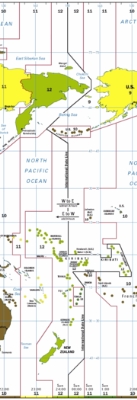
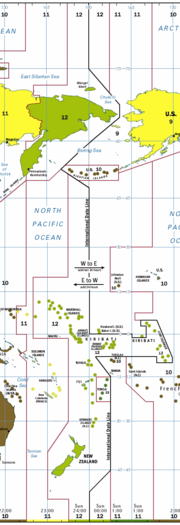
180th meridian
Encyclopedia
Prime Meridian
The Prime Meridian is the meridian at which the longitude is defined to be 0°.The Prime Meridian and its opposite the 180th meridian , which the International Date Line generally follows, form a great circle that divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.An international...
passing through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich
Royal Observatory, Greenwich
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich , in London, England played a major role in the history of astronomy and navigation, and is best known as the location of the prime meridian...
. It is common to both east longitude
Longitude
Longitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees, minutes and seconds, and denoted by the Greek letter lambda ....
and west longitude. It is used as the basis for the International Date Line
International Date Line
The International Date Line is a generally north-south imaginary line on the surface of the Earth, passing through the middle of the Pacific Ocean, that designates the place where each calendar day begins...
because it for the most part passes through the open waters of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. However, the meridian passes through Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and Fiji
Fiji
Fiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
as well as Antarctica.
Starting at the North Pole
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
and heading south to the South Pole
South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole...
, the 180th meridian passes through:
| Co-ordinates (approximate) |
Country, territory or sea | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 90°0′N 180°0′E | Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... |
|
| 71°32′N 180°0′E | Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... |
|
| 70°58′N 180°0′E | Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... |
|
| 68°59′N 180°0′E | Chukotka Autonomous Okrug Chukotka Autonomous Okrug Chukotka Autonomous Okrug , or Chukotka , is a federal subject of Russia located in the Russian Far East.Chukotka has a population of 53,824 according to the 2002 Census, and a surface area of . The principal town and the administrative center is Anadyr... |
|
| 65°02′N 180°0′E | Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... |
|
| 52°0′N 180°0′E | Amchitka Pass Amchitka Pass Amchitka Pass is a strait in Alaska, United States. It is located in the Aleutian Islands, between the Rat Islands group to the west and the Delarof Islands to the east. Amchitka Pass has a least width of 50 miles and depths of 49 to over 1,000 fathoms. The islands on both sides of the pass should... |
Passing just east of Semisopochnoi Island Semisopochnoi Island Semisopochnoi Island is part of the Rat Islands group in the western Aleutian Islands of Alaska. The island is uninhabited and provides an important nesting area for maritime birds. The island is of volcanic origin, containing several volcanoes including Mount Cerberus... , Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , (at 51°57′N 179°47′E) |
| 51°0′N 180°0′E | Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... |
Passing just east of Nukulaelae Nukulaelae Nukulaelae is an atoll that is part of the nation of Tuvalu, and has a population of 393. It has the form of an oval and consists of at least 15 islets... atoll, (at 9°25′S 179°52′E) > Passing just west of the island of Cikobia, (at 15°43′S 179°59′W) |
| 16°9′S 180°0′E | Islands of Vanua Levu Vanua Levu Vanua Levu , formerly known as Sandalwood Island, is the second largest island of Fiji. Located 64 kilometres to the north of the larger Viti Levu, the island has an area of 5,587.1 km² and a population of some 130,000.- Geography :... , Rabi Rabi Island Rabi is a volcanic island in northern Fiji. It is an outlier to Taveuni , in the Vanua Levu Group. It covers an area of 66.3 square kilometers, reaching a maximum altitude of 463 meters and has a shoreline of 46.2 kilometers... , and Taveuni Taveuni Taveuni is the third-largest island in Fiji, after Vanua Levu and Viti Levu, with a total land area of 435 square kilometers . The cigar-shaped island, a massive shield volcano which rises from the floor of the Pacific Ocean, is situated 6.5 kilometers to the east of Vanua Levu, across the... |
|
| 16°59′S 180°0′E | Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... |
Passing just east of the island of Moala, (at 18°33′S 179°57′E) > Passing just west of the island of Totoya Totoya Totoya is a volcanic island in the Moala subgroup of Fiji's Lau archipelago. It occupies an area of 28 square kilometers, making it the smallest of the Moalas. Its maximum altitude is 366 meters. The main economic activity is coconut farming.... , (at 19°0′S 179°52′W) > Passing just east of the island of Matuku Matuku Island Matuku is a volcanic island in the Moala subgroup of Fiji's Lau archipelago. Located at 19.18° South and 179.75° East, Matuku covers an area of 57 square kilometers. It has a maximum elevation of 385 meters... , (at 19°10′S 179°47′E) |
| 60°0′S 180°0′E | Southern Ocean Southern Ocean The Southern Ocean comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60°S latitude and encircling Antarctica. It is usually regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions... |
|
| 78°13′S 180°0′E | Antarctica | Ross Dependency Ross Dependency The Ross Dependency is a region of Antarctica defined by a sector originating at the South Pole, passing along longitudes 160° east to 150° west, and terminating at latitude 60° south... , claimed by |

- the Gilbert IslandsGilbert IslandsThe Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean. They are the main part of Republic of Kiribati and include Tarawa, the site of the country's capital and residence of almost half of the population.-Geography:The atolls and islands of the Gilbert Islands...
and the Phoenix IslandsPhoenix IslandsThe Phoenix Islands are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs, lying in the central Pacific Ocean east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands. They are a part of the Republic of Kiribati. During the late 1930s they became the site of the last attempted colonial...
islands of ; - between North IslandNorth IslandThe North Island is one of the two main islands of New Zealand, separated from the much less populous South Island by Cook Strait. The island is in area, making it the world's 14th-largest island...
and the Kermadec IslandsKermadec IslandsThe Kermadec Islands are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga...
of ; - between the Bounty IslandsBounty IslandsThe Bounty Islands at are a small group of 13 granite islets and numerous rocks, with a combined area of , in the south Pacific Ocean that are territorially part of New Zealand. They are located between 47°44'35" and 47°46'10" S, and 179°01' and 179°04'20" E, southeast of the South Island of New...
and the Chatham IslandsChatham IslandsThe Chatham Islands are an archipelago and New Zealand territory in the Pacific Ocean consisting of about ten islands within a radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Their name in the indigenous language, Moriori, means Misty Sun...
, also of .
See also
- 179th meridian east179th meridian eastThe meridian 179° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole....
- 179th meridian west179th meridian westThe meridian 179° west of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole....

