Windows Search
Encyclopedia
Windows Search is an indexed desktop search
platform released by Microsoft
for the Windows
operating system.
Windows Search for Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 (also referred to as Instant Search) is a successor of the Windows Indexing Service
, a remnant of the Object File System feature of the Cairo project
which never materialized. Windows Search uses a different architecture and a new indexer compared to Indexing Service. For Windows XP, Windows Search is available as an add-on application.
Windows Search collectively refers to both Indexed Search on Windows Vista
and later versions of Windows, and WDS on Windows XP. They not only share a common architecture and indexing technology, but also are API-compatible with one another.
Windows Search supports IFilters, which are a set of interfaces which enable search programs to scan files, discarding words (such as "the" and "an") which would be irrelevant in a search and retaining words and phrases which would be useful. IFilters also retain information about the document itself which might be useful to search engines seeking to identify the document by its attributes in addition to its content. Once an appropriate IFilter has been installed for a particular file format, the IFilter is used to extract the text from files which were saved in that format. Windows Search by default includes handlers for common filetypes, including Word documents, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, HTML documents
, text files, MP3
and WMA
music files, WMV, ASF
and AVI
videos, JPEG
, BMP and PNG images, among others. Windows Search also uses property handlers to handle metadata from file formats. A property handler needs a property description and a schema for the property for WDS to index the metadata. Protocol handlers are used for indexing specific data stores. For example, files are accessed using File System Protocol Handler, Outlook datastores using the Outlook Protocol Handler and IE cache
using the IE History/Cache Protocol Handler. In Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Vista, network shares can be added to the index by installing proper property-handlers, though the use of this protocol handler has been deprecated in Windows 7.
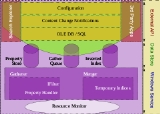
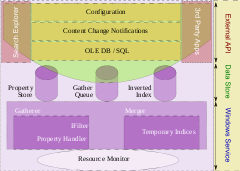
. The search service implements the Windows Search configuration and query APIs and also controls, as all indexing and query components. The most important component of Windows Search is the Indexer, which crawls the file system on initial setup, and then listens for file system notifications to pick up changed files in order to create and maintain the index of data. It achieves this using three processes:
The search service consists of several components, including the Gatherer, the Merger, the Backoff Controller, and the Query Processor, among others. The Gatherer retrieves the list of URIs that need to be crawled and invokes proper protocol handler to access the store that hosts the URI, and then the proper property-handler (to extract metadata) and IFilter to extract the document text. Different indices are created during different runs; it is the job of the Merger to periodically merge the indices. While indexing, the indices are generally maintained in-memory and then flushed to disk after a merge to reduce disk I/O. The metadata is stored in property store, which is a database maintained by the ESE
database engine. The text is tokenized and the tokens are stored in a custom database built using Inverted Indices
. Apart from the indices and property store, another persistent data structure is maintained: the Gather Queue. The Gather Queue maintains a prioritized queue of URIs that needs indexing. The Backoff Controller mentioned above monitors the available system resources, and controls the rate at which the indexer runs. It has three states:
operations on searched terms (AND, OR, NOT) as well as to specify further filters based on file metadata
or file type. It can also be used to limit results from specific information stores like regular files, offline files cache, or email stores. File type specific operators are available as well. WDS also supports wildcard
prefix matching searches. It also includes several SQL
-like operators like GROUP BY. AQS is locale dependent and uses different keywords in international versions of Windows 7.
as well as native code. Native code connects to the index catalog by using a Data Source Object retrieved from the Indexing Service OLE DB
provider. Managed code use the MSIDXS ADO.NET
provider. A catalog on a remote machine can also be queried by specifying a UNC path. The criteria for the search is specified using SQL
-like syntax. The SQL query can either be created by hand, or by using an implementation of the
. Windows Search provides implementations of the interface to convert an AQS or NQS queries to their SQL counterpart.
The OLE DB/SQL API implements the functionality for searching and querying across the indices and property stores. It uses a variant of SQL in which to represent the query (regular SQL with certain restrictions). Results are returned as OLE DB Rowsets. Whenever a query is executed, the parts of the index it used are temporarily cached so that further searches filtering the result set need not access the disk again, to improve performance. Windows Search stores its index in an Extensible Storage Engine
file named
The index store is called SystemIndex and contains all retrievable Windows IPropertyStore values, for indexed items. For example, the name and location of documents in the system is exposed as a table with the column names System. ItemName and System. ItemURL respectively. A SQL query can directly refer these tables and index catalogues and use the MSIDXS provider to run queries against them. The search index can also be used via OLE DB, using the CollatorDSO provider. However, the OLE DB provider is read-only, supporting only SELECT and GROUP ON SQL statements.
