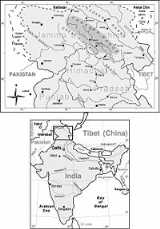
Zanskar
Encyclopedia
Tehsil
A Tehsil or Tahsil/Tahasil , also known as Taluk and Mandal, is an administrative division of some country/countries of South Asia....
of the Kargil district
Kargil District
Kargil is a district of Ladakh, Kashmir, India. Kargil lies near the Line of Control facing Pakistan-occupied Kashmir's Baltistan to the west, and Kashmir valley to the south. Zanskar is part of Kargil district along with Suru, Wakha and Dras valleys...
, which lies in the eastern half of the India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n state of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
. The administrative centre is Padum
Padum
Padum is the largest town and administrative centre of Zanskar tehsil of Kargil district in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It is 240 km away from Kargil.-Description:...
. Zanskar, together with the neighbouring region of Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
, was briefly a part of the kingdom of Guge
Guge
Guge was an ancient kingdom in Western Tibet. The kingdom was centered in present-day Zanda County, within Ngari Prefecture of Tibet Autonomous Region, China. At various points in history after 10th century AD, the kingdom held sway over a vast area including south-eastern Zanskar, Upper Kinnaur,...
in Western Tibet.
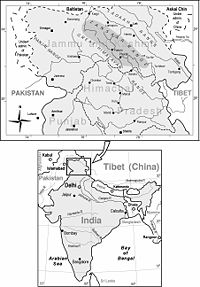
The Zanskar Range is a mountain range
Mountain range
A mountain range is a single, large mass consisting of a succession of mountains or narrowly spaced mountain ridges, with or without peaks, closely related in position, direction, formation, and age; a component part of a mountain system or of a mountain chain...
in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
that separates Zanskar from Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
. Geologically, the Zanskar Range is part of the Tethys Himalaya
Geology of the Himalaya
The geology of the Himalaya is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of modern plate tectonic forces. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namche Barwa syntaxis in Tibet and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis in Pakistan, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the result...
, an approximately 100-km-wide synclinorium formed by strongly folded and imbricated, weakly metamorphosed sedimentary series. The average height of the Zanskar Range is about 6,000 m (19,700 ft). Its eastern part is known as Rupshu
Rupshu
Rupshu is a valley in southeast Ladakh, on the Leh-Manali highway. The altitude of the valley is between 4,500 and 5,500 metres. It is inhabited by the Changpa nomads.- External links :* published in The Statesman, 16 June 2004....
.







Etymology
Zanskar appears as “Zangskar” mostly in academic studies in social sciences (anthropologyAnthropology
Anthropology is the study of humanity. It has origins in the humanities, the natural sciences, and the social sciences. The term "anthropology" is from the Greek anthrōpos , "man", understood to mean mankind or humanity, and -logia , "discourse" or "study", and was first used in 1501 by German...
, gender studies
Gender studies
Gender studies is a field of interdisciplinary study which analyses race, ethnicity, sexuality and location.Gender study has many different forms. One view exposed by the philosopher Simone de Beauvoir said: "One is not born a woman, one becomes one"...
), reflecting the Ladakhi pronunciation, although the Zanskari pronunciation is Zãhar. Older geographical accounts and maps may use the alternate spelling "Zaskar". An etymological study (Snellgrove and Skorupsky, 1980) of the name reveals that its origin might refer to the natural occurrence of copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
in this region, the Tibetan word for which is “Zangs”. The second syllable however seems to be more challenging as it has various meanings: “Zangs-dkar” (white copper), “Zangs-mkhar” (copper palace), or “Zangs-skar” (copper star). Others claim it derives from zan = copper + skar = valley. Crook (1994) partly shares this interpretation but suggests that the origin of this name might also be “Zan-mKhar” (food palace), because the staple food crops are so abundant in an otherwise rather arid region. The locally accepted spelling of the name in Tibetan script is zangs-dkar.
