
Voseo
Encyclopedia
Grammatical person
Grammatical person, in linguistics, is deictic reference to a participant in an event; such as the speaker, the addressee, or others. Grammatical person typically defines a language's set of personal pronouns...
singular
Grammatical number
In linguistics, grammatical number is a grammatical category of nouns, pronouns, and adjective and verb agreement that expresses count distinctions ....
pronoun
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun is a pro-form that substitutes for a noun , such as, in English, the words it and he...
vos in many dialects of Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
. In dialects that have it, it is used either instead of tú, or alongside it.
Vos is used extensively as the primary form of the second person singular in Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish or River Plate Spanish is a dialectal variant of the Spanish language spoken mainly in the areas in and around the Río de la Plata basin of Argentina and Uruguay, and also in Rio Grande do Sul, although features of the dialect are shared with the varieties of Spanish spoken...
for Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, Uruguay
Uruguay
Uruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
, Paraguay
Paraguay
Paraguay , officially the Republic of Paraguay , is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the...
. El Salvador
El Salvador
El Salvador or simply Salvador is the smallest and the most densely populated country in Central America. The country's capital city and largest city is San Salvador; Santa Ana and San Miguel are also important cultural and commercial centers in the country and in all of Central America...
and Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
also exhibit an extensive use of the vos pronoun through the Central American Spanish
Central American Spanish
Central American Spanish is the general name of the Spanish language dialects spoken in Central America...
dialect. A similar but less intensive following of the pronoun is exhibited in Guatemala
Guatemala
Guatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
, Honduras
Honduras
Honduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
and Costa Rica
Costa Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
. The pronoun is also widely used in Bolivia
Bolivia
Bolivia officially known as Plurinational State of Bolivia , is a landlocked country in central South America. It is the poorest country in South America...
, though the media use tú more.
Vos had traditionally not been used in formal writing, except in Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay. This gradually changed in Central America, where even the most prestigious media networks and press began to use the pronoun vos, reflecting the informal address in Spanish as opposed to the formal address of usted. This is particularly true in El Salvador, Nicaragua and to a similar but lesser extent in Costa Rica
Costa Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
, Honduras, Guatemala; all of which speak in the Central American Spanish
Central American Spanish
Central American Spanish is the general name of the Spanish language dialects spoken in Central America...
dialect. Nowadays it is very common to see billboards and other advertising media using voseo. In the dialect of Argentina, Paraguay and Uruguay (known as Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish or River Plate Spanish is a dialectal variant of the Spanish language spoken mainly in the areas in and around the Río de la Plata basin of Argentina and Uruguay, and also in Rio Grande do Sul, although features of the dialect are shared with the varieties of Spanish spoken...
), vos is also the standard form for use in television media.
Vos is present in other countries as a regionalism, for instance in the Maracucho Spanish of Zulia State, Venezuela
Venezuela
Venezuela , officially called the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela , is a tropical country on the northern coast of South America. It borders Colombia to the west, Guyana to the east, and Brazil to the south...
(see Venezuelan Spanish
Venezuelan Spanish
Venezuelan Spanish is a dialect of the Spanish language spoken in Venezuela.Spanish was introduced in Venezuela by the conquistadors. Most of them were from Andalusia, Galicia, Basque Country, and the Canary Islands...
), in the Azuero peninsula of Panama
Panama
Panama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
, in various departments in Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
, and in parts of Ecuador
Ecuador
Ecuador , officially the Republic of Ecuador is a representative democratic republic in South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and by the Pacific Ocean to the west. It is one of only two countries in South America, along with Chile, that do not have a border...
(Sierra down to Esmeraldas
Esmeraldas
Esmeraldas is the Spanish word for 'emeralds'. It is a toponym that may refer to the following:*Brazil**Esmeraldas, Minas Gerais*Ecuador**Esmeraldas, Ecuador**Esmeraldas River**Esmeraldas Province**Esmeraldas Canton*Special:Allpages/Esmeraldas...
