
Wind triangle
Encyclopedia
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
motion and wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
. It is used extensively in dead reckoning
Dead reckoning
In navigation, dead reckoning is the process of calculating one's current position by using a previously determined position, or fix, and advancing that position based upon known or estimated speeds over elapsed time, and course...
navigation
Navigation
Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks...
.
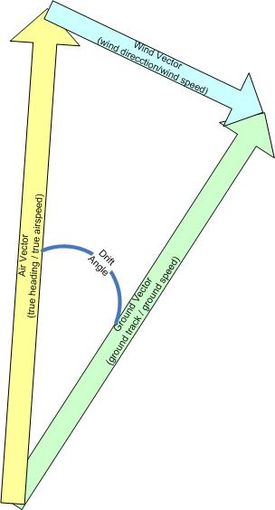
The wind triangle is a vector diagram, with three vectors.
- The air vector represents the motion of the aircraft through the airmass. It is described by true airspeedTrue airspeedTrue airspeed of an aircraft is the speed of the aircraft relative to the airmass in which it is flying. True airspeed is important information for accurate navigation of an aircraft.-Performance:...
and true headingHeadingHeading can refer to:*Heading , a process which incorporates the extruding and upsetting processes*Headline, text at the top of a newspaper article*The direction a person or vehicle is facing, usually similar to its course...
. - The wind vector represents the motion of the airmass over the ground. It is described by wind speedWind speedWind speed, or wind velocity, is a fundamental atmospheric rate.Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aircraft and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rate of many plant species, and countless other implications....
and the inverse of wind direction. Note that by convention wind direction is given as the direction the wind is from. In a vector diagram such as the wind triangle, wind direction must be stated as the direction the wind is blowing to, or 180 degrees different from the convention. - The ground vector represents the motion of the aircraft over the ground. It is described by ground track and ground speedGround speedGround speed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the ground. Information displayed to passengers through the entertainment system often gives the aircraft groundspeed rather than airspeed....
. The ground vector is the resultant of algebraically adding the air vector and the wind vector.
The wind triangle describes the relationships among the quantities used in air navigation
Air navigation
The basic principles of air navigation are identical to general navigation, which includes the process of planning, recording, and controlling the movement of a craft from one place to another....
. When two of the three vectors, or four of the six components, are known, the remaining quantities can be derived. The three principal types of problems to solve are:
- Solve for the ground vector. This type of problem arises when true heading and true airspeed are known by reading the flight instruments and when wind direction and speed are known from either the meteorological forecast or from determination in flight.
- Solve for the wind vector. This type of problem arises when determination of heading and true airspeed can be done by reading the flight instruments and ground track and ground speed can be found either by measuring the direction and distance between two established points of the aircraft or by determining the drift angle and ground speed by reference to the ground.
- Solve for true heading and ground speed. This type of problem arises during flight planningFlight planningFlight planning is the process of producing a flight plan to describe a proposed aircraft flight. It involves two safety-critical aspects: fuel calculation, to ensure that the aircraft can safely reach the destination, and compliance with air traffic control requirements, to minimise the risk of...
or during a flight, when there is a need to determine a true heading to fly and a ground speed with which to compute an estimated time of arrivalEstimated time of arrivalThe estimated time of arrival or ETA is a measure of when a ship, vehicle, aircraft, cargo, emergency service or computer file is expected to arrive at a certain place...
.
The traditional method of solving wind triangle equations is graphical. The known vectors are drawn to scale and in the proper direction on an aeronautical chart
Aeronautical chart
An aeronautical chart is a map designed to assist in navigation of aircraft, much as nautical charts do for watercraft, or a roadmap for drivers...
, using protractor
Protractor
In geometry, a protractor is a circular or semicircular tool for measuring an angle or a circle. The units of measurement utilized are usually degrees.Some protractors are simple half-discs; these have existed since ancient times...
and dividers. The unknown quantities are read from the chart using the same tools. Alternatively, the E6B
E6B
The E6B Flight Computer, or simply the "whiz wheel", is a form of circular slide rule used in aviation. They are mostly used in flight training, but many professional and even airline pilots still carry and use these flight computers...
flight computer (a circular slide rule with a translucent "wind face" on which to plot the vectors) can be used to graphically solve the wind triangle equations.
On aircraft equipped with advanced navigation equipment, the wind triangle is often solved within the flight management system
Flight management system
A flight management system is a fundamental part of a modern airliner's avionics. An FMS is a specialized computer system that automates a wide variety of in-flight tasks, reducing the workload on the flight crew to the point that modern aircraft no longer carry flight engineers or navigators. A...
, (FMS
FMS
-Government agencies:* Federal Magistrates Service, the former name of the Federal Magistrates' Court of Australia* Federated Malay States , historical British protectorate in then British Malaya...
) using inputs from the air data computer
Air data computer
An air data computer is an essential avionics component found in modern glass cockpits. This computer, rather than individual instruments, can determine the calibrated airspeed, Mach number, altitude, and altitude trend from input data from sensors such as an aircraft's pitot-static system,...
(ADC), inertial navigation system
Inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system is a navigation aid that uses a computer, motion sensors and rotation sensors to continuously calculate via dead reckoning the position, orientation, and velocity of a moving object without the need for external references...
(INS), global positioning system
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
(GPS), and other instruments, (VOR
VHF omnidirectional range
VOR, short for VHF omnidirectional radio range, is a type of radio navigation system for aircraft. A VOR ground station broadcasts a VHF radio composite signal including the station's identifier, voice , and navigation signal. The identifier is typically a two- or three-letter string in Morse code...
), (DME
Distance Measuring Equipment
Distance measuring equipment is a transponder-based radio navigation technology that measures distance by timing the propagation delay of VHF or UHF radio signals....
), (ADF). The pilot simply reads the solution provided to him.
External links
See also
Set and driftSet and drift
In navigation set and drift are characteristics of the current or the velocity of water over the ground in which a ship is sailing.Drift is the magnitude, or speed of the current and set is the bearing in the direction the current is flowing. Bearing is measured in degrees clockwise from either...
are used to describe the current vector in marine navigation, analogous to wind in air navigation.
E6B
E6B
The E6B Flight Computer, or simply the "whiz wheel", is a form of circular slide rule used in aviation. They are mostly used in flight training, but many professional and even airline pilots still carry and use these flight computers...
flight computer.