Some of the religious scholars of the district, also cited by Snellgrove and Skorupsky (1980) and Crook (1994), hold that it was originally “bzang-dkar”, meaning good (or beautiful) and white. “Good” would refer to the triangular shape of the Padum plain, the triangle being the symbol of Dharma
Dharma
Dharma means Law or Natural Law and is a concept of central importance in Indian philosophy and religion. In the context of Hinduism, it refers to one's personal obligations, calling and duties, and a Hindu's dharma is affected by the person's age, caste, class, occupation, and gender...
and religion; “white” would refer to the simplicity, goodness, and religious inclinations of the Zanskaris. Thus, even if etymologically it would be more correct to use “Zangskar”, the most frequently found spelling for this region is undoubtedly “Zanskar”.
Geography
Zanskar covers an area of some 7000 square kilometres (2,702.7 sq mi), at a height of between 3,500 and 7,000 metres (11,500–23,000 feet). It consists of the country lying along the two main branches of the Zanskar river. The first, the Doda, has its source near the Pensi-laPensi-la
Pensi-la is a mountain pass in the Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir, which is known as the Gateway to Zanskar. Pensi La is 4,400 m above sea level and connects the Suru Valley region to the Zanskar Valley region...
(4,400 m) (14,450 ft) mountain-pass, and then flows south-eastwards along the main valley leading towards Padum, the capital of Zanskar.
The second branch is formed by two main tributaries known as Kargyag river, with its source near the Shingo La (5,091 m) (16,703 ft), and Tsarap river, with its source near the Baralacha-La. These two rivers unite below the village of Purne to form the Lungnak river (also known as the Lingti or Tsarap). The Lungnak river then flows north-westwards along a narrow gorge towards Zanskar's central valley (known locally as gzhung khor), where it unites with the Doda river to form the Zanskar river.
- "The Shingo La, the main route into Zanskar from Lahaul, is an unpleasant pass. It isn't particularly high, at just 17,000 feet, but it is squalid and sordid and lacks grandeur."
The Zanskar river then takes a north-eastern course until it joins the Indus
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
in Ladakh. High mountain ridges lie on both sides of the Doda and Lingti–kargyag valleys, which run north-west to south-east. To the south-west is the Great Himalayan
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
Range which separates Zanskar from the Kisthwar and Chamba basins. To the north-east lies the Zanskar Range, which separates Zanskar from Ladakh. The only outlet for the whole Zanskar hydrographic system is thus the Zanskar river, which cuts a deep and narrow gorge through the Zanskar range.
These topographical features explain why access to Zanskar is difficult from all sides. Communication with the neighbouring Himalayan areas is maintained across mountain passes or along the Zanskar river when frozen. The easiest approach leads from Kargil
Kargil town
Kargil is a town, which serves as the headquarters of Kargil District of Ladakh in the state of Jammu and Kashmir in India. It is the second largest town in Ladakh after Leh...
through the Suru valley
Suru valley
The Suru valley is a valley in the Ladakh region of Jammu and Kashmir, which is drained by the Suru River , a powerful tributary of the Indus river. The valley's most significant town is Kargil.-People of the Suru Valley:...
and over the Pensi La. It is along this track that in 1979 the first and only road in Zanskar was built to connect Padum with the main road from Srinagar into Ladakh. One of the first Tibetologists to spend an extended period in the region was Alexander Csoma de Koros, who spent over a year living in the region in 1823. After being integrated into the newly formed state of India in 1947, Zanskar and the neighboring region of Ladakh were both declared restricted areas and only opened to foreigners in 1974. The first colour film of life in Zanskar was shot in 1958 by an expedition of three British housewives http://www.telegraph.co.uk/education/main.jhtml?xml=/education/2008/04/21/st_womenexplorers.xml&page=3.
Flora and fauna
Much of Zanskar's vegetation is found in the irrigated villages, and on the upper slopes which receive more precipitation and where it consists of alpine and tundra species. Most impressive are the meadows covered with thousands of edelweissEdelweiss
Edelweiss , Leontopodium alpinum, is a well-known European mountain flower, belonging to the sunflower family.-Names:The common name comes from German edel, meaning "noble", and weiß "white", thus signifying "noble whiteness".The scientific name Leontopodium is a Latin adaptation of Greek...
. At the foot of the Gumburanjon mountain blue poppies can be found. Crops including barley, lentils, and potatoes are grown by farmers at the lower elevations. Domesticated animals such as the yak
Yak
The yak, Bos grunniens or Bos mutus, is a long-haired bovine found throughout the Himalayan region of south Central Asia, the Tibetan Plateau and as far north as Mongolia and Russia. In addition to a large domestic population, there is a small, vulnerable wild yak population...
