
ZiU-5
Encyclopedia

Trolleybus
A trolleybus is an electric bus that draws its electricity from overhead wires using spring-loaded trolley poles. Two wires and poles are required to complete the electrical circuit...
. The ZiU acronym stands for Zavod imeni Uritskogo (Russian Завод имени Урицкого, ЗиУ, which corresponds to Plant named after Uritskiy (Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Uritsky
Moisei Solomonovich Uritsky was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader in Russia.He was born in the city of Cherkasy, Kiev Governorate, to a Jewish family. His father, a merchant, died when Moisei was little and his mother raised her son by herself.Moisei studied law at the University of Kiev...
, a Russian revolutionary). This model of city trolleybus was in mass production from 1959 to 1972. Total number of produced ZiU-5s exceeds 20000 vehicles. This allowed ZiU-5 to became dominant model of trolleybus in Soviet towns and cities of that time. Last vehicles were withdrawn from active service in the mid-1980s (the exact date varies from city to city). The small number of surviving vehicles are kept now for museum purposes.
History of development
The first decade after Second World War was a period of huge expansion of trolleybus systems in the Soviet UnionSoviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. They were considered as an innovative decision in comparison with "semi-obsolete" and expensive tram
Tram
A tram is a passenger rail vehicle which runs on tracks along public urban streets and also sometimes on separate rights of way. It may also run between cities and/or towns , and/or partially grade separated even in the cities...
s. The mainstay for trolley fleet for that time was extremely simple, reliable and durable MTB-82 vehicle. But it was medium-sized and uncomfortable for both driver and passengers. After small series and experimental TBU-1 vehicles ZiU developed completely new model for mass production with all disadvantages of MTB-82 eliminated. This was first variant of ZiU-5. More than 200 vehicles were produced for wide testing on Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
streets in 1959. This huge testing work discovered the weaknesses of new design. Trolley depots in collaboration with ZiU and "Dynamo" electric motors factory fixed the problems in their repair facilities. Using this experience ZiU engineers corrected the ZiU-5 design, in 1960 new updated mass production series was launched. During mass production some technological adjustments were made, see Variants section. In 1971 ZiU introduced completely new trolleybus design, the ZiU-9
ZiU-9
ZiU-9 is the Soviet trolleybus vehicle. Other names and indexes for the same vehicle include ZiU-682 and HTI-682 . The ZiU acronym stands for Zavod imeni Uritskogo, which means plant named after Moisei Uritsky, the Russian revolutionary...
. It was more cheap due to technology improvements and refusal from aluminium hull and was able to carry more passengers than ZiU-5. So mass production of ZiU-5 ceased in 1972.
Variants
- ZiU-5 model 1959 with pneumatic door gear, combined front glasses and three rear windows
- ZiU-5 model 1960 with electric door gear, strengthened hull, single front glasses and one rear window
- ZiU-5G with minor technological improvements, recognizable by small rear route pointer window
- ZiU-5D, small rear route window removed, new Hungarian backbridge unit installed instead Soviet-made one.
ZiU-5s in Budapest
BudapestBudapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
transport operator FVV (roughly: Electric Tramways Company of the Capital), later BKV
BKV
BKV is the unified public transport company of Budapest, established in 1968...
(Budapest Transport Company) ordered altogether 100 ZiU-5 vehicles between 1966-69. These cars, equipped with power steering and automatic controllers, were relatively modern compared to the trolleybuses running on the streets of Budapest that time. On the other hand, in some ways they proved seriously impractical.
The cars were rather long but had only two passenger doors. Moreover, having no cab window on the right side impaired the driver's vision to the right, which was worked around by further narrowing the front door. These problems ended the career of the Budapest ZiU-5 fleet very soon, and all (except for one preserved car) got scrapped by 1982. However, this is not the end of the ZiU5- story. Between 1975 and 1978, BKV obtained 79 articulated Ikarus
Ikarus Bus
Ikarus is a bus manufacturer based in Budapest, Hungary. It was established in 1895 as Uhri Imre Kovács- és Kocsigyártó Üzeme .-History:...
280 bus bodies together with an Ikarus 260 solo bus body, and installed the electric system of the ZiU-5s in parallel with the scrapping.
