
Wolter telescope
Encyclopedia
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
for X-ray
X-ray
X-radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation. X-rays have a wavelength in the range of 0.01 to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz and energies in the range 120 eV to 120 keV. They are shorter in wavelength than UV rays and longer than gamma...
s using only grazing incidence optics. Visible light telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
s are built with lenses or parabolic mirrors at nearly normal incidence. Neither works well for X-rays. Lenses for visible light are made of a transparent material with an index of refraction substantially different from one, but there is no equivalent material for x-rays. Conventional mirror telescopes work poorly in the X-rays as well, since the light hits the mirrors at near-normal incidence, where the X-rays are transmitted or absorbed, not reflected.
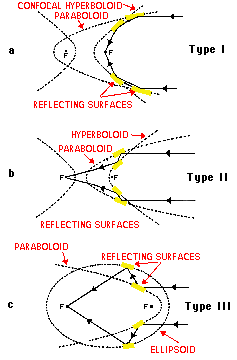
X-rays mirrors can be built, but only if the angle from the plane of reflection is very low (typically 10 arc-minutes to 2 degrees). These are called glancing (or grazing) incidence mirrors. In 1952, Hans Wolter
Hans Wolter
Hans Wolter was a German physicist who designed an aplanatic system of grazing incidence mirrors that satisfied the Abbe sine condition ....
outlined three ways a telescope could be built using only this kind of mirror.. Not surprisingly, these are called Wolter telescopes of type I, II, and III. Each has different advantages and disadvantages.
See also
- List of telescope types
- Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope ArrayNuclear Spectroscopic Telescope ArrayNuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array is a planned space-based X-ray telescope that will use grazing incidence mirrors to focus high energy X-rays at 5 to 79 keV from astrophysical sources, especially for nuclear spectroscopy...
(NuSTAR) Planned for 2012 - Swift Gamma-Ray Burst MissionSwift Gamma-Ray Burst MissionThe Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission consists of a robotic spacecraft called Swift, which was launched into orbit on 20 November 2004, 17:16:00 UTC on a Delta II 7320-10C expendable launch vehicle. Swift is managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, and was developed by an international...
Contains a Wolter Type-I X-ray telescope (2004+) - Chandra X-ray ObservatoryChandra X-ray ObservatoryThe Chandra X-ray Observatory is a satellite launched on STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. It was named in honor of Indian-American physicist Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar who is known for determining the maximum mass for white dwarfs. "Chandra" also means "moon" or "luminous" in Sanskrit.Chandra...
Orbiting observatory using a Wolter X-ray telescope. (1999+) - XMM-NewtonXMM-NewtonThe XMM-Newton is an orbiting X-ray observatory launched by ESA in December 1999 on a Ariane 5 rocket...
Orbiting X-ray observatory using a Wolter Type-I X-ray telescope. (1999+) - ROSAT Orbiting X-ray observatory (1990-1999)