Windows Search also registers a
s. The search parameters and filters are encoded in the URI using AQS, or its natural language counterpart, NQS. When the URI is invoked by Explorer, Windows Search (which is the default registered handler for the protocol) launches the Search Explorer with the results of the search. In Windows Vista SP1 or later, third party handlers can also register themselves as the application protocol handler, so that searches can be performed using any search engine which the user has set as default, and not just Windows Search.
The Windows Search service provides the Notifications API component to allow applications to "push" changed items that need indexing to the Windows Search indexer. Applications use the component to supply the URIs of the items that need to be indexed, and the URIs are written to the Gather Queue, where they are read off by the indexer. Microsoft Office Outlook 2007, as well as Microsoft Office OneNote 2007 use this ability to index the items managed by them and use Windows Search queries to provide the in-application searching features. The Notifications API is also used by the internal USN Journal
Notifier component of Windows Search, which monitors the Change Journal in an NTFS
volume to keep track of files that has changed on the volume. If the file is in a location indexed by Windows Search and does not have the FANCI (File Attribute Not Content Indexed) attribute set, the Windows Search service is notified of its path via the Notification API.
Windows Search Configuration APIs are used to specify the configuration settings, such as the root of the URIs that needs to be monitored, setting the frequency of crawling or viewing status information like number of items indexed or length of the gather queue or the reason for throttling the indexer. It also exposes APIs to register protocol handlers (via the
, property handlers (via the
and Windows Server 2003
.
Searches are specified using the Advanced Query Syntax and are executed while the user types (incremental find
). By default, it comes with a number of IFilters for the most common file types—documents, audio, video as well as protocol handlers for Microsoft Outlook
e-mails. Other protocol handlers and IFilters can be installed as needed.
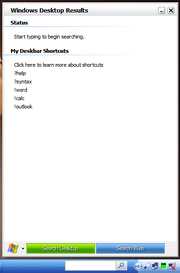 The Windows Desktop Search functionality is exposed via a Windows Taskbar mounted deskbar. It provides a text field to type the query and the results are presented in a flyout pane. It also integrates as a Windows Explorer
The Windows Desktop Search functionality is exposed via a Windows Taskbar mounted deskbar. It provides a text field to type the query and the results are presented in a flyout pane. It also integrates as a Windows Explorer
window. On selecting a file in the Explorer window, a preview of the file is shown in the right hand side of the window, without opening the application which created the file. Web searches can be initiated from both interfaces, but that will open the browser to search the terms using the default search engine.
The deskbar also has the capability to create application aliases, which are short strings which can be set to open different applications. This functionality is accessed by prefixing the ! character to the predefined string. For example "!calc" opens the Windows Calculator. The help documentation includes syntax for creating application aliases out of any text string, regardless of prefix. This feature can also be used to create shortcut for URLs, which when entered, will open the specified URL in browser. It can also be used to send parametrized information over the URL, which are used to create search aliases. For example, "w text" can be configured to search "text" in Wikipedia.
 Windows Desktop Search was initially released as MSN Desktop Search, as a part of the MSN Toolbar suite. It was re-introduced as Windows Desktop Search with version 2, while still being distributed with MSN Toolbar Suite.
Windows Desktop Search was initially released as MSN Desktop Search, as a part of the MSN Toolbar suite. It was re-introduced as Windows Desktop Search with version 2, while still being distributed with MSN Toolbar Suite.
For Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, it came in two flavors, one for home users and the other for enterprise use. The only difference between the two was that the latter could be configured via group policy. The home edition was bundled with MSN Toolbar, while the other was available as a stand alone application. Later, when MSN Toolbar was discontinued in favor of Windows Live Toolbar
, the home edition of Windows Desktop Search was discontinued as well. The last version available for Windows 2000 is Windows Desktop Search 2.66.
For Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, version 3.0 of Windows Desktop Search was provided as a standalone release - separate from Windows Live Toolbar. One of the significant new features is Windows Desktop Search 3.0 also installs the Property System on Windows XP introduced in Windows Vista. Windows Desktop Search 3.0 is geared for pre-Windows Vista users, hence the indexer was implemented as a Windows Service
, rather than as a per-user application, so that the same index as well as a single instance of the service can be shared across all users - thereby improving performance. Windows Desktop Search found itself in the midst of a controversy on October 25, 2007 when Windows Desktop Search 3.01 was automatically pushed out and installed on Windows when updated via Windows Server Update Services
(WSUS). Microsoft responded with two posts on the WSUS Product Team Blog.
, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008, and offers a superset of the features provided by Windows Desktop Search, while being API compatible with it. Unlike WDS, it can seamlessly search indexed as well as non-indexed locations - for indexed locations the index is used and for non-indexed locations, the property handlers and IFilters are invoked on the fly as the search is being performed. This allows for more consistent results, though, at the cost of searching speed over non-indexed locations. Windows Search uses Group Policy
for centralized management.
Windows Search indexes offline caches of network shares, in addition to the local file systems, Microsoft Outlook
e-mail stores and Microsoft OneNote stores indexed by WDS Windows Search also supports queries against a remote index. This means if the file server, on which a network file share is hosted, is running either Windows Vista or a later version of Windows or Windows Search 4.0 on Windows XP, any searches against the share will be queried against the server's index and present the results to the client system, filtering out the files the user does not have access to. This procedure is transparent to the user.
Unlike Windows Desktop Search on Windows XP, the Windows Search indexer performs the I/O operations with low priority, the process also runs with low CPU priority. As a result, whenever other processes require the I/O bandwidth or processor time, it is able to pre-empt the indexer, thereby significantly reducing the performance hit associated with the indexer running in the background.
Windows Search supports natural language searches; so the user can search for things like "photo taken last week" or "email sent from Dave". However, this is disabled by default. Natural language search expresses the queries in Natural Query Syntax (NQS), which is the natural language equivalent of AQS.
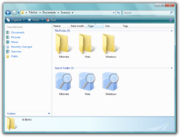 The search functionality is exposed using the search bars in the Start menu
The search functionality is exposed using the search bars in the Start menu
and the upper right hand corner of Windows Explorer windows, as well as Open/Save dialog boxes. When searching from the Start menu, the results are shown in the Start menu itself, overlapping the recently used programs. From the Start menu, it is also possible to launch an application by searching for its executable image name or display name. Searching from the search bars in Explorer windows replaces the content of the current folder with the search results. The Explorer windows can also render thumbnails in the search results if a Thumbnail Handler is registered for a particular file type. It can also render enhanced previews of items in a Preview Pane without launching the default application, if the application has registered a Preview Handler. This can provide functionality such as file type-specific navigation (such a browsing a presentation using next/previous controls, or seeking inside a media file). Preview handlers can also allow certain kind of selections (such as highlighting a text snippet) to be performed from the preview pane itself. In the Control Panel
, the search bar in the window can also search for Control Panel options. However, unlike WDS, Windows Search does not support creating aliases.
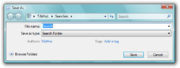 There is also a Search Explorer, which is an integrated Windows Explorer window that is used for searches. It presents the user interface to specify the search parameters, including locations and file types that should be searched, and certain operators, without crafting the AQS queries by hand. With Windows Vista SP1, third party applications will be able to override the Search Explorer as the default search interface so that the registered third party application will be launched, instead of bringing up the Search Explorer, when invoked by any means.
There is also a Search Explorer, which is an integrated Windows Explorer window that is used for searches. It presents the user interface to specify the search parameters, including locations and file types that should be searched, and certain operators, without crafting the AQS queries by hand. With Windows Vista SP1, third party applications will be able to override the Search Explorer as the default search interface so that the registered third party application will be launched, instead of bringing up the Search Explorer, when invoked by any means.
In Windows Search, which is part of Windows Vista, it is also possible to save a search query as a Virtual Folder, called a Saved Search or Search Folderwhich, when accessed, runs the search with the saved query and returns the results as a folder listing. Physically, a search folder is just an XML file (with a
. They can also be shared as a SearchMelt, which is accessible over a network. Accessing a SearchMelt over the network, like a regular Search Folder, makes the results of the search available as a virtual shared folder. The search will be performed on the machine which shares the SearchMelt, and will return only the results accessible from the network. However, by default, search folders are scoped for local use only; before sharing, they must be configured for remote access. Microsoft makes a SearchMelt Creator tool available for this as well.
The first beta of Windows Search 4.0 was released on March 27, 2008. It included numerous performance improvements to the indexer and brought new features, including previously Vista-exclusive ones, to XP, including Group Policy
integration, federation of searches to remote indexes, support for EFS
-encrypted files and Vista-style preview handlers that allow document-type specific browsing of documents in the preview pane. Windows Search 4.0 is supported on XP, Windows Server 2003, Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Home Server
.