). In Peru
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
, voseo is present in some Andean regions and Cajamarca
Cajamarca
Cajamarca may refer to:Colombia*Cajamarca, Tolima a town and municipality in Tolima DepartmentPeru* Cajamarca, city in Peru.* Cajamarca District, district in the Cajamarca province.* Cajamarca Province, province in the Cajamarca region....
, but the younger generations have ceased to use it. It is also present in the Ladino dialect of Spanish, spoken by Sephardic Jews throughout Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
, Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, the Balkans, Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
, Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
.
Voseo can also be used in the context of using verb conjugation of vos with tú as the subject pronoun, as in the case of Chilean Spanish
Chilean Spanish
Chilean Spanish is the variety of Spanish spoken in most of Chile. Though still entirely mutually intelligible with standard Spanish, Chilean Spanish has distinctive pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and slang usage...
.
History
Originally a second-person plural, Vos came to be used as a more polite second-person singular pronoun to be used among one's familiar friends. The following extract from a late 18th-century textbook is illustrative of usage at the time:We seldom make use in Spanish of the second Person Singular or Plural, except through a great familiarity among friends, or speaking to God; also between a wife and husband to themselves, or when parents address their children, or to servants. Examples: O Dios, sois vos mi Padre verdadero, O God, thou art my true Father; Tu eres un buen amigo, Thou art a good friend.
The correct formal way to address a person you were not on familiar terms with was to address such a person as vuestra merced ("your grace" originally abbreviated as v.m.) in the singular and vuestras mercedes in the plural. These forms logically used a third person verb form. Other formal forms of address included vuestra excelencia (abbreviated as ussencia) and vuestra señoria (abbreviated as ussia). Today, both vos and tú are considered to be informal pronouns, with vos being somewhat synonymous with tú in regions where both are used. This was the situation when Castilian was brought to the Río de la Plata
Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata —sometimes rendered River Plate in British English and the Commonwealth, and occasionally rendered [La] Plata River in other English-speaking countries—is the river and estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River on the border between Argentina and...
area (around Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires is the capital and largest city of Argentina, and the second-largest metropolitan area in South America, after São Paulo. It is located on the western shore of the estuary of the Río de la Plata, on the southeastern coast of the South American continent...
and Montevideo
Montevideo
Montevideo is the largest city, the capital, and the chief port of Uruguay. The settlement was established in 1726 by Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst a Spanish-Portuguese dispute over the platine region, and as a counter to the Portuguese colony at Colonia del Sacramento...
) and to Chile.
In time, vos lost currency in Spain but survived in Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, Guatemala, Nicaragua, and many other countries and regions in Latin America, while Vuestra merced evolved into usted (vuestra merced > usarced > usted, in fact, "usted" is still abbreviated as either Vd or Ud). Note that the term vosotros is a combined form of vos otros (meaning literally "you others"), while the term nosotros comes from nos otros ("us others"); otros was added to avoid confusion.
Vos as a replacement for other forms of tú
The independent disjunctive pronoun ti is also replaced by vos. That is, vos is both nominativeNominative case
The nominative case is one of the grammatical cases of a noun or other part of speech, which generally marks the subject of a verb or the predicate noun or predicate adjective, as opposed to its object or other verb arguments...
and the form to use after prepositions. Therefore para ti "for you" becomes para vos, etc.
The preposition-pronoun compound contigo "with you" becomes con vos.
The direct and indirect object form te remains the same, unlike in the case of vosotros, where it becomes os.
