
Working capital
Encyclopedia
Accounting liquidity
In accounting, liquidity is a measure of the ability of a debtor to pay his debts as and when they fall due. It is usually expressed as a ratio or a percentage of current liabilities.-Calculating liquidity:...
available to a business, organization or other entity, including governmental entity. Along with fixed assets such as plant and equipment, working capital is considered a part of operating capital. Net working capital is calculated as current assets minus current liabilities. It is a derivation of working capital, that is commonly used in valuation techniques such as DCFs (Discounted cash flows). If current assets are less than current liabilities, an entity has a working capital deficiency, also called a working capital deficit.
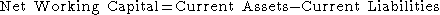
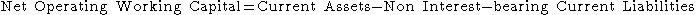
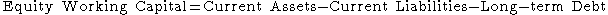
A company can be endowed with assets and profitability
Profit (accounting)
In accounting, profit can be considered to be the difference between the purchase price and the costs of bringing to market whatever it is that is accounted as an enterprise in terms of the component costs of delivered goods and/or services and any operating or other expenses.-Definition:There are...
but short of liquidity if its assets cannot readily be converted into cash. Positive working capital is required to ensure that a firm is able to continue its operations and that it has sufficient funds to satisfy both maturing short-term debt
Money market
The money market is a component of the financial markets for assets involved in short-term borrowing and lending with original maturities of one year or shorter time frames. Trading in the money markets involves Treasury bills, commercial paper, bankers' acceptances, certificates of deposit,...
and upcoming operational expenses. The management of working capital involves managing inventories, accounts receivable and payable, and cash.
Calculation
Current assets and current liabilities include three accounts which are of special importance. These accounts represent the areas of the business where managers have the most direct impact:- accounts receivableAccounts receivableAccounts receivable also known as Debtors, is money owed to a business by its clients and shown on its Balance Sheet as an asset...
(current asset) - inventoryInventoryInventory means a list compiled for some formal purpose, such as the details of an estate going to probate, or the contents of a house let furnished. This remains the prime meaning in British English...
(current assets), and - accounts payableAccounts payableAccounts payable is a file or account sub-ledger that records amounts that a person or company owes to suppliers, but has not paid yet , sometimes referred as trade payables. When an invoice is received, it is added to the file, and then removed when it is paid...
(current liability)
The current portion of debt
Debt
A debt is an obligation owed by one party to a second party, the creditor; usually this refers to assets granted by the creditor to the debtor, but the term can also be used metaphorically to cover moral obligations and other interactions not based on economic value.A debt is created when a...
(payable within 12 months) is critical, because it represents a short-term claim to current assets and is often secured by long term assets. Common types of short-term debt are bank loans and lines of credit.
An increase in working capital indicates that the business has either increased current assets (that is has increased its receivables, or other current assets) or has decreased current liabilities, for example has paid off some short-term creditors.
Implications on M&A: The common commercial definition of working capital for the purpose of a working capital adjustment in an M&A transaction (i.e. for a working capital adjustment mechanism in a sale and purchase agreement) is equal to:
Current Assets – Current Liabilities excluding deferred tax assets/liabilities, excess cash, surplus assets and/or deposit balances.
Cash balance items often attract a one-for-one purchase price adjustment.
Working capital management
Decisions relating to working capital and short term financing are referred to as working capital management. These involve managing the relationship between a firm's short-term assets and its short-term liabilitiesCurrent liability
In accounting, current liabilities are often understood as all liabilities of the business that are to be settled in cash within the fiscal year or the operating cycle of a given firm, whichever period is longer...
. The goal of working capital management is to ensure that the firm is able to continue its operations
Operations management
Operations management is an area of management concerned with overseeing, designing, and redesigning business operations in the production of goods and/or services. It involves the responsibility of ensuring that business operations are efficient in terms of using as little resources as needed, and...
and that it has sufficient cash flow to satisfy both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses.
Decision criteria
By definition, working capital management entails short term decisions - generally, relating to the next one year period - which are "reversible". These decisions are therefore not taken on the same basis as Capital Investment Decisions (NPVNet present value
In finance, the net present value or net present worth of a time series of cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is defined as the sum of the present values of the individual cash flows of the same entity...
or related, as above) rather they will be based on cash flows and / or profitability.
- One measure of cash flow is provided by the cash conversion cycleCash conversion cycleIn management accounting, the Cash Conversion Cycle measures how long a firm will be deprived of cash if it increases its investment in resources in order to expand customer sales. It is thus a measure of the liquidity risk entailed by growth...
- the net number of days from the outlay of cash for raw materialMaterialMaterial is anything made of matter, constituted of one or more substances. Wood, cement, hydrogen, air and water are all examples of materials. Sometimes the term "material" is used more narrowly to refer to substances or components with certain physical properties that are used as inputs to...
to receiving payment from the customer. As a management tool, this metric makes explicit the inter-relatedness of decisions relating to inventories, accounts receivable and payable, and cash. Because this number effectively corresponds to the time that the firm's cash is tied up in operations and unavailable for other activities, management generally aims at a low net count.
- In this context, the most useful measure of profitability is Return on capital (ROC). The result is shown as a percentage, determined by dividing relevant income for the 12 months by capital employedCapital employedCapital employed has many definitions. In general, it represents the capital investment necessary for a business to function. Consequently, it is not a measure of assets, but of capital investment: stock or shares and long-term liabilities.- Definitions :...
; Return on equityReturn on equityReturn on equity measures the rate of return on the ownership interest of the common stock owners. It measures a firm's efficiency at generating profits from every unit of shareholders' equity . ROE shows how well a company uses investment funds to generate earnings growth...