Windows Search 4.0 was released on June 3, 2008.
Desktop search
Desktop search is the name for the field of search tools which search the contents of a user's own computer files, rather than searching the Internet...
platform released by Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
for the Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
operating system.
Windows Search for Windows Vista, Windows 7, and Windows Server 2008 (also referred to as Instant Search) is a successor of the Windows Indexing Service
Windows indexing service
Indexing Service was a Windows service that maintained an index of most of the files on a computer to improve searching performance on PCs and corporate computer networks. It updated indexed without user intervention...
, a remnant of the Object File System feature of the Cairo project
Cairo (operating system)
Cairo was the code name for a project at Microsoft from 1991 to 1996. Its charter was to build technologies for a next generation operating system that would fulfill Bill Gates' vision of "information at your fingertips." Cairo never shipped, although portions of its technologies have since...
which never materialized. Windows Search uses a different architecture and a new indexer compared to Indexing Service. For Windows XP, Windows Search is available as an add-on application.
Windows Search collectively refers to both Indexed Search on Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
and later versions of Windows, and WDS on Windows XP. They not only share a common architecture and indexing technology, but also are API-compatible with one another.
Overview
Upon installation, Windows Search (and Windows Desktop Search) builds a full-text index of the files on a user's hard drive. It does not by default index network drives, nor is it trivial to index mapped network drives even if the default settings are edited. Internet searches reveal many users who have been unable to do so at all, and solutions, if they exist, are obscure. It also, by default, creates the index on the local drive. The time required for the initial creation of this index depends on the amount and type of data to be indexed, and can take up to several hours, but this is a one-time event. Once a file’s contents have been added to this index, Windows Search is able to use the index to search results more rapidly than it would take to search through all the files on the computer. Searches are performed not only on file names, but also on the contents of the file (provided a proper handler for the file type is installed) as well as the keywords, comments and metadata the file might be tagged with. For instance, searching the computer for The Beatles would return a list of the Beatles music on the computer, as well as any e-mails and documents that include the phrase "The Beatles" in their titles or contents. Windows Search also features word-wheeled search (or search-as-you-type). It begins searching as soon as characters are entered in the search box, and keeps on refining and filtering the search results as more characters are typed in. As an advantage, this results in finding the required files even before the full search text is entered.Windows Search supports IFilters, which are a set of interfaces which enable search programs to scan files, discarding words (such as "the" and "an") which would be irrelevant in a search and retaining words and phrases which would be useful. IFilters also retain information about the document itself which might be useful to search engines seeking to identify the document by its attributes in addition to its content. Once an appropriate IFilter has been installed for a particular file format, the IFilter is used to extract the text from files which were saved in that format. Windows Search by default includes handlers for common filetypes, including Word documents, Excel spreadsheets, PowerPoint presentations, HTML documents
HTML
HyperText Markup Language is the predominant markup language for web pages. HTML elements are the basic building-blocks of webpages....
, text files, MP3
MP3
MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 Audio Layer III, more commonly referred to as MP3, is a patented digital audio encoding format using a form of lossy data compression...
and WMA
Windows Media Audio
Windows Media Audio is an audio data compression technology developed by Microsoft. The name can be used to refer to its audio file format or its audio codecs. It is a proprietary technology that forms part of the Windows Media framework. WMA consists of four distinct codecs...
music files, WMV, ASF
ASF
In computing:* Advanced Systems Format , a Microsoft streaming format associated with Windows Media Player....
and AVI
Audio Video Interleave
Audio Video Interleave , known by its acronym AVI, is a multimedia container format introduced by Microsoft in November 1992 as part of its Video for Windows technology. AVI files can contain both audio and video data in a file container that allows synchronous audio-with-video playback...
videos, JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
, BMP and PNG images, among others. Windows Search also uses property handlers to handle metadata from file formats. A property handler needs a property description and a schema for the property for WDS to index the metadata. Protocol handlers are used for indexing specific data stores. For example, files are accessed using File System Protocol Handler, Outlook datastores using the Outlook Protocol Handler and IE cache
Internet Explorer
Windows Internet Explorer is a series of graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft and included as part of the Microsoft Windows line of operating systems, starting in 1995. It was first released as part of the add-on package Plus! for Windows 95 that year...
using the IE History/Cache Protocol Handler. In Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Vista, network shares can be added to the index by installing proper property-handlers, though the use of this protocol handler has been deprecated in Windows 7.
