
Zener card
Encyclopedia
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
s for extra-sensory perception
Extra-sensory perception
Extrasensory perception involves reception of information not gained through the recognized physical senses but sensed with the mind. The term was coined by Frederic Myers, and adopted by Duke University psychologist J. B. Rhine to denote psychic abilities such as telepathy, clairaudience, and...
(ESP), most often clairvoyance
Clairvoyance
The term clairvoyance is used to refer to the ability to gain information about an object, person, location or physical event through means other than the known human senses, a form of extra-sensory perception...
. Perceptual psychologist
Psychologist
Psychologist is a professional or academic title used by individuals who are either:* Clinical professionals who work with patients in a variety of therapeutic contexts .* Scientists conducting psychological research or teaching psychology in a college...
Karl Zener
Karl Zener
Karl Edward Zener was a perceptual psychologist best known for his affiliation with Dr. J. B. Rhine and their work in the field of Extra-sensory perception or ESP....
designed the cards in the early 1930s for experiments conducted with his colleague, parapsychologist J. B. Rhine.
Design
Originally, tests for ESP were conducted using a standard deck of playing cards. However, there are many confounding variables involved with this methodology. When this methodology is used, a participant is only credited a correct prediction for guessing both the number and suit of the card. This means that the chance of correctly guessing a card is greatly reduced, and there is a lot of ambiguity involved with statistical analysis. Another problem with using playing cards is that many people will have a preference for a particular card, number or suit (Irwin 1999) and will constantly suggest that as their prediction for the next card that will appear. This led to the development of a set of cards known as Zener cards, invented by Karl ZenerKarl Zener
Karl Edward Zener was a perceptual psychologist best known for his affiliation with Dr. J. B. Rhine and their work in the field of Extra-sensory perception or ESP....
.
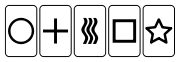
There are just five different Zener cards: a hollow circle
Circle
A circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
(one curve), a Greek cross (two lines), three vertical wavy lines (or "waves"), a hollow square
Square (geometry)
In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles...
(four lines), and a hollow five-pointed star
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
. There are 25 cards in a pack, five of each design.
When Zener cards were first used, they were made out of a fairly thin translucent white paper. Several subjects or groups of subjects scored very highly until it was discovered that they had often been able to see the symbols through the backs of the cards. A redesign made it impossible to see the designs through the cards under any conditions. A subsequent deck featured an illustration of a building at Duke University on its reverse side, but the use of a non-symmetric reverse design allowed the deck to be exploited as a one-way deck
One-way deck
A one-way deck is a deck of playing cards where the back of the cards has a pattern which can be oriented to have a "top" and "bottom". Magicians and card sharps can use the orientations of cards in one-way decks to encode information that allows them to perform card tricks.A certain number of the...
.
Use in experiments
In a test for clairvoyance, the person conducting the test (the experimenter) picks up a card in a shuffled pack, observes the symbol on the card, and records the answer of the person being tested for extra sensory perception, who must correctly determine which of the five designs is on the card in question. The experimenter continues until all the cards in the pack have been tested.Third parties may oversee or videotape an experiment to make sure it is conducted fairly. While it is especially important to ensure that the subject cannot see any cards and does not receive any vocal or visual clues from the experimenter, other methods of cheating are possible. To this end, physical separators may be placed between the experimenter and the subject. As with other ESP tests, experiments with Zener cards have used elaborate methods to keep the subject from seeing the cards or the experimenter, sometimes placing the subject in a separate room.
If the subject is informed during the test that specific guesses were correct or incorrect, card counting
Card counting
Card counting is a casino card game strategy used primarily in the blackjack family of casino games to determine whether the next hand is likely to give a probable advantage to the player or to the dealer. Card counters, also known as advantage players, attempt to decrease the inherent casino house...
can increase his or her accuracy; also, poor shuffling methods can make the order of cards in the deck easier to predict. In his experiments, Rhine first shuffled the cards by hand but later decided to use a machine for shuffling.
Online variations of Zener card tests currently exist on the internet. If properly constructed, tests of this nature can circumvent the issues of bias and cheating common to standard Zener card tests. One such online system, the Anima Project, gathers user results into a master database which is then analyzed using a variety of statistical techniques.
Although Zener cards are usually used to test for clairvoyance, they may also be used to test for telepathy
Telepathy
Telepathy , is the induction of mental states from one mind to another. The term was coined in 1882 by the classical scholar Fredric W. H. Myers, a founder of the Society for Psychical Research, and has remained more popular than the more-correct expression thought-transference...
, in which case one subject will draw a card and attempt to mentally project the image on it to the mind of another subject. Here, the statistical tendency of the receiver to report a specific design must be taken into account – for example, he or she might tend to report receiving an image of a square more than other images – so the deck used must contain an equal number of cards of each design.
Statistics
If the null-hypothesisNull hypothesis
The practice of science involves formulating and testing hypotheses, assertions that are capable of being proven false using a test of observed data. The null hypothesis typically corresponds to a general or default position...
(no psychic ability) is assumed and each card selected for testing is chosen in a truly random fashion, a user's success ratio is expected to approach 20% (1 hit per 5 trials) as their number of trials increases. The further the observed scenario is from the expected scenario, the more cause for believing the null-hypothesis is not true (the results are not simply due to chance).