(ROE) shows this result for the firm's shareholders. Firm value is enhanced when, and if, the return on capital, which results from working capital management, exceeds the cost of capitalCost of capitalThe cost of capital is a term used in the field of financial investment to refer to the cost of a company's funds , or, from an investor's point of view "the shareholder's required return on a portfolio of all the company's existing securities"...
, which results from capital investment decisions as above. ROC measures are therefore useful as a management tool, in that they link short-term policy with long-term decision making. See Economic value addedEconomic value addedIn corporate finance, Economic Value Added or EVA, a registered trademark of Stern Stewart & Co., is an estimate of a firm's economic profit – being the value created in excess of the required return of the company's investors . Quite simply, EVA is the profit earned by the firm less the cost of...
(EVA).
- Credit policy of the firm: Another factor affecting working capital management is credit policy of the firm. It includes buying of raw material and selling of finished goods either in cash or on credit. This affects the cash conversion cycleCash conversion cycleIn management accounting, the Cash Conversion Cycle measures how long a firm will be deprived of cash if it increases its investment in resources in order to expand customer sales. It is thus a measure of the liquidity risk entailed by growth...
.
Management of working capital
Guided by the above criteria, management will use a combination of policies and techniques for the management of working capital. These policies aim at managing the current assets (generally cashCash
In common language cash refers to money in the physical form of currency, such as banknotes and coins.In bookkeeping and finance, cash refers to current assets comprising currency or currency equivalents that can be accessed immediately or near-immediately...
and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are the most liquid assets found within the asset portion of a company's balance sheet. Cash equivalents are assets that are readily convertible into cash, such as money market holdings, short-term government bonds or Treasury bills, marketable securities and commercial...
, inventories
Inventory
Inventory means a list compiled for some formal purpose, such as the details of an estate going to probate, or the contents of a house let furnished. This remains the prime meaning in British English...
and debtor
Debtor
A debtor is an entity that owes a debt to someone else. The entity may be an individual, a firm, a government, a company or other legal person. The counterparty is called a creditor...
s) and the short term financing, such that cash flows and returns are acceptable.
- Cash managementCash managementIn United States banking, cash management, or treasury management, is a marketing term for certain services offered primarily to larger business customers...
. Identify the cash balance which allows for the business to meet day to day expenses, but reduces cash holding costs. - Inventory management. Identify the level of inventory which allows for uninterrupted production but reduces the investment in raw materials - and minimizes reordering costs - and hence increases cash flow. Besides this, the lead times in production should be lowered to reduce Work in Progress (WIP)Work in progressWork in progress may refer to:-Film:* A Work in Progress, a documentary film of the recording of Rush's Test for Echo album* Work in Progress , a computer-animated short film-Music:* Work in Progress , by Man Alive...
and similarly, the Finished GoodsFinished goodFinished goods are goods that have completed the manufacturing process but have not yet been sold or distributed to the end user.-Manufacturing:Manufacturing has three classes of inventory:#Raw material#Work in process#Finished goods...
should be kept on as low level as possible to avoid over production - see Supply chain managementSupply chain managementSupply chain management is the management of a network of interconnected businesses involved in the ultimate provision of product and service packages required by end customers...
; Just In Time (JIT); Economic order quantityEconomic order quantityEconomic order quantity is the level of inventory that minimizes total inventory holding costs and ordering costs. It is one of the oldest classical production scheduling models. The framework used to determine this order quantity is also known as Wilson EOQ Model or Wilson Formula. The model was...
(EOQ); Economic quantity - Debtors management. Identify the appropriate credit policyCredit (finance)Credit is the trust which allows one party to provide resources to another party where that second party does not reimburse the first party immediately , but instead arranges either to repay or return those resources at a later date. The resources provided may be financial Credit is the trust...
, i.e. credit terms which will attract customers, such that any impact on cash flows and the cash conversion cycle will be offset by increased revenue and hence Return on Capital (or vice versa); see Discounts and allowancesDiscounts and allowancesDiscounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services.They can occur anywhere in the distribution channel, modifying either the manufacturer's list price , the retail price , or the list price Discounts and allowances are reductions to a basic price of goods or services.They...
. - Short term financing. Identify the appropriate source of financing, given the cash conversion cycle: the inventory is ideally financed by credit granted by the supplier; however, it may be necessary to utilize a bank loanLoanA loan is a type of debt. Like all debt instruments, a loan entails the redistribution of financial assets over time, between the lender and the borrower....
(or overdraft), or to "convert debtors to cash" through "factoringFactoring (finance)Factoring is a financial transaction whereby a business job sells its accounts receivable to a third party at a discount...
".
See also
- Cash conversion cycleCash conversion cycleIn management accounting, the Cash Conversion Cycle measures how long a firm will be deprived of cash if it increases its investment in resources in order to expand customer sales. It is thus a measure of the liquidity risk entailed by growth...
- Working capital management
- OvertradingOvertradingOvertrading is a term in financial statement analysis. Overtrading often occurs when companies expand its own operations too quickly . Overtraded companies enter a negative cycle, where increase in interest expenses negatively impact net profit leads to lesser working capital leads to increase...
- Quick ratio analysis
- Sustainable growth rateSustainable growth rateAccording to PIMS an important lever of business success is growth. Among 37 variables, growth is mentioned as one of the most important variables for success: market share, market growth, marketing expense to sales ratio or a strong market position.The question how much growth is sustainable is...