, dzo
Dzo
A dzo is a hybrid of yak and domestic cattle. The word dzo technically refers to a male hybrid, while a female is known as a dzomo or zhom. Alternative Romanizations of the Tibetan names include zho and zo. In Mongolian it is called khainag...
, sheep, horse, and dog are found in the region.
Among the wildlife that can be found in Zanskar are the marmot
Marmot
The marmots are a genus, Marmota, of squirrels. There are 14 species in this genus.Marmots are generally large ground squirrels. Those most often referred to as marmots tend to live in mountainous areas such as the Alps, northern Apennines, Eurasian steppes, Carpathians, Tatras, and Pyrenees in...
, bear
Bear
Bears are mammals of the family Ursidae. Bears are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans, with the pinnipeds being their closest living relatives. Although there are only eight living species of bear, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout the Northern...
, wolf, snow leopard
Snow Leopard
The snow leopard is a moderately large cat native to the mountain ranges of South Asia and Central Asia...
, kiang
Kiang
The kiang is the largest of the wild asses. It is native to the Tibetan Plateau, where it inhabits montane and alpine grasslands. Its current range is restricted to Ladakh in Jammu and Kashmir, plains of the Tibetan plateau and northern Nepal along the Tibetan border...
, bharal
Bharal
The bharal or Himalayan blue sheep or naur, Pseudois nayaur, is a caprid found in the high Himalayas of Nepal, Tibet, China, India, Pakistan, and Bhutan...
, alpine ibex, wild sheep and goats, and the lammergeier
Lammergeier
The Lammergeier, Lammergeyer, or Bearded Vulture, Gypaetus barbatus , is the only member of the genus Gypaetus. Traditionally considered an Old World vulture, it actually forms a minor lineage of Accipitridae together with the Egyptian Vulture , its closest living relative...
.
Climate
Zanskar is a high altitude semi-desert lying on the Northern flank of the Great Himalayan Range. This mountain range acts as a climatic barrier protecting Ladakh and Zanskar from most of the monsoon, resulting in a pleasantly warm and dry climate in the summer. Rain and snowfall during this period are scarce, although recent decades have shown a trend towards increasing precipitation. Several water-driven mills were built during ancient periods of drought at a great distance from the villages, but have been abandoned because running water is now available nearer to the settlements. Zanskari houses, though otherwise well built, are not adapted to the recently increasing rainfall, as their roofs leak, catching their surprised inhabitants unprepared. Most of the precipitation occurs as snowfall during the harsh and extremely long winter period. These winter snowfalls are of vital importance, since they feed the glaciers which melt in the summer and provide most of the irrigation water. Parts of Zanskar valley are considered some of the coldest continually inhabited places in the world.Population
Zanskar's population is small, the April 2006 medical census records a population of 13,849 people. The medical census is the most accurate indicator of population as it collects birth, death, and census information from Zangskar's 22 medical aid centers. Roughly 95% of the inhabitants practice Tibetan Buddhism, while the remainder are Sunni Muslims, whose ancestors settled in Padum and its environs in the 19th century. The majority of Zanskaris are of mixed TibetanTibetan people
The Tibetan people are an ethnic group that is native to Tibet, which is mostly in the People's Republic of China. They number 5.4 million and are the 10th largest ethnic group in the country. Significant Tibetan minorities also live in India, Nepal, and Bhutan...
and Indo-European origins; notably Dard
Dard people
The Dards are a group of people defined by linguistic similarities, and not common ethnicity, predominantly found in Eastern Afghanistan, in the Indian State of Jammu and Kashmir and in the Northern Areas and North West Frontier Province of Pakistan...
and Mon. The latter are in fact ethnically Dard, but "Mon" is used in order to distinguish them from later Dard settlers.
The population lives mainly in scattered small villages, the largest being the capital Padum
Padum
Padum is the largest town and administrative centre of Zanskar tehsil of Kargil district in the state of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It is 240 km away from Kargil.-Description:...
, with nearly 700 inhabitants. Most of the villages are located in the valleys of the Zanskar river and its two main tributaries. Given the isolation of this region, the inhabitants tend towards self-sufficiency, and until recently lived in almost complete autarky
Autarky
Autarky is the quality of being self-sufficient. Usually the term is applied to political states or their economic policies. Autarky exists whenever an entity can survive or continue its activities without external assistance. Autarky is not necessarily economic. For example, a military autarky...