Architecture
Windows Search is implemented as a Windows ServiceWindows Service
On Microsoft Windows operating systems, a Windows service is a long-running executable that performs specific functions and which is designed not to require user intervention. Windows services can be configured to start when the operating system is booted and run in the background as long as...
. The search service implements the Windows Search configuration and query APIs and also controls, as all indexing and query components. The most important component of Windows Search is the Indexer, which crawls the file system on initial setup, and then listens for file system notifications to pick up changed files in order to create and maintain the index of data. It achieves this using three processes:
- SearchIndexer.exe, which hosts the indexes and the list of URIÚriÚriis a village and commune in the comitatus of Pest in Hungary....
s that require indexing, as well as exposes the external configuration and query APIs that other applications use to leverage the Windows Search features. - SearchProtocolHost.exe, which hosts the protocol handlers. It runs with the least permission required for the protocol handler. For example, when accessing filesystem, it runs with the credentials of the system account, but on accessing network shares, it runs with the credentials of the user.
- SearchFilterHost.exe, which hosts the IFilters and property handlers to extract metadata and textual content. It is a low integrity process, which means that it does not have any permission to change the system settings. So, even if it encounters files with malicious content, and by any chance if they manage to take over the process, they will not be able to change any system settings.
The search service consists of several components, including the Gatherer, the Merger, the Backoff Controller, and the Query Processor, among others. The Gatherer retrieves the list of URIs that need to be crawled and invokes proper protocol handler to access the store that hosts the URI, and then the proper property-handler (to extract metadata) and IFilter to extract the document text. Different indices are created during different runs; it is the job of the Merger to periodically merge the indices. While indexing, the indices are generally maintained in-memory and then flushed to disk after a merge to reduce disk I/O. The metadata is stored in property store, which is a database maintained by the ESE
Extensible Storage Engine
Extensible Storage Engine , also known as JET Blue, is an Indexed Sequential Access Method data storage technology from Microsoft. ESE is notably a core of Microsoft Exchange Server and Active Directory. Its purpose is to allow applications to store and retrieve data via indexed and sequential...
database engine. The text is tokenized and the tokens are stored in a custom database built using Inverted Indices
Inverted index
In computer science, an inverted index is an index data structure storing a mapping from content, such as words or numbers, to its locations in a database file, or in a document or a set of documents...
. Apart from the indices and property store, another persistent data structure is maintained: the Gather Queue. The Gather Queue maintains a prioritized queue of URIs that needs indexing. The Backoff Controller mentioned above monitors the available system resources, and controls the rate at which the indexer runs. It has three states:

- Running: In this state, the indexer runs without any restrictions. The indexer runs in this state only when there is no contention for resources.
- Throttled: In this state, the crawling of URIs and extraction of text and metadata is deliberately throttled, so that the number of operations per minute are kept under a tight control. The indexer is in this state when there is contention for resources, for example, when other applications are running. By throttling the operations, it is ensured that the other operations are not starved of resources they might need.
- Backed off: In this state, no indexing is done. Only the Gather Queues are kept active so that items do not go unindexed. This state is activated on extreme resource shortage (less than 5 MB of RAM or 200 MB of disk space), or if indexing is configured to be disabled when the computer is on battery power, or if the indexer is manually paused by the user.
Advanced Query Syntax
Windows Search queries are specified in Advanced Query Syntax (AQS) which supports not only simple text searches but provides advanced property-based query operations as well. AQS defines certain keywords which can be used to refine the search query, such as specifying booleanBoolean logic
Boolean algebra is a logical calculus of truth values, developed by George Boole in the 1840s. It resembles the algebra of real numbers, but with the numeric operations of multiplication xy, addition x + y, and negation −x replaced by the respective logical operations of...
operations on searched terms (AND, OR, NOT) as well as to specify further filters based on file metadata
Metadata
The term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
or file type. It can also be used to limit results from specific information stores like regular files, offline files cache, or email stores. File type specific operators are available as well. WDS also supports wildcard
Wildcard character
-Telecommunication:In telecommunications, a wildcard character is a character that may be substituted for any of a defined subset of all possible characters....
prefix matching searches. It also includes several SQL
SQL
SQL is a programming language designed for managing data in relational database management systems ....
-like operators like GROUP BY. AQS is locale dependent and uses different keywords in international versions of Windows 7.
