
Zero-crossing rate
Encyclopedia
The zero-crossing rate is the rate of sign-changes along a signal, i.e., the rate at which the signal changes from positive to negative or back. This feature has been used heavily in both speech recognition
and music information retrieval
and is defined formally as
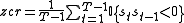
where is a signal of length
is a signal of length 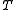 and the indicator function
and the indicator function 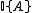 is 1 if its argument
is 1 if its argument 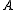 is true and 0 otherwise.
is true and 0 otherwise.
For monophonic
tonal signals, the zero-crossing rate can be used as a primitive pitch detection algorithm
.
Speech recognition
Speech recognition converts spoken words to text. The term "voice recognition" is sometimes used to refer to recognition systems that must be trained to a particular speaker—as is the case for most desktop recognition software...
and music information retrieval
Music information retrieval
Music information retrieval is the interdisciplinary science of retrieving information from music. MIR is a small but growing field of research with many real-world applications...
and is defined formally as
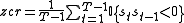
where
 is a signal of length
is a signal of length 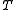 and the indicator function
and the indicator function 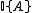 is 1 if its argument
is 1 if its argument 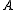 is true and 0 otherwise.
is true and 0 otherwise.For monophonic
Monaural
Monaural or monophonic sound reproduction is single-channel. Typically there is only one microphone, one loudspeaker, or channels are fed from a common signal path...
tonal signals, the zero-crossing rate can be used as a primitive pitch detection algorithm
Pitch detection algorithm
A pitch detection algorithm is an algorithm designed to estimate the pitch or fundamental frequency of a quasiperiodic or virtually periodic signal, usually a digital recording of speech or a musical note or tone. This can be done in the time domain or the frequency domain.PDAs are used in various...
.

