the "passage" from one register to another by hiding their "lift" (where the voice changes).
However, many pedagogists disagree with this distinction of boundaries blaming such breaks on vocal problems which have been created by a static laryngeal adjustment that does not permit the necessary changes to take place. This difference of opinion has affected the different views on vocal registration.
. This register may be used therapeutically to improve the lower part of the modal register. This register is not used often in singing, but male quartet pieces, male Russian choral pieces, and certain styles of folk music for both men and women have been known to do so.
two octaves or more in the modal register with consistent production, beauty of tone, dynamic variety, and vocal freedom. This is possible only if the singer or speaker avoids static laryngeal
adjustments and allows the progression from the bottom to the top of the register to be a carefully graduated continuum of readjustments.
. The characteristic sound of falsetto is inherently breathy and flute-like with few overtones present. Both men and women can phonate
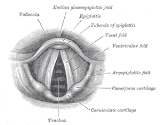
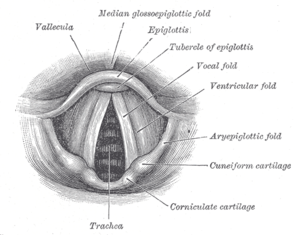
in the falsetto register. The essential difference between the modal and falsetto registers lies in the amount and type of vocal cord involvement. The falsetto voice is produced by the vibration of the ligamentous edges of the vocal cords, in whole or in part, and the main body of the fold is more or less relaxed. In contrast, the modal voice involves the whole vocal cord with the glottis
opening at the bottom first and then at the top. The falsetto voice is also more limited in dynamic variation and tone quality than the modal voice.
, whereas the modal register tends to have a warmer, less shrill timbre. Women of all voice types can use the whistle register. With proper vocal training, it is possible for most women to develop this part of the voice, but some women are unable to do so. Children can also phonate in the whistle register and men can as well in very rare instances.
Registers originate in laryngeal
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
function. They occur because the vocal folds are capable of producing several different vibratory patterns. Each of these vibratory patterns appears within a particular range of pitches
Pitch (music)
Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
and produces certain characteristic sounds.
In speech pathology, the vocal register has three components: a certain vibratory pattern of the vocal folds, a certain series of pitches, and a certain type of sound. Although this view is also adopted by many vocal pedagogists
Vocal pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished....
, others define vocal registration more loosely than in the sciences, using the term to denote various theories of how the human voice changes, both subjectively and objectively, as it moves through its pitch range. There are many divergent theories on vocal registers within vocal pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy
Vocal pedagogy is the study of the art and science of voice instruction. It is used in the teaching of singing and assists in defining what singing is, how singing works, and how proper singing technique is accomplished....
, making the term somewhat confusing and at times controversial within the field of singing
Singing
Singing is the act of producing musical sounds with the voice, and augments regular speech by the use of both tonality and rhythm. One who sings is called a singer or vocalist. Singers perform music known as songs that can be sung either with or without accompaniment by musical instruments...
. Vocal pedagogists may use the term vocal register to refer to any of the following :

- A particular part of the vocal rangeVocal rangeVocal range is the measure of the breadth of pitches that a human voice can phonate. Although the study of vocal range has little practical application in terms of speech, it is a topic of study within linguistics, phonetics, and speech and language pathology, particularly in relation to the study...
such as the upper, middle, or lower registers. - A resonanceResonanceIn physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
area such as chest voiceChest voiceChest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regards to this term...
or head voiceHead voiceHead voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals regarding this term...
. - A phonatoryPhonationPhonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, phonation is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology...
process - A certain vocal timbreTimbreIn music, timbre is the quality of a musical note or sound or tone that distinguishes different types of sound production, such as voices and musical instruments, such as string instruments, wind instruments, and percussion instruments. The physical characteristics of sound that determine the...
- A region of the voice which is defined or delimited by vocal breaks.