Programmability
The Windows Search index can be accessed programmatically using both managed.NET Framework
The .NET Framework is a software framework that runs primarily on Microsoft Windows. It includes a large library and supports several programming languages which allows language interoperability...
as well as native code. Native code connects to the index catalog by using a Data Source Object retrieved from the Indexing Service OLE DB
OLE DB
OLE DB is an API designed by Microsoft for accessing data from a variety of sources in an uniform manner. It is a set of interfaces implemented using the Component Object Model ; it is otherwise unrelated to OLE...
provider. Managed code use the MSIDXS ADO.NET
ADO.NET
ADO.NET is a set of computer software components that programmers can use to access data and data services. It is a part of the base class library that is included with the Microsoft .NET Framework. It is commonly used by programmers to access and modify data stored in relational database systems,...
provider. A catalog on a remote machine can also be queried by specifying a UNC path. The criteria for the search is specified using SQL
SQL
SQL is a programming language designed for managing data in relational database management systems ....
-like syntax. The SQL query can either be created by hand, or by using an implementation of the
ISearchQueryHelper interfaceInterface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
. Windows Search provides implementations of the interface to convert an AQS or NQS queries to their SQL counterpart.
The OLE DB/SQL API implements the functionality for searching and querying across the indices and property stores. It uses a variant of SQL in which to represent the query (regular SQL with certain restrictions). Results are returned as OLE DB Rowsets. Whenever a query is executed, the parts of the index it used are temporarily cached so that further searches filtering the result set need not access the disk again, to improve performance. Windows Search stores its index in an Extensible Storage Engine
Extensible Storage Engine
Extensible Storage Engine , also known as JET Blue, is an Indexed Sequential Access Method data storage technology from Microsoft. ESE is notably a core of Microsoft Exchange Server and Active Directory. Its purpose is to allow applications to store and retrieve data via indexed and sequential...
file named
Windows.edb that exists, by default, in the \ProgramData\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\ folder at the root of the system drive in Windows Vista or later versions of Windows. (The corresponding location in Windows XP is \All Users\Application Data\Microsoft\Search\Data\Applications\Windows\ inside the Documents and Settings folder.)The index store is called SystemIndex and contains all retrievable Windows IPropertyStore values, for indexed items. For example, the name and location of documents in the system is exposed as a table with the column names System. ItemName and System. ItemURL respectively. A SQL query can directly refer these tables and index catalogues and use the MSIDXS provider to run queries against them. The search index can also be used via OLE DB, using the CollatorDSO provider. However, the OLE DB provider is read-only, supporting only SELECT and GROUP ON SQL statements.
Windows Search also registers a
search-ms application protocol, which can be used to represent searches as URIÚri
Úriis a village and commune in the comitatus of Pest in Hungary....
s. The search parameters and filters are encoded in the URI using AQS, or its natural language counterpart, NQS. When the URI is invoked by Explorer, Windows Search (which is the default registered handler for the protocol) launches the Search Explorer with the results of the search. In Windows Vista SP1 or later, third party handlers can also register themselves as the application protocol handler, so that searches can be performed using any search engine which the user has set as default, and not just Windows Search.
The Windows Search service provides the Notifications API component to allow applications to "push" changed items that need indexing to the Windows Search indexer. Applications use the component to supply the URIs of the items that need to be indexed, and the URIs are written to the Gather Queue, where they are read off by the indexer. Microsoft Office Outlook 2007, as well as Microsoft Office OneNote 2007 use this ability to index the items managed by them and use Windows Search queries to provide the in-application searching features. The Notifications API is also used by the internal USN Journal
Usn Journal
USN Journal is a function of recording the changes on NTFS volumes....
Notifier component of Windows Search, which monitors the Change Journal in an NTFS
NTFS
NTFS is the standard file system of Windows NT, including its later versions Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista, and Windows 7....
volume to keep track of files that has changed on the volume. If the file is in a location indexed by Windows Search and does not have the FANCI (File Attribute Not Content Indexed) attribute set, the Windows Search service is notified of its path via the Notification API.
Windows Search Configuration APIs are used to specify the configuration settings, such as the root of the URIs that needs to be monitored, setting the frequency of crawling or viewing status information like number of items indexed or length of the gather queue or the reason for throttling the indexer. It also exposes APIs to register protocol handlers (via the
ISearchProtocol interfaceInterface (computer science)
In the field of computer science, an interface is a tool and concept that refers to a point of interaction between components, and is applicable at the level of both hardware and software...
, property handlers (via the
IPropertyStore interface) or IFilter implementations (via the IFilter interface). IFilter implementations allow only read-only extraction of text and properties, whereas IPropertyStore allows properties to be written as well.Windows Desktop Search
Windows Desktop Search is the implementation of Windows Search for Windows XPWindows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
and Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003 is a server operating system produced by Microsoft, introduced on 24 April 2003. An updated version, Windows Server 2003 R2, was released to manufacturing on 6 December 2005...
