
Yank (physics)
Encyclopedia
In physics
, yank is the derivative of force
with respect to time
. Expressed as an equation, yank Y is:
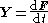
where F is force and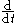 is the derivative with respect to time
is the derivative with respect to time  .
.
The term yank is not universally recognized but is commonly used. The units of yank are force per time, or equivalently, mass times length per time cubed; in the SI unit system this is kilogram
metre
s per second
cubed (kg·m/s3), or Newtons per second (N/s).
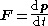
where p is momentum
, so if we combine the above two equations:
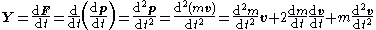
where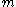 is mass
is mass
and v is velocity
. If the mass isn't changing over time (i.e. it's constant), then:
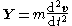
which can also be written as:
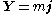
where j is jerk.
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, yank is the derivative of force
Force
In physics, a force is any influence that causes an object to undergo a change in speed, a change in direction, or a change in shape. In other words, a force is that which can cause an object with mass to change its velocity , i.e., to accelerate, or which can cause a flexible object to deform...
with respect to time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
. Expressed as an equation, yank Y is:
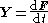
where F is force and
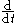 is the derivative with respect to time
is the derivative with respect to time  .
.The term yank is not universally recognized but is commonly used. The units of yank are force per time, or equivalently, mass times length per time cubed; in the SI unit system this is kilogram
Kilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
s per second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
cubed (kg·m/s3), or Newtons per second (N/s).
Relation to other physical quantities
Newton's second law of motion says that: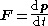
where p is momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
, so if we combine the above two equations:
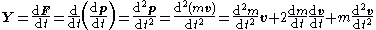
where
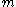 is mass
is massMass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
and v is velocity
Velocity
In physics, velocity is speed in a given direction. Speed describes only how fast an object is moving, whereas velocity gives both the speed and direction of the object's motion. To have a constant velocity, an object must have a constant speed and motion in a constant direction. Constant ...
. If the mass isn't changing over time (i.e. it's constant), then:
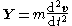
which can also be written as:
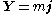
where j is jerk.

