X-FEN
Encyclopedia
X-FEN is an extension of Forsyth-Edwards Notation
(FEN).
The traditional Forsyth-Edwards Notation is not sufficient to represent all possible positions in 8x8 Chess960
(aka Fischer Random Chess
) or 10x8 Capablanca random chess
(CRC). Consequently, an extension of FEN was needed, with the requirement of being fully backward compatible
. X-FEN (formerly FRC-FEN), introduced by Reinhard Scharnagl
in 2003, accomplishes this.
and en passant
tags are used. Moreover, 10x8 positions, which rely on José Raúl Capablanca
's extended piece set (additional pieces Chancellor and Archbishop), are supported.
format (Portable Game Notation). Unlike traditional chess games, Chess960
or CRC games (Capablanca random chess
) require storing the particular starting positions. This is done using a SetUp tag and a FEN string, using the definitions for traditional chess games.
target differs slightly from standard Forsyth-Edwards Notation
. FEN records the en passant square field as the square just behind a pawn that has made a two-square push forward in the latest move. As such, whenever a pawn makes a two-square move, the "en passant" square is recorded. From the sample game given in Forsyth-Edwards Notation
, we see that FEN includes the square e3 as an en passant square after White makes the first move of the game 1. e4. This is somewhat misleading, as no en passant captures can be made by Black from the position.
X-FEN, on the other hand, includes only true en passant squares. That is, X-FEN records a value in the field for an en passant square only if there are one or more enemy pawns on the same rank on an adjacent file. Thus, after 1. e4, the field for the en passant square is left blank, as Black cannot make an en passant capture. However, it is possible that even if an X-FEN records an en passant square, making that capture would be illegal, either because of discovered check (where the king lies on the same rank as the two pawns, or same diagonal as one of them, or same file as the capturing pawn, in line with an enemy queen, rook or bishop), or because making the move leaves the player in check.
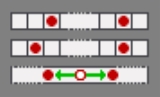
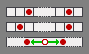 Usually the King's castling target is either two squares away from the left (white) border or one square from the right border. But there are also variants having symmetrically distributed target squares (e.g. Janus Chess
Usually the King's castling target is either two squares away from the left (white) border or one square from the right border. But there are also variants having symmetrically distributed target squares (e.g. Janus Chess
), both a single field distant each. Then an additional "s" has to precede the castling tokens. Another prefix "m" means: modern castling (e.g. Embassy Chess or Chess480). Here the King will move a regular castling distance (8x8: two steps, 10x8: three steps) aside, but at most just before the border.
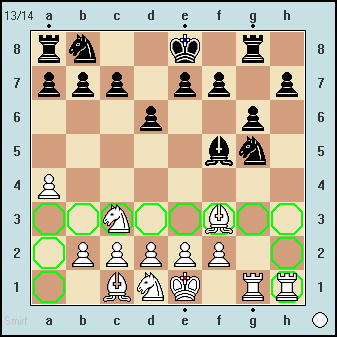
X-FEN = rn2k1r1/ppp1pp1p/3p2p1/5bn1/P7/2N2B2/1PPPPP2/2BNK1RR w Gkq - 4 11
[Event "SmirfGUI Computerchess Game"]
[Site "CHESSBOX"]
[Date "2005.06.19"]
[Time "10:22:29"]
[Round "Test"]
[White "White"]
[Black "Black"]
[Result "*"]
[Annotator "R. Scharnagl"]
[SetUp "1"]
[FEN "rnbnkqrb/pppppppp/8/8/8/8/PPPPPPPP/RNBNKQRB w KQkq - 0 1"]
1. h4 g6 2. g3 Bf6 3. a4 Qh6 4. Ra3 Bxh4 5. gxh4 Qxh4 6. Qh3 Qxh3 7. Rxh3 Ne6
8. Bf3 d6 9. Nbc3 Ng5 10. Rhh1 Bf5 11. O-O *
Forsyth-Edwards Notation
Forsyth–Edwards Notation is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position....
(FEN).
The traditional Forsyth-Edwards Notation is not sufficient to represent all possible positions in 8x8 Chess960
Chess960
Chess960 is a chess variant invented and advocated by former World Chess Champion Bobby Fischer, originally announced on June 19, 1996 in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It employs the same board and pieces as standard chess, but the starting position of the pieces is randomized along the players' home...
(aka Fischer Random Chess
Chess
Chess is a two-player board game played on a chessboard, a square-checkered board with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. It is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide at home, in clubs, online, by correspondence, and in tournaments.Each player...
) or 10x8 Capablanca random chess
Capablanca random chess
Capablanca Random Chess is a chess variant invented by Reinhard Scharnagl in 2004. It combines the piece set and 10x8 board from Capablanca Chess with the permutation idea of Fischer Random Chess...
(CRC). Consequently, an extension of FEN was needed, with the requirement of being fully backward compatible
Backward compatibility
In the context of telecommunications and computing, a device or technology is said to be backward or downward compatible if it can work with input generated by an older device...
. X-FEN (formerly FRC-FEN), introduced by Reinhard Scharnagl
Reinhard Scharnagl
Reinhard Scharnagl is author of a book about the future of the game of Chess, inventor of Capablanca Random Chess and the Chess960 numbering scheme and developer of the chess variant program SMIRF.- Chessbook author :...
in 2003, accomplishes this.