.
Searches are specified using the Advanced Query Syntax and are executed while the user types (incremental find
Incremental find
In computing, incremental search, incremental find or real-time suggestions is a user interface interaction method to progressively search for and filter through text. As the user types text, one or more possible matches for the text are found and immediately presented to the user...
). By default, it comes with a number of IFilters for the most common file types—documents, audio, video as well as protocol handlers for Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager from Microsoft, available both as a separate application as well as a part of the Microsoft Office suite...
e-mails. Other protocol handlers and IFilters can be installed as needed.
User interface

Windows Explorer
This article is about the Windows file system browser. For the similarly named web browser, see Internet ExplorerWindows Explorer is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface...
window. On selecting a file in the Explorer window, a preview of the file is shown in the right hand side of the window, without opening the application which created the file. Web searches can be initiated from both interfaces, but that will open the browser to search the terms using the default search engine.
The deskbar also has the capability to create application aliases, which are short strings which can be set to open different applications. This functionality is accessed by prefixing the ! character to the predefined string. For example "!calc" opens the Windows Calculator. The help documentation includes syntax for creating application aliases out of any text string, regardless of prefix. This feature can also be used to create shortcut for URLs, which when entered, will open the specified URL in browser. It can also be used to send parametrized information over the URL, which are used to create search aliases. For example, "w text" can be configured to search "text" in Wikipedia.
Releases

For Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, it came in two flavors, one for home users and the other for enterprise use. The only difference between the two was that the latter could be configured via group policy. The home edition was bundled with MSN Toolbar, while the other was available as a stand alone application. Later, when MSN Toolbar was discontinued in favor of Windows Live Toolbar
Windows Live Toolbar
Windows Live Toolbar was an browser extension toolbar for Internet Explorer. It superseded MSN Search Toolbar. Windows Live Toolbar provided a simple search interface that starts to list results as the user types in a search query, and uses Bing as its search engine...
, the home edition of Windows Desktop Search was discontinued as well. The last version available for Windows 2000 is Windows Desktop Search 2.66.
For Windows XP and Windows Server 2003, version 3.0 of Windows Desktop Search was provided as a standalone release - separate from Windows Live Toolbar. One of the significant new features is Windows Desktop Search 3.0 also installs the Property System on Windows XP introduced in Windows Vista. Windows Desktop Search 3.0 is geared for pre-Windows Vista users, hence the indexer was implemented as a Windows Service
Windows Service
On Microsoft Windows operating systems, a Windows service is a long-running executable that performs specific functions and which is designed not to require user intervention. Windows services can be configured to start when the operating system is booted and run in the background as long as...
, rather than as a per-user application, so that the same index as well as a single instance of the service can be shared across all users - thereby improving performance. Windows Desktop Search found itself in the midst of a controversy on October 25, 2007 when Windows Desktop Search 3.01 was automatically pushed out and installed on Windows when updated via Windows Server Update Services
Windows Server Update Services
- External links :* * * – contains many detailed documents on WSUS operation, known issues, and troubleshooting* - German WSUS-Community * - Control installation of WSUS updates from command line...
(WSUS). Microsoft responded with two posts on the WSUS Product Team Blog.
Windows Search
Windows Search is the indexed search platform in Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008, and offers a superset of the features provided by Windows Desktop Search, while being API compatible with it. Unlike WDS, it can seamlessly search indexed as well as non-indexed locations - for indexed locations the index is used and for non-indexed locations, the property handlers and IFilters are invoked on the fly as the search is being performed. This allows for more consistent results, though, at the cost of searching speed over non-indexed locations. Windows Search uses Group Policy
Group Policy
Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems. Group Policy is a set of rules that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides the centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and...
for centralized management.
Windows Search indexes offline caches of network shares, in addition to the local file systems, Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook
Microsoft Outlook is a personal information manager from Microsoft, available both as a separate application as well as a part of the Microsoft Office suite...
e-mail stores and Microsoft OneNote stores indexed by WDS Windows Search also supports queries against a remote index. This means if the file server, on which a network file share is hosted, is running either Windows Vista or a later version of Windows or Windows Search 4.0 on Windows XP, any searches against the share will be queried against the server's index and present the results to the client system, filtering out the files the user does not have access to. This procedure is transparent to the user.