| Nominative | Objective Objective (grammar) An objective pronoun in grammar functions as the target of a verb, as distinguished from a subjective pronoun, which is the initiator of a verb. Objective pronouns are instances of the oblique case.... |
Reflexive Reflexive Reflexive may refer to:In fiction:*MetafictionIn grammar:*Reflexive pronoun, a pronoun with a reflexive relationship with its self-identical antecedent*Reflexive verb, where a semantic agent and patient are the same... |
|||
| subject Subject -Philosophy:*Hypokeimenon or subiectum, in metaphysics, the essential being of a thing**Subject , a being that has subjective experiences, subjective consciousness, or a relationship with another entity... |
direct object | indirect object | prepositional object Object (grammar) An object in grammar is part of a sentence, and often part of the predicate. It denotes somebody or something involved in the subject's "performance" of the verb. Basically, it is what or whom the verb is acting upon... |
con + form | plain |
| vos | te | te | vos | con vos | te |
| usted | lo / la | le | usted | con usted | usted |
| tú | te | te | ti | contigo | te |
| vosotros | os | os | vosotros | con vosotros | os |
The possessive pronouns of vos also coincide with tú
Conjugation with vos

Infinitive
In grammar, infinitive is the name for certain verb forms that exist in many languages. In the usual description of English, the infinitive of a verb is its basic form with or without the particle to: therefore, do and to do, be and to be, and so on are infinitives...
s are stress
Stress (linguistics)
In linguistics, stress is the relative emphasis that may be given to certain syllables in a word, or to certain words in a phrase or sentence. The term is also used for similar patterns of phonetic prominence inside syllables. The word accent is sometimes also used with this sense.The stress placed...
ed on the last syllable; the tú forms are stressed on the penultimate one. Note the absence of diphtongization in the root
Root (linguistics)
The root word is the primary lexical unit of a word, and of a word family , which carries the most significant aspects of semantic content and cannot be reduced into smaller constituents....
s of poder and venir.
| Verb | Meaning | Tú | Usted | Vos (General) | Vos (Venezuela/Panama(Azuero) | Vos/Tú (Chile) | Vos (Ladino) | Vosotros | Ustedes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hablar | "to speak" | hablas | habla | hablás | habláis | hablái | favlásh | habláis | hablan |
| comer | "to eat" | comes | come | comés | coméis | comís | komésh | coméis | comen |
| poder | "to be able" | puedes | puede | podés | podéis | podís | podésh | podéis | pueden |
| vivir | "to live" | vives | vive | vivís | vivís | vivís | bivísh | vivís | viven |
| ser | "to be" | eres | es | sos | sois | soi/erís | sosh | sois | son |
| haber | "to have" | has | ha | has | habéis | habís/hai | habéis | han | |
| venir | "to come" | vienes | viene | venís | venís | venís | benísh | venís | vienen |
General conjugation is the one that is most widely accepted and used in various countries such as Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, parts of Bolivia, Ecuador, and Colombia, as well as Central American countries.
Some Uruguayan speakers combine the pronoun tú with the vos conjugation (for example, tú sabés). Conversely, speakers in some other places where both tú and vos are used combine vos with the tú conjugation (for example, vos sabes).
The verb forms employed with vos are also different in Chilean Spanish:
Chileans with voseo delete the final -s from the final diphthong -áis (and -ois): (vos/tú soi/erís; vos/tú estái).
In the case of the ending -ís (such as in comís, podís, vivís, erís, venís), the final -s is not totally dropped. Rather, in most cases, especially before a consonant, an aspiration similar to the h sound in English is still audible.
Both Chilean Spanish and Venezuelan Maracucho Spanish are notable in that they preserve the diphthongized plural verb forms in all tenses, as still used with vosotros in Spain. The same happens in the Azuero peninsula of Panama.
In Ladino
Judaeo-Spanish
Judaeo-Spanish , in Israel commonly referred to as Ladino, and known locally as Judezmo, Djudeo-Espanyol, Djudezmo, Djudeo-Kasteyano, Spaniolit and other names, is a Romance language derived from Old Spanish...
, the -áis, -éis, -ís, & -ois endings are pronounced /aʃ/, /eʃ/, /iʃ/, & /oʃ/.
In Chile, it is much more usual to use tú + vos verb conjugation (tú sabís). The use of pronominal vos (vos sabís) is reserved for very informal situations and may even be considered vulgar in some cases.
Present Indicative
1. General conjugation: The final -R of the infinitive is replaced by an -S, and an acute accentAcute accent
The acute accent is a diacritic used in many modern written languages with alphabets based on the Latin, Cyrillic, and Greek scripts.-Apex:An early precursor of the acute accent was the apex, used in Latin inscriptions to mark long vowels.-Greek:...
is added to the final vowel, the one preceding the final -S, to keep the stress.
