
ΔP
Encyclopedia
ΔP is a mathematical term used to illustrate a change (Δ) in pressure (P).
loss Δp as the height of a column of fluid,
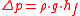
where ρ is the density of the fluid, the Darcy–Weisbach equation can also be written in terms of pressure loss:
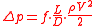
, compliance can be influenced by 3 key physiologic factors:
Lung compliance is influenced by a variety of primary abnormalities of lung parenchyma, both chronic and acute. Airway resistance
is typically increased by bronchospasm
and airway secretions. Chest wall compliance can be decreased by fixed abnormalities (eg, kyphoscoliosis
, morbid obesity) or more variable problems driven by patient agitation while intubated.
Calculating Compliance on minute volume (VE: ΔV is always defined by tidal volume
(VT), but ΔP is different for the measurement of dynamic vs. static compliance.
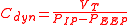
Cdyn — VT / (PIP - P_{EEP}), where PIP = peak inspiratory pressure
(the maximum pressure during inspiration). Alterations in airway resistance, lung compliance and chest wall compliance influence Cdyn.

Cstat — Vt / (Pplat - PEEP), where Pplat = plateau pressure. Pplat is measured at the end of inhalation and prior to exhalation using an inspiratory hold maneuver. During this maneuver, airflow is transiently (~0.5 sec) discontinued, which eliminates the effects of airway resistance. Pplat is never > PIP and is typically < 3-5 cmH2O lower than PIP when airway resistance is not elevated.
Darcy–Weisbach equation
As used in the Darcy–Weisbach equation — Given that the head loss hf expresses the pressurePressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
loss Δp as the height of a column of fluid,
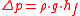
where ρ is the density of the fluid, the Darcy–Weisbach equation can also be written in terms of pressure loss:
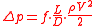
Lung compliance
In general, compliance is defined by the change in volume (ΔV) versus the associated change in pressure (ΔP), or ΔV/ΔP. During mechanical ventilationMechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
, compliance can be influenced by 3 key physiologic factors:
- Lung compliance
- Chest wall compliance
- Airway resistanceAirway resistanceAirway resistance is a concept used in respiratory physiology to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow....
Lung compliance is influenced by a variety of primary abnormalities of lung parenchyma, both chronic and acute. Airway resistance
Airway resistance
Airway resistance is a concept used in respiratory physiology to describe mechanical factors which limit the access of inspired air to the pulmonary alveoli, and thus determine airflow....
is typically increased by bronchospasm
Bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylatoxins...
and airway secretions. Chest wall compliance can be decreased by fixed abnormalities (eg, kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both a coronal and sagittal plane. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. Kyphoscoliosis is a musculoskeletal disorder causing chronic underventilation of the lungs and may be one of the major causes of pulmonary hypertension...
, morbid obesity) or more variable problems driven by patient agitation while intubated.
Calculating Compliance on minute volume (VE: ΔV is always defined by tidal volume
Tidal volume
Tidal volume is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inspiration and expiration when extra effort is not applied.Typical values are around 500ml or 7ml/kg bodyweight.-Mechanical Ventilation:...
(VT), but ΔP is different for the measurement of dynamic vs. static compliance.
Dynamic Compliance (Cdyn)
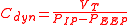
Cdyn — VT / (PIP - P_{EEP}), where PIP = peak inspiratory pressure
Peak inspiratory pressure
Peak inspiratory pressure is the highest level of pressure applied to the lungs during inhalation. In mechanical ventilation the number reflects a positive pressure in centimeters of water pressure . In normal breathing, it may sometimes be referred to as the maximal inspiratory pressure , which...
(the maximum pressure during inspiration). Alterations in airway resistance, lung compliance and chest wall compliance influence Cdyn.
Static Compliance (Cstat)

Cstat — Vt / (Pplat - PEEP), where Pplat = plateau pressure. Pplat is measured at the end of inhalation and prior to exhalation using an inspiratory hold maneuver. During this maneuver, airflow is transiently (~0.5 sec) discontinued, which eliminates the effects of airway resistance. Pplat is never > PIP and is typically < 3-5 cmH2O lower than PIP when airway resistance is not elevated.