(The solo program was discontinued due to the cheaper obtainment of ZiU-9
ZiU-9
ZiU-9 is the Soviet trolleybus vehicle. Other names and indexes for the same vehicle include ZiU-682 and HTI-682 . The ZiU acronym stands for Zavod imeni Uritskogo, which means plant named after Moisei Uritsky, the Russian revolutionary...
solo trolleybuses. The only Ikarus 260 trolleybus is preserved as a heritage car and is restored in its original livery.)
These articulated Ikarus-ZiU trolleys were in service by the 90's, when they got replaced by more modern, although similar looking, Ikarus trolleys equipped with Ganz
Ganz
The Ganz electric works in Budapest is probably best known for the manufacture of tramcars, but was also a pioneer in the application of three-phase alternating current to electric railways. Ganz also made / makes: ships , bridge steel structures , high voltage equipment...
chopper-based electronics.
Technical details
ZiU-5 is a high-floor big class trolleybus for city mass transit. It's duraluminium hull mounted on the steelSteel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
frame and carcass constructions. The hull has two doors in its front and rear ends. The doors open and close automatically by electric gear under driver's control. The vehicle is powered by DK-207A 95-kilowatt electric motor. The current regulation system (controller unit) is an automatic indirect one. All commutation of power-circuit resistors is performed by a low-voltage electric servomotor. These resistors limit the electric current through the main motor and, therefore, regulate its speed and torque. ZiU-5 is equipped with motor-generator for transformation of the input DC high voltage (550V) to low service DC voltage of 24V. This transformation is quite simple - 550V electric motor has coaxial connection with 24V electric generator. However, the drawback of this simplicity is a constant noise of this device. However good oilment and centring procedures can reduce this noise to tolerant level. The low voltage subsystem includes mentioned above controller unit, internal and external lights, door gear and two accumulator
Accumulator (energy)
An accumulator is an apparatus by means of which energy can be stored, such as a rechargeable battery or a hydraulic accumulator. Such devices may be electrical, fluidic or mechanical and are sometimes used to convert a small continuous power source into a short surge of energy or vice versa...
batteries. Due to differentiating voltage levels the hazard of electric shock
Electric shock
Electric Shock of a body with any source of electricity that causes a sufficient current through the skin, muscles or hair. Typically, the expression is used to denote an unwanted exposure to electricity, hence the effects are considered undesirable....
to driver and passengers was reduced greatly. All electric devices inside passengers' saloon and driver cabin are supplied only with safe 24V voltage. Power 550V circuits are placed under the floor. The brake system includes electrodynamic, mechanical and pneumatic brakes. The pneumatic brake has the electric compressor unit to maintain the pressure in air reservoirs.
ZiU-5 has 38 passengers seats and is able to transport 122 persons with full load. The maximal speed is limited by 68 km/h, but some drivers were able to accelerate the vehicle up to 100 km/h without passengers.
Technical data
- Length, mm : 11870
- Width, mm : 2680
- Height, mm : 3530
- Clearance, mm : 200
- Mass without load, t : 9.8
- Mass with moderate load, t : 14.6
- Maximal speed, km/h : 68
- Input voltage, V : 550
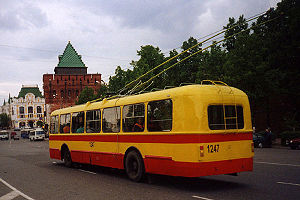
Survivors
There are a few number of operable ZiU-5s today. None of them work on the city lines and became museum vehicles. Many of them were reconstructed from empty abandoned hulls. They are available for observation (and sometimes for hire for city excursions) in Saint PetersburgSaint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
and Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod , colloquially shortened to Nizhny, is, with the population of 1,250,615, the fifth largest city in Russia, ranking after Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk, and Yekaterinburg...
. The group of city electric transport enthusiasts from many cities in Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
, with guests from Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
and United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, hired the Nizhny Novgorod Museum ZiU-5 for their meeting in 2004 (see photo above).
In Budapest there is a completely restored and operational heritage Ziu5, number 573, and also an Ikarus 260 trolley with Ziu5 electronics, number 600.
External links
- ZiU-5 page on Nizhny Novgorod tram site (in Russian)
- ZiU-5 page on Kharkiv transport site (in Russian)
- Trolleybus in Budapest (English)

