
Warburg element
Encyclopedia
The Warburg diffusion element is a common diffusion circuit element that can be used to model semi-infinite linear diffusion, that is, unrestricted diffusion to a large planar electrode. A Warburg impedance element can be difficult to recognize because it is nearly always associated with a charge-transfer resistance (see charge transfer complex
) and a double layer capacitance (see double layer (interfacial)
), but is common in many systems.
The Warburg diffusion element (ZW) is a constant phase element
(CPE), with a constant phase of 45º (phase independent of frequency) and with a magnitude inversely proportional to the square root of the frequency by:
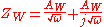
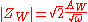
where AW is the Warburg coefficient
(or Warburg constant), j is the imaginary number
and ω is the angular frequency
. The presence of the Warburg element can be recognised if a linear relationship on the log of a Bode plot
(log|Z| versus log(w)) exists with a slope of value –1/2.
Charge transfer complex
A charge-transfer complex or electron-donor-acceptor complex is an association of two or more molecules, or of different parts of one very large molecule, in which a fraction of electronic charge is transferred between the molecular entities. The resulting electrostatic attraction provides a...
) and a double layer capacitance (see double layer (interfacial)
Double layer (interfacial)
A double layer is a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid. The object might be a solid particle, a gas bubble, a liquid droplet, or a porous body. The DL refers to two parallel layers of charge surrounding the object...
), but is common in many systems.
The Warburg diffusion element (ZW) is a constant phase element
Constant phase element
A constant phase element is an equivalent electrical circuit component that models the behaviour of a double layer, that is an imperfect capacitor....
(CPE), with a constant phase of 45º (phase independent of frequency) and with a magnitude inversely proportional to the square root of the frequency by:
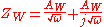
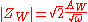
where AW is the Warburg coefficient
Warburg coefficient
The Warburg coefficient , A_W, is the diffusion coefficient of ions in solution, associated to the Warburg element, Z_W.The value of A_W can be obtained by the gradient of the Warburg plot, a linear plot of the real impedance against the reciprocal of the square root of the frequency...
(or Warburg constant), j is the imaginary number
Imaginary number
An imaginary number is any number whose square is a real number less than zero. When any real number is squared, the result is never negative, but the square of an imaginary number is always negative...
and ω is the angular frequency
Angular frequency
In physics, angular frequency ω is a scalar measure of rotation rate. Angular frequency is the magnitude of the vector quantity angular velocity...
. The presence of the Warburg element can be recognised if a linear relationship on the log of a Bode plot
Bode plot
A Bode plot is a graph of the transfer function of a linear, time-invariant system versus frequency, plotted with a log-frequency axis, to show the system's frequency response...
(log|Z| versus log(w)) exists with a slope of value –1/2.