2. As for the Chilean voseo, the -AR ending of the infinitive is replaced by -ÁI, whereas both -ER and -IR are replaced by -ÍS, which sounds more like -ÍH.
| Infinitive | General voseo | Chilean voseo |
|---|---|---|
| oír | oís | oís |
| venir | venís | venís |
| decir | decís | decís |
| dormir | dormís | dormís |
| sentir | sentís | sentís |
| salir | salís | salís |
| concluir | concluís | concluís |
| poder | podés | podís |
| querer | querés | querís |
| mover | movés | movís |
| pensar | pensás | pensái |
| contar | contás | contái |
| jugar | jugás | jugái |
| errar | errás | errái |
Unlike tú, which has many irregular forms, the only verb that is conjugated irregularly in the voseo forms in the indicative present is ser (vos sos).
The Chilean forms are tú/vos soi/erís, tú/vos vai, and tú/vos hai....
Affirmative imperative
Vos also differs in its affirmative imperativeImperative mood
The imperative mood expresses commands or requests as a grammatical mood. These commands or requests urge the audience to act a certain way. It also may signal a prohibition, permission, or any other kind of exhortation.- Morphology :...
conjugation from both tú and vosotros. Specifically, the vos imperative is formed by dropping the final -r from the infinitive, but keeping the stress on the last syllable. The only verb that is irregular in this regard is ir; its vos imperative is not used, with andá (the vos imperative of andar) being generally used instead.
| Verb | Meaning | Tú | Vos | Vosotros |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ser | "to be" | sé | sé | sed |
| ir | "to go" | ve | andá | id |
| hablar | "to speak" | habla | hablá | hablad |
| callar | "to become silent" | calla | callá | callad |
| soltar | "to release/let go" | suelta | soltá | soltad |
| comer | "to eat" | come | comé | comed |
| mover | "to move" | mueve | mové | moved |
| venir | "to come" | ven | vení | venid |
| poner | "to put" | pon | poné | poned |
| salir | "to leave" | sal | salí | salid |
| tener | "to have" | ten | tené | tened |
| decir | "to say" | di | decí | decid |
| pedir | "to ask/order" | pide | pedí | pedid |
Again, the conjugation tú has far more irregularities, whereas vos has only one irregular verb in the affirmative imperative.
In Chile, the general vos conjugation is not used in the affirmative imperative.
Subjunctive
Everywhere voseo is used, it is applied in the subjunctive, with the exception of Río de la PlataRío de la Plata
The Río de la Plata —sometimes rendered River Plate in British English and the Commonwealth, and occasionally rendered [La] Plata River in other English-speaking countries—is the river and estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River on the border between Argentina and...
region, where the tú-conjugation is more common. For example, in Central America it is no mintás and in Chile is no mintái; however in Río de la Plata it is no mientas, just like in Spain or México. Real Academia Española
Real Academia Española
The Royal Spanish Academy is the official royal institution responsible for regulating the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, but is affiliated with national language academies in twenty-one other hispanophone nations through the Association of Spanish Language Academies...
models its voseo conjugation tables with Río de la Plata usage and therefore omits the subjunctive voseo. In this region, the vos-form in the subjunctive has not completely disappeared. It is still used to show emphasis or emotion.