. External trade has, however, always been necessary for the acquisition of goods such as tool
Tool
A tool is a device that can be used to produce an item or achieve a task, but that is not consumed in the process. Informally the word is also used to describe a procedure or process with a specific purpose. Tools that are used in particular fields or activities may have different designations such...
s, jewellery
Jewellery
Jewellery or jewelry is a form of personal adornment, such as brooches, rings, necklaces, earrings, and bracelets.With some exceptions, such as medical alert bracelets or military dog tags, jewellery normally differs from other items of personal adornment in that it has no other purpose than to...
, or religious artefact
Cultural artifact
A cultural artifact is a term used in the social sciences, particularly anthropology, ethnology, and sociology for anything created by humans which gives information about the culture of its creator and users...
s.
The Zanskaris' main occupations are cattle-rearing and farming of land that they almost always own. Cultivable land is scarce, and restricted to alluvial fans and terraces, cultivated fields being rarely found above an altitude of 4,000 metres. The Zanskaris have developed a system of intensive arable agriculture and complex irrigation to produce enough food in these conditions. The scarcity of cultivable land has also resulted in a tendency towards a stable, zero-growth population. An efficient birth-control system in Zanskar has historically been achieved by the common practice of polyandrous
Polyandry
Polyandry refers to a form of marriage in which a woman has two or more husbands at the same time. The form of polyandry in which a woman is married to two or more brothers is known as "fraternal polyandry", and it is believed by many anthropologists to be the most frequently encountered...
marriage, in which several brothers are married to the same wife, and the widespread adoption of a celibate religious life. A high infant mortality rate also contributes to population stability.
In the summer, the women and children stay far away from the villages to tend to the livestock. This system, known as transhumance
Transhumance
Transhumance is the seasonal movement of people with their livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and to lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Only the herds travel, with...
, is similar to the one found in the Alps where the animals are sent during the summer higher up in the mountains (the alpages) and were kept by the children and women.
Religion
Aside from some 300 Sunni Muslims living in Padum (out of a population of about 700), almost the whole population of Zanskar is Buddhist However, most of the senior government posts are filled by Muslims of Tehsil centre Padum. Almost every village has a local monastery, often containing ancient wall-paintings and images. There are two main branches of Tibetan Buddhism here — the Drugpa, including Sani MonasterySani Monastery
Sani Monastery , Sa-ni-[tshog], is located next to the village of Sani where the Stod Valley broadens into the central plain of Zanskar in Jammu and Kashmir in northern India. It is about 6 km to the northwest of the regional centre of Padum, a gentle two hour walk...
, Dzongkhul, Stagrimo and Bardan Monastery
Bardan Monastery
Bardan Monastery or Bardan Gompa is a 17th century Buddhist monastery, approximately 12 kilometres south of Padum, in Zanskar, Ladakh, northern India. It belongs to the Dugpa-Kargyud monastic order and was one of the first monasteries of this sect to be established in Zanskar...
- all loosely affiliated with Stakna in the Indus valley. The Gelugpa control Rangdum Monastery
Rangdum Monastery
Rangdum Monastery is a Tibetan Buddhist monastery belonging to the Gelugpa sect, situated on top of a small but steep sugarloaf hill at an altitude of 3,657 m at the head of the Suru Valley, in Ladakh...
, Karsha, Stongde and Phugtal Monastery
Phugtal Monastery
Phugtal Monastery or Phugtal Gompa is a monastery in south-eastern Zanskar, Ladakh in northern India....
, which all pay allegiance to the Ngari Rinpoche, who has his main seat at Likir Monastery
Likir Monastery
Likir Monastery or Likir Gompa is a Buddhist monastery in Ladakh, northern India, located approximately west of Leh. It is picturesquely situated on a little hill in the valley near the Indus River and the village of Saspol about north of the Srinigar to Leh highway...
in Ladakh. The present emanation of the Ngari Rinpoche is the younger brother of the Dalai Lama.
Livestock
Livestock, and especially the yakYak
The yak, Bos grunniens or Bos mutus, is a long-haired bovine found throughout the Himalayan region of south Central Asia, the Tibetan Plateau and as far north as Mongolia and Russia. In addition to a large domestic population, there is a small, vulnerable wild yak population...
