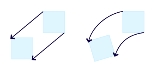
Vorticity
Overview
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
. In the simplest sense, vorticity is the tendency for elements of the fluid to "spin."
More formally, vorticity can be related to the amount of "circulation" or "rotation" (or more strictly, the local angular rate of rotation) in a fluid.
The average vorticity
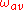 in a small region of fluid flow is equal to the circulation
in a small region of fluid flow is equal to the circulation  around the boundary of the small region, divided by the area A of the small region.
around the boundary of the small region, divided by the area A of the small region.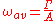
Notionally, the vorticity at a point in a fluid is the limit
Limit of a function
In mathematics, the limit of a function is a fundamental concept in calculus and analysis concerning the behavior of that function near a particular input....
as the area of the small region of fluid approaches zero at the point:
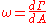
Mathematically, vorticity is a vector field
Vector field
In vector calculus, a vector field is an assignmentof a vector to each point in a subset of Euclidean space. A vector field in the plane for instance can be visualized as an arrow, with a given magnitude and direction, attached to each point in the plane...
and is defined as the curl of the velocity field:
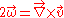
In fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
, vorticity is the curl of the fluid velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
.
Unanswered Questions
Discussions