| Central America Bolivia |
Río de la Plata Río de la Plata The Río de la Plata —sometimes rendered River Plate in British English and the Commonwealth, and occasionally rendered [La] Plata River in other English-speaking countries—is the river and estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River on the border between Argentina and... region |
Chile | Venezuela (Zulia State) & Panama (Azuero) |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No quiero que mintás. | No quiero que mientas. | No quiero que mintái. | No quiero que mintáis. | I do not want you to lie. |
| No temás. | No temas. | No temái | No temáis. | Do not fear. |
| Que durmás bien | Que duermas bien. | Que durmái bien | Que durmáis bien. | Sleep well. |
| No te preocupés. | No te preocupes. | No te preocupís. | No te preocupéis. | Do not worry. |
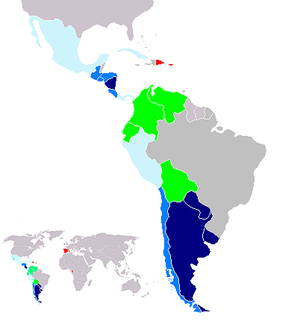
Countries where voseo is predominant


- ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
* (pronominal and verbal voseo, the pronoun tú is practically not used) - ParaguayParaguayParaguay , officially the Republic of Paraguay , is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to the east and northeast, and Bolivia to the northwest. Paraguay lies on both banks of the Paraguay River, which runs through the center of the...
* (pronominal and verbal voseo, the pronoun tú is practically not used) - UruguayUruguayUruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
* (both pronoun+verb and pronoun "tú" + verb conjugated in the "vos" form.)
In Central America
- El SalvadorEl SalvadorEl Salvador or simply Salvador is the smallest and the most densely populated country in Central America. The country's capital city and largest city is San Salvador; Santa Ana and San Miguel are also important cultural and commercial centers in the country and in all of Central America...
* - GuatemalaGuatemalaGuatemala is a country in Central America bordered by Mexico to the north and west, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, Belize to the northeast, the Caribbean to the east, and Honduras and El Salvador to the southeast...
- HondurasHondurasHonduras is a republic in Central America. It was previously known as Spanish Honduras to differentiate it from British Honduras, which became the modern-day state of Belize...
- NicaraguaNicaraguaNicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
* - Costa RicaCosta RicaCosta Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
* In Argentina, El Salvador, Paraguay, Uruguay and Nicaragua, voseo is used in most of the written language. In the rest of the countries, tú is common in formal language (media, correspondence, when addressing foreigners, etc.)
Countries where both forms are used
In the following countries, voseo is used in certain areas:- Bolivia in Santa CruzSanta Cruz de la SierraSanta Cruz de la Sierra, commonly known as Santa Cruz, is the capital of the Santa Cruz department in eastern Bolivia and the largest city in the country...
, BeniBeniBeni may refer to:Places*Beni Department, Beni River and the Beni savanna, Bolivia*Beni Suef and Beni Hasan, Egypt*Beni Mellal and Beni Amir, Morocco*Beni, Nord-Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo*Beni, Nepal Culture...
, PandoPando-People:*Pando of Capua , "Pando the Rapacious", Count of Capua*Gabriela Pando , Argentine field hockey player*José Manuel Pando , 29th President of Bolivia*Juan Pando , Spanish historian...
and TarijaTarija, BoliviaTarija or San Bernardo de la Frontera de Tarixa is a city in southern Bolivia. Founded in 1574, Tarija is both the capital and largest city within the Tarija Department, with an airport offering regular service to primary Bolivian cities, as well as a regional bus terminal with domestic and...
the voseo is used universally, while in the West of the country tú is predominant but there still a strong use of the voseo. - Chile verbal voseo is spreading north- and southwards from the center, whereas the pronominal voseo is reserved only for very intimate situations or to offend someone. In addition, voseo in Chile is only used in informal situations; in every other situation, the normal tú conjugation is used (or usted).
- Colombia, in the departments
- in the west (Pacific Coast)
- Chocó
- Valle del Cauca
- Cauca
- Nariño
- in the center, primarily Paisa RegionPaisa RegionThe Paisas are a people who inhabit a region over the northwest Colombia in the Andes.The region is formed by the departments of Antioquia, Caldas, Risaralda and Quindío. Some regions of Valle del Cauca Department and Tolima Department belong to the cultural identity of paisas...
(Departments of Antioquia, Risaralda, Quindío, and Caldas). - in the (North) East
- Norte de Santander - Ocaña RegionOcañaOcaña may refer to:*Ocaña, Colombia, a city in Norte de Santander department*Ocaña, Spain, a town in the province of Toledo, site of:**Battle of Ocana, during the Peninsular War*Luis Ocana, a Spanish cyclistSee also:...
