
1 E7 m
Encyclopedia
Length
In geometric measurements, length most commonly refers to the longest dimension of an object.In certain contexts, the term "length" is reserved for a certain dimension of an object along which the length is measured. For example it is possible to cut a length of a wire which is shorter than wire...
s starting at 107 metre
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
s (10 megametre
Megametre
A megametre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one million metres, the SI base unit of length, hence to 1,000 km or approximately 621.37 miles....
s or 10,000 kilometre
Kilometre
The kilometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one thousand metres and is therefore exactly equal to the distance travelled by light in free space in of a second...
s).
Distances shorter than 107 metres
Conversions
10 megametres (10 Mm) is- 6,215 mileMileA mile is a unit of length, most commonly 5,280 feet . The mile of 5,280 feet is sometimes called the statute mile or land mile to distinguish it from the nautical mile...
s. - side of a squareSquare (geometry)In geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral. This means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles...
of area 100,000,000 square kilometreSquare kilometreSquare kilometer, symbol km2, is a decimal multiple of the SI unit of surface area, the square metre, one of the SI derived units.1 km2 is equal to:* 1,000,000 m2* 100 ha * 0.386302 square miles* 247.105381 acresConversely:...
s (km2) - radius of a circleCircleA circle is a simple shape of Euclidean geometry consisting of those points in a plane that are a given distance from a given point, the centre. The distance between any of the points and the centre is called the radius....
of area 314,159,265 km2
Human-defined scales and structures
- 11.085 Mm — Length of the KievKievKiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press....
-VladivostokVladivostokThe city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m...
railway, a longer variant of the Trans-Siberian railwayTrans-Siberian RailwayThe Trans-Siberian Railway is a network of railways connecting Moscow with the Russian Far East and the Sea of Japan. It is the longest railway in the world... - 13.300 Mm — Length of roads being rehabilitated and widened under the National Highway Development Project (launched in 1998) in IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
- 39.000 Mm — Length of the SEA-ME-WE 3 optical submarine telecommunications cable, joining 39 points between NordenNorden, Lower SaxonyNorden is a town in the district of Aurich, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the North Sea shore, in East Frisia.-External links:* *...
, Germany and Okinawa, Japan - 67.000 Mm — Total length of National Highways in India
Nature
- 10 Mm — Approximate altitude of the outer boundary of the exosphereExosphereThe exosphere is the uppermost layer of Earth's atmosphere. In the exosphere, an upward travelling molecule moving fast enough to attain escape velocity can escape to space with a low chance of collisions; if it is moving below escape velocity it will be prevented from escaping from the celestial...
- 10.001 Mm — Length of the meridian arcMeridian arcIn geodesy, a meridian arc measurement is a highly accurate determination of the distance between two points with the same longitude. Two or more such determinations at different locations then specify the shape of the reference ellipsoid which best approximates the shape of the geoid. This...
from the North PoleNorth PoleThe North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface...
to the EquatorEquatorAn equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
(the original definition of the metreMetreThe metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
was based on this length). - 60.000 Mm — Total length of the mid-ocean ridgeMid-ocean ridgeA mid-ocean ridge is a general term for an underwater mountain system that consists of various mountain ranges , typically having a valley known as a rift running along its spine, formed by plate tectonics. This type of oceanic ridge is characteristic of what is known as an oceanic spreading...
s
Astronomical
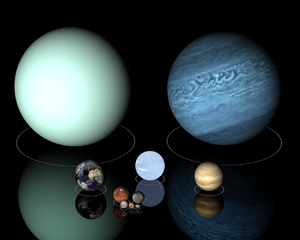
- 12.000 Mm — Diameter of Sirius BSiriusSirius is the brightest star in the night sky. With a visual apparent magnitude of −1.46, it is almost twice as bright as Canopus, the next brightest star. The name "Sirius" is derived from the Ancient Greek: Seirios . The star has the Bayer designation Alpha Canis Majoris...
, a white dwarfWhite dwarfA white dwarf, also called a degenerate dwarf, is a small star composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. They are very dense; a white dwarf's mass is comparable to that of the Sun and its volume is comparable to that of the Earth. Its faint luminosity comes from the emission of stored... - 12.104 Mm — Diameter of VenusVenusVenus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
- 12.742 Mm — Diameter of EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
- 12.900 Mm — Minimum distance of the meteoroidMeteoroidA meteoroid is a sand- to boulder-sized particle of debris in the Solar System. The visible path of a meteoroid that enters Earth's atmosphere is called a meteor, or colloquially a shooting star or falling star. If a meteoroid reaches the ground and survives impact, then it is called a meteorite...
from the center of Earth on March 31, 2004, closest on record - 14.000 Mm — Smallest diameter of Jupiter's Great Red Spot
- 34.770 Mm — Minimum distance of the asteroidAsteroidAsteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
99942 Apophis99942 Apophis99942 Apophis is a near-Earth asteroid that caused a brief period of concern in December 2004 because initial observations indicated a small probability that it would strike the Earth in 2029. Additional observations provided improved predictions that eliminated the possibility of an impact on...
on April 13, 2029 from the center of Earth - 35.786 Mm — Altitude of geostationary orbitGeostationary orbitA geostationary orbit is a geosynchronous orbit directly above the Earth's equator , with a period equal to the Earth's rotational period and an orbital eccentricity of approximately zero. An object in a geostationary orbit appears motionless, at a fixed position in the sky, to ground observers...
- 40.005 Mm — Polar circumference of the EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
- 40.077 Mm — Equatorial circumference of the EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
- 49.528 Mm — Diameter of NeptuneNeptuneNeptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
- 51.118 Mm — Diameter of UranusUranusUranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
Distances longer than 108 m