Unlike Windows Desktop Search on Windows XP, the Windows Search indexer performs the I/O operations with low priority, the process also runs with low CPU priority. As a result, whenever other processes require the I/O bandwidth or processor time, it is able to pre-empt the indexer, thereby significantly reducing the performance hit associated with the indexer running in the background.
Windows Search supports natural language searches; so the user can search for things like "photo taken last week" or "email sent from Dave". However, this is disabled by default. Natural language search expresses the queries in Natural Query Syntax (NQS), which is the natural language equivalent of AQS.
User interface

Start menu
The Start Menu and Start Button are user interface elements used in the later versions of the Microsoft Windows operating systems and in some X window managers...
and the upper right hand corner of Windows Explorer windows, as well as Open/Save dialog boxes. When searching from the Start menu, the results are shown in the Start menu itself, overlapping the recently used programs. From the Start menu, it is also possible to launch an application by searching for its executable image name or display name. Searching from the search bars in Explorer windows replaces the content of the current folder with the search results. The Explorer windows can also render thumbnails in the search results if a Thumbnail Handler is registered for a particular file type. It can also render enhanced previews of items in a Preview Pane without launching the default application, if the application has registered a Preview Handler. This can provide functionality such as file type-specific navigation (such a browsing a presentation using next/previous controls, or seeking inside a media file). Preview handlers can also allow certain kind of selections (such as highlighting a text snippet) to be performed from the preview pane itself. In the Control Panel
Control Panel (Windows)
The Control Panel is a part of the Microsoft Windows graphical user interface which allows users to view and manipulate basic system settings and controls via applets, such as adding hardware, adding and removing software, controlling user accounts, and changing accessibility options...
, the search bar in the window can also search for Control Panel options. However, unlike WDS, Windows Search does not support creating aliases.

In Windows Search, which is part of Windows Vista, it is also possible to save a search query as a Virtual Folder, called a Saved Search or Search Folderwhich, when accessed, runs the search with the saved query and returns the results as a folder listing. Physically, a search folder is just an XML file (with a
.search-ms extension) which stores the search query (in either AQS or NQS), including the search operators as well. Windows Vista also supports query composition, where a saved search (called a scope) can be nested within the query string of another search. Search Folders are also distributable via RSSRSS (file format)
RSS is a family of web feed formats used to publish frequently updated works—such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video—in a standardized format...
. They can also be shared as a SearchMelt, which is accessible over a network. Accessing a SearchMelt over the network, like a regular Search Folder, makes the results of the search available as a virtual shared folder. The search will be performed on the machine which shares the SearchMelt, and will return only the results accessible from the network. However, by default, search folders are scoped for local use only; before sharing, they must be configured for remote access. Microsoft makes a SearchMelt Creator tool available for this as well.
Windows Search 4.0
Windows Search 4.0 is the successor to the Windows Search platform for both Windows Desktop Search 3.0 on Windows XP as well as Instant Search on Windows Vista. It is mainly an update to the indexing components, with few changes to the XP user interface and none on Vista. It also enables remote query support on XP and Windows Server 2003 based systems, which previously was a Vista-only feature. This allows a user with a Vista client (or an XP client with Windows Search 4.0) to search the index of networked machines which are also running a supported operating system (Windows 7, Vista, Windows Server 2008, or XP/2003 with Windows Search 4.0).The first beta of Windows Search 4.0 was released on March 27, 2008. It included numerous performance improvements to the indexer and brought new features, including previously Vista-exclusive ones, to XP, including Group Policy
Group Policy
Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems. Group Policy is a set of rules that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides the centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and...
integration, federation of searches to remote indexes, support for EFS
Encrypting File System
The Encrypting File System on Microsoft Windows is a feature introduced in version 3.0 of NTFS that provides filesystem-level encryption...
-encrypted files and Vista-style preview handlers that allow document-type specific browsing of documents in the preview pane. Windows Search 4.0 is supported on XP, Windows Server 2003, Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Home Server
Windows Home Server
Windows Home Server, code-named Quattro, is a home server operating system from Microsoft. Announced on 7 January 2007, at the Consumer Electronics Show by Bill Gates, Windows Home Server is intended to be a solution for homes with multiple connected PCs to offer file sharing, automated backups,...
.
Windows Search 4.0 was released on June 3, 2008.
See also
- List of desktop search engines
- Microsoft Search ServerMicrosoft Search ServerMicrosoft Search Server is an enterprise search platform from Microsoft, based on the search capabilities of Microsoft Office SharePoint Server. MSS shares its architectural underpinnings with the Windows Search platform for both the querying engine as well as the indexer...
- Microsoft Enterprise Search