The number of vocal registers
Vocal registers arise from different vibratory patterns produced by the vocal cords. Research by speech pathologists and some vocal pedagogists has revealed that the vocal cords are capable of producing at least four distinct vibratory forms, although not all persons can produce all of them. The first of these vibratory forms is known as natural or normal voice; another name for it is modal voiceModal voice
Modal voice is the vocal register used most frequently in speech and singing in most languages. It is also the term used in linguistics for the most common phonation of vowels...
, a term currently widely used in both speech pathology and vocal pedagogy publications. In this usage, modal refers to the natural disposition or manner of action of the vocal cords. The other three vibratory forms are known as vocal fry, falsetto, and whistle. Each of these four registers has its own vibratory pattern, its own pitch area (although there is some overlapping), and its own characteristic sound. Arranged by the pitch areas covered, vocal fry is the lowest register, modal voice
Modal voice
Modal voice is the vocal register used most frequently in speech and singing in most languages. It is also the term used in linguistics for the most common phonation of vowels...
is next, then falsetto
Falsetto
Falsetto is the vocal register occupying the frequency range just above the modal voice register and overlapping with it by approximately one octave. It is produced by the vibration of the ligamentous edges of the vocal folds, in whole or in part...
, and finally the whistle register
Whistle register
The whistle register is the highest register of the human voice, lying above the modal register and falsetto register...
.
While speech pathologists and scholars of phonetics consistently divide the voice into these four registers, vocal pedagogists are divided on this issue. Indiscriminate use of the word register has led to much confusion and controversy about the number of registers in the human voice within vocal pedagogical circles. This controversy does not exist within speech pathology and the other sciences as vocal registers are viewed from a purely physiological standpoint that is concerned with laryngeal function. Various writers concerned with the art of singing state that there are from anywhere from one to seven registers present. The diversity of opinion in this area is quite wide and there is no one consensus or point of view.
One prevailing practice within vocal pedagogy is to divide both men and women's voices into three registers. Men's voices are designated "chest," "head," and "falsetto" and woman's voices are "chest," "middle," and "head." This way of classifying registers, however, is not universally accepted. Many vocal pedagogists partially blame this confusion on the incorrect use of the terms "chest register" and "head register". These professionals argue that since all registers originate in laryngeal function, it is meaningless to speak of registers being produced in the chest or head. The vibratory sensations which are felt in these areas are resonance
Resonance
In physics, resonance is the tendency of a system to oscillate at a greater amplitude at some frequencies than at others. These are known as the system's resonant frequencies...
phenomena and should be described in terms related to resonance, not to registers. These vocal pedagogists prefer the terms "chest voice
Chest voice
Chest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regards to this term...
" and "head voice
Head voice
Head voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals regarding this term...
" over the term register. Many of the problems which people identify as register problems are really problems of resonance adjustment. This helps to explain the multiplicity of registers which some vocal pedagogists advocate. For the purposes of this article, resonance problems are relegated to their own area since their usage here is controversial and without an overall supporting consensus. For more information on resonance see Vocal resonation
Vocal resonation
Vocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air...
.
The confusion which exists concerning what a register is, and how many registers there are, is due in part to what takes place in the modal register when a person sings from the lowest pitches
Pitch (music)
Pitch is an auditory perceptual property that allows the ordering of sounds on a frequency-related scale.Pitches are compared as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies,...
of that register to the highest pitches. The frequency of vibration of the vocal folds is determined by their length, tension, and mass. As pitch rises, the vocal folds are lengthened, tension increases, and their thickness decreases. In other words, all three of these factors are in a state of flux in the transition from the lowest to the highest tones.
If a singer holds any of these factors constant and interferes with their progressive state of change, his laryngeal
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
function tends to become static and eventually breaks occur, with obvious changes of tone quality. These breaks are often identified as register boundaries or as transition areas between registers. The distinct change or break between registers is called a passaggio
Passaggio
Passaggio is a term used in classical singing to describe the pitch ranges in which vocal registration events occur. Beneath passaggio is the chest voice where any singer can produce a powerful sound, and above it lies the head voice, where a powerful and resonant sound is accessible, but usually...
or a ponticello. Vocal pedagogists teach that with study a singer can move effortlessly from one register to the other with ease and consistent tone. Registers can even overlap while singing. Teachers who like to use this theory of "blending registers" usually help students through the "passage" from one register to another by hiding their "lift" (where the voice changes).