- La GuajiraDepartment of La GuajiraLa Guajira is a department of Colombia. It occupies most of its namesake peninsula, the Guajira Peninsula in the northeast region of the country, facing the Caribbean Sea and Venezuela in the northern most part of South America...
- Cesar
- Norte de Santander - Ocaña Region
- in the west (Pacific Coast)
- Ecuador in the Sierra, the center, and Esmeraldas
- PanamaPanamaPanama , officially the Republic of Panama , is the southernmost country of Central America. Situated on the isthmus connecting North and South America, it is bordered by Costa Rica to the northwest, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. The...
in the west along the border to Costa Rica and in the Azuero Peninsula. - Venezuela in the northwest (primarily in Zulia State)
Countries where vos is practically out of use
In the following countries, the use of vos has disappeared completely or survives only very marginally in daily speech- SpainSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
* - Dominican RepublicDominican RepublicThe Dominican Republic is a nation on the island of La Hispaniola, part of the Greater Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean region. The western third of the island is occupied by the nation of Haiti, making Hispaniola one of two Caribbean islands that are shared by two countries...
- Puerto RicoPuerto RicoPuerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
- MexicoMexicoThe United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
** - PeruPeruPeru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
*** - CubaCubaThe Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
****
* The pronoun can be he heard used in constituent parts of Castile, León and in Eastern Galicia; otherwise it is used only rhetorically or in old or liturgical writings.
**Only used in some small parts of Chiapas and Tabasco, being completely unused in the rest of the country;
***Occurs in the Northern and Southern extremities of the country and is virtually unused in the rest of the country;
****The use of the pronoun is vanishing and is now only heard of on the Eastern side of the country.
Attitudes
The pronoun vos is used with family and friends (T-formT-V distinction
In sociolinguistics, a T–V distinction is a contrast, within one language, between second-person pronouns that are specialized for varying levels of politeness, social distance, courtesy, familiarity, or insult toward the addressee....
), like tú in other varieties of Spanish, and contrasts with the respectful usted (V-form) which is used with strangers; appropriate usage varies by dialect. In Central America, vos can be used among those considered equals, while usted maintains its respectful usage. In Ladino, the pronoun usted is completely absent, so the use of vos with strangers and elders is the standard.
Voseo was long considered a reprehensible practice by prescriptivist grammarians (with the idea that only Castilian Spanish was good Spanish), but it is now regarded simply as a local variant.
See also
- Similar trends of personal pronouns in Portuguese
- Spanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varieties are the regional variants of the Spanish language, some of which are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar....
- Spanish verbsSpanish verbsSpanish verbs are one of the most complex areas of Spanish grammar. Spanish is a relatively synthetic language with a moderate-to-high degree of inflection, which shows up mostly in the verb conjugation....
- T–V distinction
Sources
- Voseo Spanish Site dedicated to teaching Argentine Voseo usage Voseo at the Diccionario Panhispánico de Dudas. Real Academia Española (2005). El voseo at Spanish Wikibooks. Norma Beatriz Carricaburo (2003). El voseo en la historia y en la lengua de hoy - Las fórmulas de tratamiento en el español actual. Hotta Hideo (2000). La estandarización y el regionalismo en el voseo del español argentino. Ángel Rosenblat (2000). El castellano en Venezuela. Luis Alberto Roca (2007). Breve historia del habla cruceña y su mestizaje. Anton Toursinov (2005). Formas pronominales de tratamiento en el español actual de Guatemala. Le Voseo
Further reading
- Acevedo-Halvick, Ana. "Cortesía verbal (introducción)" Voces 1 (2006): 21-72.
- Almasov, Alexey. "'Vos' and 'Vosotros' as Formal Address in Modern Spanish." Hispania: A Journal Devoted to the Teaching of Spanish and Portuguese 57.2 (1974): 304-310.
- Alvar, Manuel. Manual de Dialectologia Hispanica: El Español de America. Barcelona : Editorial Ariel, 1996.