, is of paramount importance in Zanskar. Yaks are used to plough the land, to thresh the grain, to carry heavy loads (up to 200 kilograms), and their dung not only serves as fertiliser but is also the only heating fuel available in the region. They are a vital source of milk and sometimes, but rarely, of meat. The yak's fur is used to make clothes, carpets, ropes, and bed covers.
History
The first traces of human activity in Zanskar seem to go back as far as the Bronze AgeBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
. Petroglyph
Petroglyph
Petroglyphs are pictogram and logogram images created by removing part of a rock surface by incising, picking, carving, and abrading. Outside North America, scholars often use terms such as "carving", "engraving", or other descriptions of the technique to refer to such images...
s attributed to that period suggest that their creators were hunters on the steppes of central Asia, living between Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. It is suspected that an Indo-European population known as the Mon might then have lived in this region, before mixing with or being replaced by the next settlers, the Dards. Early Buddhism coming from Kashmir spread its influence in Zanskar, possibly as early as 200 BC. The earliest monuments date from the Kushan period. After this eastward propagation of Buddhism, Zanskar and large parts of the Western Himalaya were overrun in the 7th century by the Tibetans, who imposed their then animistic Bön religion.
Buddhism regained its influence over Zanskar in the 8th century when Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
was also converted to this religion. Between the 10th and 11th centuries, two Royal Houses were founded in Zanskar, and the monasteries of Karsha and Phugtal (see picture) were built. Until the 15th century Zanskar existed as a more or less independent Buddhist Kingdom ruled by between two and four related royal families. Since the 15th century, Zanskar has been subordinate to Ladakh, sharing its fortunes and misfortunes. In 1822 a coalition of Kulu, Lahoul, and Kinnaur invaded Zanskar, plundering the country and destroying the Royal palace at Padum.
In the mid-20th century, border conflicts between India, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, and China caused Ladakh and Zanskar to be closed to foreigners. During these wars Ladakh lost two thirds of its original territory, losing Baltistan
Baltistan
Baltistan , also known as بلتیول བལིུལ་ in the Balti language, is a region in northern Pakistan which forms Gilgit-Baltistan, bordering the Xinjiang Autonomous Region of China. In addition, a part of Baltistan also falls into Jammu and Kashmir of India. It is situated in the Karakoram mountains...
to Pakistan and the Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
to China. Ladakh and Zanskar, despite a tumultuous history of internal wars and external aggressions, have never lost their cultural and religious heritage since the 8th century. Thanks to its adherence to the Indian Union, this is also one of the rare regions in the Himalaya where traditional Tibetan culture, society, and buildings survived the Chinese Cultural Revolution
Cultural Revolution
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, commonly known as the Cultural Revolution , was a socio-political movement that took place in the People's Republic of China from 1966 through 1976...
. In the last twenty years, the opening of a road and the massive influx of tourists and researchers have brought many changes to the traditional social organisation of Zanskar. In 2007 the valley suffered its third year of a desert locust infestation with many villages losing their crops. The response of the monasteries was to carry out Puja ( prayer ) to get rid of them whilst the government was advocating the use of insecticides which the Buddhists were reluctant to use, but in some cases were forced to try with as yet undocumented success. In 2008 it was reported that the Locusts had left the central Zanskar plains.
Tourism
Tourism is probably the major disruption that Zanskar has experienced during recent times. The opening of this region to foreigners has brought benefits such as the financing of schools and the restoration of monasteries and roads, but has also taken its toll on this fragile mountain environment and its population. Not only do the campsites along the trekking routes look more and more like junkyards at the end of the tourist season, but the local population has sometimes developed a questionable attitude towards visitors, involving begging, and very occasionally theft.Languages
Most of the people living in Zanskar speak ZanskariZanskari
Zanskari may refer to:* the people of Zanskar, a tehsil of Kargil district, Jammu and Kashmir, India* the Zaniskari pony, a breed of pony found around Leh and Laddakh, Jammu and Kashmir, India...
, which is closely related to Ladakhi, and can communicate in Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
or Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
. Monks who have studied outside of Zanskar may know Tibetan, and some Zanskaris know enough English to be able to communicate with tourists.

