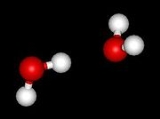
Water dimer
Encyclopedia
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the attractive interaction of a hydrogen atom with an electronegative atom, such as nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine, that comes from another molecule or chemical group. The hydrogen must be covalently bonded to another electronegative atom to create the bond...
. It is the smallest water cluster
Water cluster
In chemistry a water cluster is a discrete hydrogen bonded assembly or cluster of molecules of water. These clusters have been found experimentally or predicted in silico in various forms of water; in ice, in crystal lattices and in bulk liquid water, the simplest one being the water dimer 2...
. Because it is the simplest model system for studying hydrogen bonding in water, it has been the target of so many theoretical (and later experimental) studies that it has been called "a theoretical Guinea pig" (Jeffrey, 1997).
Structure and properties
The ab initioAb initio quantum chemistry methods
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initiowas first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene.The background is described by Parr...
binding energy between the two water molecules is estimated to be 5-6 kcal/mol, although values between 3 and 8 have been obtained depending on the method. The actual dissociation energy (including nuclear quantum effects) is most likely around 3.4 kcal/mol. The O-O distance of the vibrational ground-state is experimentally measured at ca. 2.98 Å; the hydrogen bond is almost linear, but the angle with the plane of the acceptor molecule is about 57°. The vibrational ground-state is known as the linear water dimer (shown in the figure above), which is a near prolate top (viz., in terms of rotational constants, A > B ≈ C). Other configurations of interest include the cyclic dimer and the bifurcated dimer.
History and relevance
The first theoretical study of the water dimer was an ab initioAb initio quantum chemistry methods
Ab initio quantum chemistry methods are computational chemistry methods based on quantum chemistry. The term ab initiowas first used in quantum chemistry by Robert Parr and coworkers, including David Craig in a semiempirical study on the excited states of benzene.The background is described by Parr...
calculation published in 1968 by Morokuma and Pedersen. Since then, the water dimer has been the focus of sustained interest by theoretical chemists concerned with hydrogen bonding—a search of the CAS
Chemical Abstracts Service
Chemical Abstracts is a periodical index that provides summaries and indexes of disclosures in recently published scientific documents. Approximately 8,000 journals, technical reports, dissertations, conference proceedings, and new books, in any of 50 languages, are monitored yearly, as are patent...
database up to 2006 returns over 1100 related references (73 of them in 2005). The water dimer is a hotly studied topic in Physical Chemistry for several reasons. (H2O)2 is thought to play a significant role in many atmospheric processes, including acid rain formation, absorption of excess solar radiation, condensation of water droplets, and chemical reactions. In addition, a complete understanding of the water dimer is thought to play a key role in a more thorough understanding of hydrogen bonding in liquid and solid forms of water.