- Arrizabalaga, Carlos. "Noticias de la desaparicion del voseo en la costa norte del Peru." Linguistica Española Actual 23.2 (2001): 257-274.
- Baumel-Schreffler, Sandra. "The Voseo: Second Person Singular Pronouns in Guatemalan Speech." The Language Quarterly 33.1-2 (1995): 33-44.
- Benavides, Carlos. "La distribucion del voseo en Hispanoamerica." Hispania: A Journal Devoted to the Teaching of Spanish and Portuguese 86.3 (2003): 612-623.
- Blanco Botta, Ivonne. "El voseo en Cuba: Estudio sociolinguistico de una zona de la isla." Beitrage zur Romanischen Philologie 21.2 (1982): 291-304.
- Chart, Ira E. "The voseo and tuteo in America." Modern Language Forum 28.(1944): 17-24.
- Fontanella de Weinberg, Maria Beatriz. "La constitucion del paradigma pronominal de voseo." Thesaurus: Boletin del Instituto Caro y Cuervo 32.(1977): 227-241.
- King, Jeremy. "Societal Change and Language History in Cervantes' Entremeses: The Status of the Golden Age Vos." Cervantes: Bulletin of the Cervantes Society of America 29.1 (2009): 167-195.
- Lapesa, Rafael. "Las formas verbales de segunda persona y los origenes del 'voseo'." Actas del Tercer Congreso Internacional de Hispanistas. 519-531. Mexico: El Colegio de Mexico por la Asociacion Internacional de Hispanistas, 1970.
- Lapesa, Rafael. Historia de la lengua española. Madrid : Gredos, 1981.
- Leon-Luporsi, Ana Emilia. Dinamica sociolinguistica e historica de 'vos' en el español peninsular. Diss. The University of Texas at Austin, 1994.
- Lipski, John. Latin American Spanish. New York : Longman, 1994.
- Ortiz, Martha D. "Voseo" in El Salvador. Diss. San Jose State University, 2000
- Pierris, Marta de. "El preludio del voseo en el español medieval." Romance Philology 31.(1977): 235-243.
- Pinkerton, Anne. "Observations on the Tú/Vos Option in Guatemalan Ladino Spanish." Hispania: A Journal Devoted to the Teaching of Spanish and Portuguese 69.3 (1986): 690-698.
- Primorac, Karen Johnson. "Tu, vos, and vuestra merced: Social and Stylistic Variation in Medieval Spanish." Dissertation Abstracts International, Section A: The Humanities and Social Sciences 57.11 (1997): 4720-4721.
- Quilis, Antonio, and Matilde Graell Stanziola. "El voseo en Panama." Revista de Filologia Española 69.1-2 (1989): 173-178.
- Rey, Alberto. "Social Correlates of the Voseo of Managua, Nicaragua: Workplace, Street, and Party Domains." Hispanic Journal 18.1 (1997): 109-126.
- Rey, Alberto. "Social Correlates of the Voseo of Managua, Nicaragua: Workplace, Street, and Party Domains." Hispanic Journal 17.1 (1996): 113-127.
- Rey, Alberto. "Social Correlates of the Voseo of Managua: Family and Neighborhood Domains." Hispanic Journal 16.1 (1995): 39-53.
- Stevenson, Jeffrey Lee. "The Sociolinguistic Variables of Chilean Voseo." Dissertation Abstracts International, Section A: The Humanities and Social Sciences 68.5 (2007): 1914-1915.
- Toursinov, Antón. "Stylistic variability of pronoun addresses in modern Spanish of Guatemala." Language and Literature 17(3). Tyumen State University (2002): 68-78
- Villegas, Francisco. "The Voseo in Costa Rican Spanish." Hispania: A Journal Devoted to the Teaching of Spanish and Portuguese 46.3 (1963): 612-615.
- Weeks, Patricia C.. El voseo en Chile: Factores historico-morfologicos que explican su aparicion y mantenimiento. Diss. State University of New York at Albany, 2005.