X-FEN definition
X-FEN is based on traditional FEN. It differs only in the way that castlingCastling
Castling is a special move in the game of chess involving the king and either of the original rooks of the same color. It is the only move in chess in which a player moves two pieces at the same time. Castling consists of moving the king two squares towards a rook on the player's first rank, then...
and en passant
En passant
En passant is a move in the board game of chess . It is a special pawn capture which can occur immediately after a player moves a pawn two squares forward from its starting position, and an enemy pawn could have captured it had it moved only one square forward...
tags are used. Moreover, 10x8 positions, which rely on José Raúl Capablanca
José Raúl Capablanca
José Raúl Capablanca y Graupera was a Cuban chess player who was world chess champion from 1921 to 1927. One of the greatest players of all time, he was renowned for his exceptional endgame skill and speed of play...
's extended piece set (additional pieces Chancellor and Archbishop), are supported.
X-FEN inside of PGN
Games are translated into PGNPortable Game Notation
Portable Game Notation is a computer-processible format for recording chess games ; many chess programs recognize this extremely popular format due to its being stored in plain text.-History:...
format (Portable Game Notation). Unlike traditional chess games, Chess960
Chess960
Chess960 is a chess variant invented and advocated by former World Chess Champion Bobby Fischer, originally announced on June 19, 1996 in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It employs the same board and pieces as standard chess, but the starting position of the pieces is randomized along the players' home...
or CRC games (Capablanca random chess
Capablanca random chess
Capablanca Random Chess is a chess variant invented by Reinhard Scharnagl in 2004. It combines the piece set and 10x8 board from Capablanca Chess with the permutation idea of Fischer Random Chess...
) require storing the particular starting positions. This is done using a SetUp tag and a FEN string, using the definitions for traditional chess games.
Encoding en-passant
The specification of an en passantEn passant
En passant is a move in the board game of chess . It is a special pawn capture which can occur immediately after a player moves a pawn two squares forward from its starting position, and an enemy pawn could have captured it had it moved only one square forward...
target differs slightly from standard Forsyth-Edwards Notation
Forsyth-Edwards Notation
Forsyth–Edwards Notation is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position....
. FEN records the en passant square field as the square just behind a pawn that has made a two-square push forward in the latest move. As such, whenever a pawn makes a two-square move, the "en passant" square is recorded. From the sample game given in Forsyth-Edwards Notation
Forsyth-Edwards Notation
Forsyth–Edwards Notation is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position....
, we see that FEN includes the square e3 as an en passant square after White makes the first move of the game 1. e4. This is somewhat misleading, as no en passant captures can be made by Black from the position.
X-FEN, on the other hand, includes only true en passant squares. That is, X-FEN records a value in the field for an en passant square only if there are one or more enemy pawns on the same rank on an adjacent file. Thus, after 1. e4, the field for the en passant square is left blank, as Black cannot make an en passant capture. However, it is possible that even if an X-FEN records an en passant square, making that capture would be illegal, either because of discovered check (where the king lies on the same rank as the two pawns, or same diagonal as one of them, or same file as the capturing pawn, in line with an enemy queen, rook or bishop), or because making the move leaves the player in check.
Encoding castling rights
Castling tags "KkQq" are used as known from FEN. As usual lower case letters indicate castling rights for Black, and upper case letters those for White. "Kk" identifies the ability of g-castling, and "Qq" indicates c-castling (rsp. i-castling at 10x8 Chess). The new and crucial point of the arrangement is, that the castling rights provided by this as default are related to the outermost Rook of the affected side. If instead an inner Rook is associated with that right, the traditional castling tag will be replaced by the file letter of the involved Rook, using upper case for White.
Janus chess
Janus Chess is a chess variant played on a 10×8 board. It features a new piece, the Janus , with the combined moves of a bishop and a knight. This piece is named after the Roman god Janus because this god was usually depicted with two faces looking in opposite directions...
), both a single field distant each. Then an additional "s" has to precede the castling tokens. Another prefix "m" means: modern castling (e.g. Embassy Chess or Chess480). Here the King will move a regular castling distance (8x8: two steps, 10x8: three steps) aside, but at most just before the border.
10x8 chess
Ten consecutive free squares in a rank are encoded by "10", and nine free squares are represented with a "9". For an Archbishop (Knight + Bishop) the letter "A" is used; a Chancellor (Knight + Rook) is encoded using the letter "C". As usual, lowercase letters are used for black pieces.Compatibility
The starting position of traditional chess and moreover all of the 18 Pseudo FRC starting position arrays (with castling enabled Rooks and Kings situated in their traditional places) and positions resulting from those entirely will be identically encoded by X-FEN just as usual. Thus X-FEN is fully downwards compatible with traditional FEN.Selecting games
To use only traditional chess games from within a PGN file (a problem present since Shuffle chess), simply select only PGN entries that do not include any FEN tags.X-FEN example
Castling Right inner Rook before 11. O-O
X-FEN = rn2k1r1/ppp1pp1p/3p2p1/5bn1/P7/2N2B2/1PPPPP2/2BNK1RR w Gkq - 4 11
[Event "SmirfGUI Computerchess Game"]
[Site "CHESSBOX"]
[Date "2005.06.19"]
[Time "10:22:29"]
[Round "Test"]
[White "White"]
[Black "Black"]
[Result "*"]
[Annotator "R. Scharnagl"]
[SetUp "1"]
[FEN "rnbnkqrb/pppppppp/8/8/8/8/PPPPPPPP/RNBNKQRB w KQkq - 0 1"]
1. h4 g6 2. g3 Bf6 3. a4 Qh6 4. Ra3 Bxh4 5. gxh4 Qxh4 6. Qh3 Qxh3 7. Rxh3 Ne6
8. Bf3 d6 9. Nbc3 Ng5 10. Rhh1 Bf5 11. O-O *

