
Yoyo@home
Encyclopedia
Yoyo@home is a distributed computing
project and running on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing
(BOINC) software platform. There are over 7,500 users committing computer cycles to the project. Yoyo@home integrates existing distributing computing projects using the Boinc Wrapper technology in the Boinc world. The largest benefits of this is a much large user base for the otherwise less known projects.
Subprojects include:
In the past the OGR-subproject has helped searching for the optimal golomb ruler of length 25 and 26.
Distributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system consists of multiple autonomous computers that communicate through a computer network. The computers interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal...
project and running on the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing
Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing
The Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing is an open source middleware system for volunteer and grid computing. It was originally developed to support the SETI@home project before it became useful as a platform for other distributed applications in areas as diverse as mathematics,...
(BOINC) software platform. There are over 7,500 users committing computer cycles to the project. Yoyo@home integrates existing distributing computing projects using the Boinc Wrapper technology in the Boinc world. The largest benefits of this is a much large user base for the otherwise less known projects.
Subprojects include:
- OGR-27, The original Distributed.netDistributed.netdistributed.net is a worldwide distributed computing effort that is attempting to solve large scale problems using otherwise idle CPU or GPU time. It is officially recognized as a non-profit organization under U.S...
client is integrated. This project will find an optimal golomb rulerGolomb rulerIn mathematics, a Golomb ruler is a set of marks at integer positions along an imaginary ruler such that no two pairs of marks are the same distance apart. The number of marks on the ruler is its order, and the largest distance between two of its marks is its length...
with the length of 27. - Evolution@HomeEvolution@HomeEvolution@Home is the first parallel computing project for evolutionary biology. The aim of Evolution@Home is to improve understanding of evolutionary processes. This is achieved by simulating individual-based models. The first such model targets the accumulation of mutations in asexual populations...
- Muon
- ECMLenstra elliptic curve factorizationThe Lenstra elliptic curve factorization or the elliptic curve factorization method is a fast, sub-exponential running time algorithm for integer factorization which employs elliptic curves. For general purpose factoring, ECM is the third-fastest known factoring method...
-factoring, in 2009 a user found the then largest known factor ever discovered by ECM-factoring - EulerNet, searching for the first known solution of
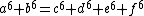
In the past the OGR-subproject has helped searching for the optimal golomb ruler of length 25 and 26.