However, many pedagogists disagree with this distinction of boundaries blaming such breaks on vocal problems which have been created by a static laryngeal adjustment that does not permit the necessary changes to take place. This difference of opinion has affected the different views on vocal registration.
Vocal fry register
The vocal fry register is the lowest vocal register and is produced through a loose glottal closure which will permit air to bubble through with a popping or rattling sound of a very low frequency. The chief use of vocal fry in singing is to obtain pitches of very low frequency which are not available in modal voiceModal voice
Modal voice is the vocal register used most frequently in speech and singing in most languages. It is also the term used in linguistics for the most common phonation of vowels...
. This register may be used therapeutically to improve the lower part of the modal register. This register is not used often in singing, but male quartet pieces, male Russian choral pieces, and certain styles of folk music for both men and women have been known to do so.
Modal voice register
The modal voice is the usual register for speaking and singing, and the vast majority of both are done in this register. As pitch rises in this register, the vocal folds are lengthened, tension increases, and their edges become thinner. A well-trained singer or speaker can phonatePhonation
Phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, phonation is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology...
two octaves or more in the modal register with consistent production, beauty of tone, dynamic variety, and vocal freedom. This is possible only if the singer or speaker avoids static laryngeal
Larynx
The larynx , commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the neck of amphibians, reptiles and mammals involved in breathing, sound production, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. It manipulates pitch and volume...
adjustments and allows the progression from the bottom to the top of the register to be a carefully graduated continuum of readjustments.
Falsetto register
The falsetto register lies above the modal voice register and overlaps the modal register by approximately one octaveOctave
In music, an octave is the interval between one musical pitch and another with half or double its frequency. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referred to as the "basic miracle of music", the use of which is "common in most musical systems"...
. The characteristic sound of falsetto is inherently breathy and flute-like with few overtones present. Both men and women can phonate
Phonation
Phonation has slightly different meanings depending on the subfield of phonetics. Among some phoneticians, phonation is the process by which the vocal folds produce certain sounds through quasi-periodic vibration. This is the definition used among those who study laryngeal anatomy and physiology...
in the falsetto register. The essential difference between the modal and falsetto registers lies in the amount and type of vocal cord involvement. The falsetto voice is produced by the vibration of the ligamentous edges of the vocal cords, in whole or in part, and the main body of the fold is more or less relaxed. In contrast, the modal voice involves the whole vocal cord with the glottis
Glottis
The glottis is defined as the combination of the vocal folds and the space in between the folds .-Function:...
opening at the bottom first and then at the top. The falsetto voice is also more limited in dynamic variation and tone quality than the modal voice.
Whistle register
The whistle register is the highest register of the human voice. The whistle register is so called because the timbre of the notes that are produced from this register are similar to that of a whistle or the upper notes of a fluteFlute
The flute is a musical instrument of the woodwind family. Unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is an aerophone or reedless wind instrument that produces its sound from the flow of air across an opening...
, whereas the modal register tends to have a warmer, less shrill timbre. Women of all voice types can use the whistle register. With proper vocal training, it is possible for most women to develop this part of the voice, but some women are unable to do so. Children can also phonate in the whistle register and men can as well in very rare instances.
See also
- Chest voiceChest voiceChest voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals in regards to this term...
- Head voiceHead voiceHead voice is a term used within vocal music. The use of this term varies widely within vocal pedagogical circles and there is currently no one consistent opinion among vocal music professionals regarding this term...
- Human voiceHuman voiceThe human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal folds for talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, etc. Its frequency ranges from about 60 to 7000 Hz. The human voice is specifically that part of human sound production in which the vocal folds are the primary...
- Register (music)Register (music)In music, a register is the relative "height" or range of a note, set of pitches or pitch classes, melody, part, instrument or group of instruments...
- Register language
- Vocal resonationVocal resonationVocal resonation is the process by which the basic product of phonation is enhanced in timbre and/or intensity by the air-filled cavities through which it passes on its way to the outside air...

